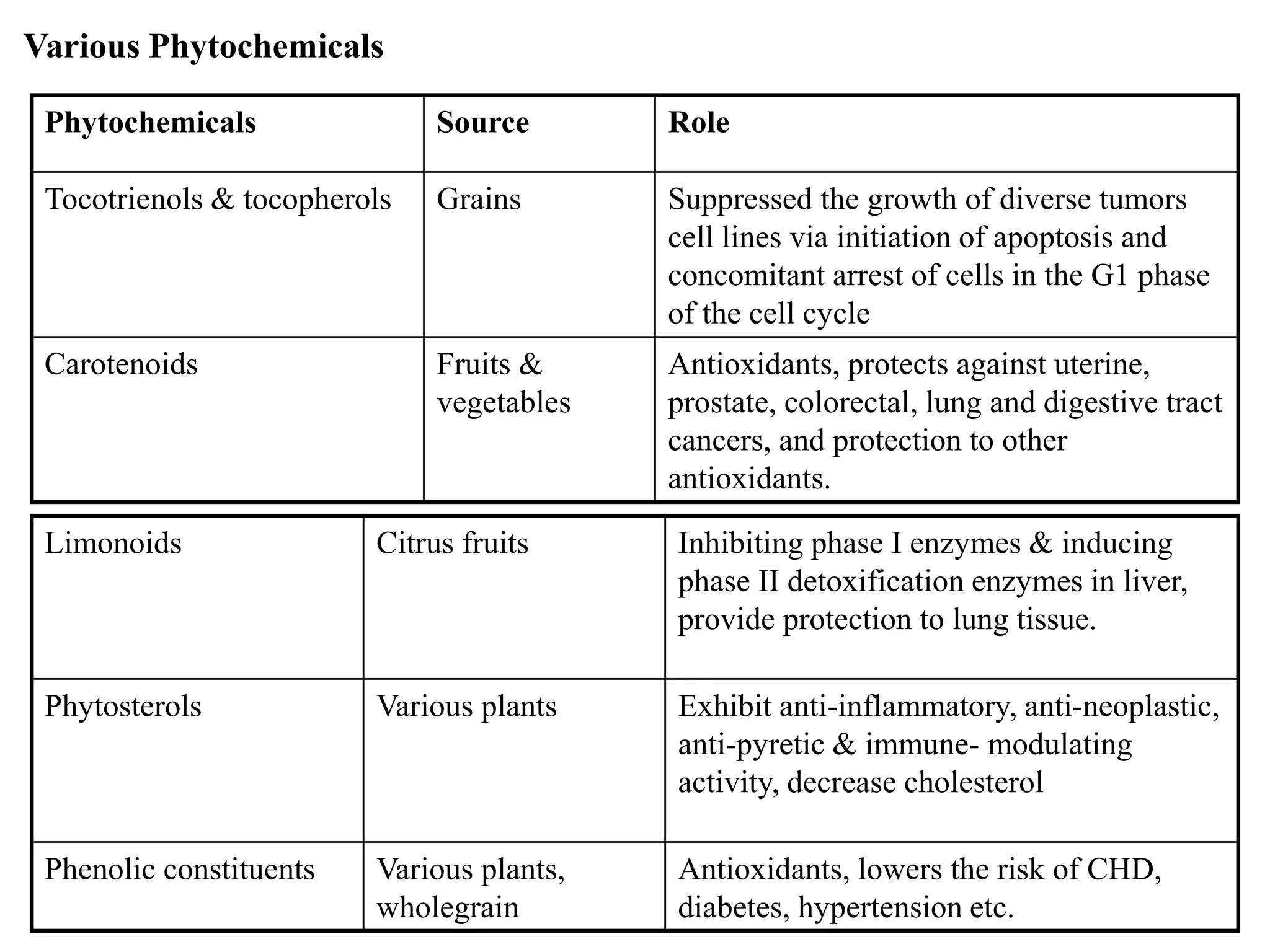
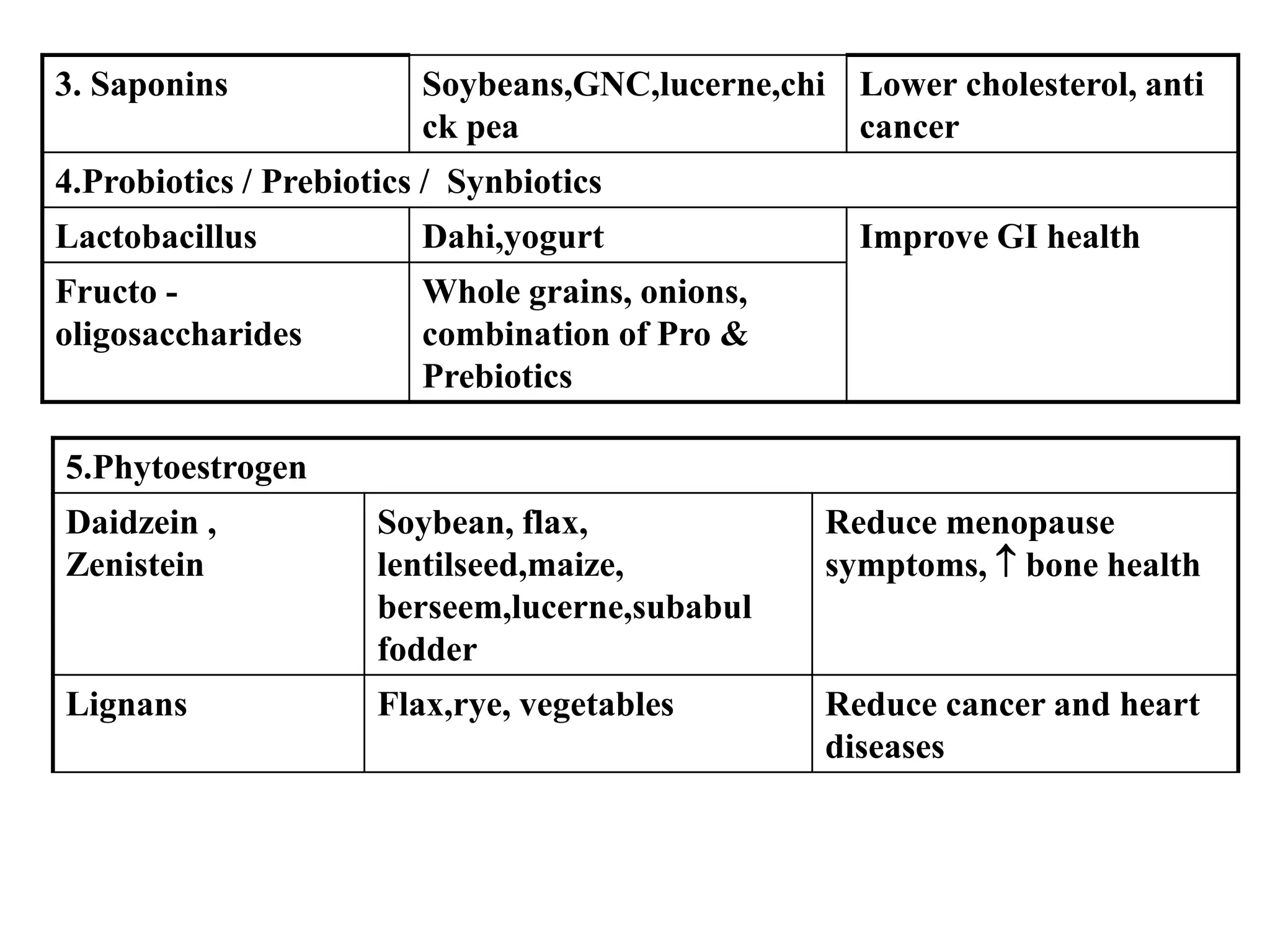
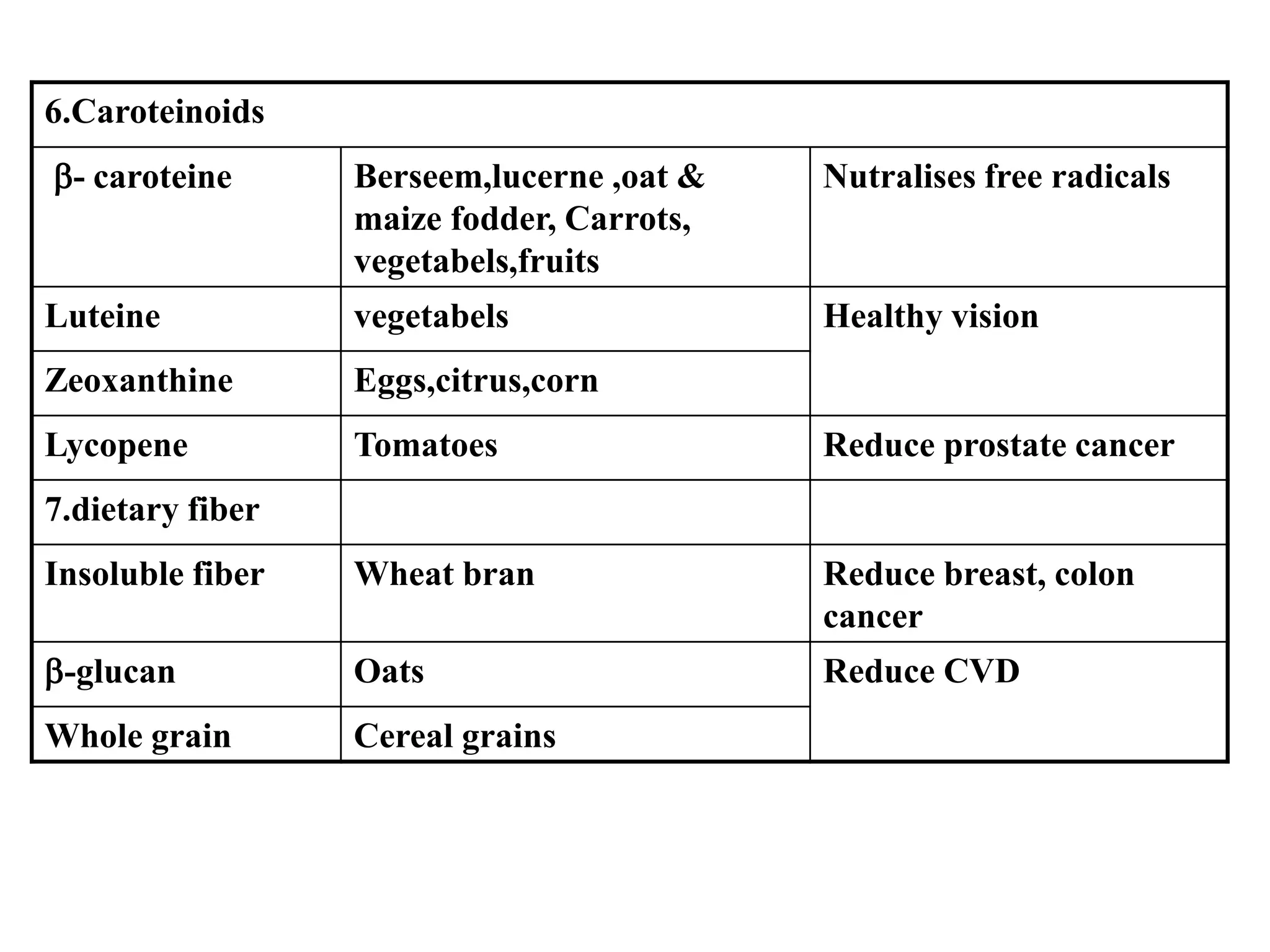
This document provides information about nutraceuticals from K.Sudheer Kumar of the Department of Pharmacognosy at Chilkur Balaji College of Pharmacy in Hyderabad. It defines nutraceuticals as nutrient and non-nutrient compounds in food that have health promoting or disease preventing properties. Some examples of nutraceuticals described include prebiotics, probiotics, dietary fibers, omega-3 fatty acids, and antioxidants. The document also discusses various nutrients and herbal compounds that are commonly used as nutraceuticals and provides examples of their health benefits.