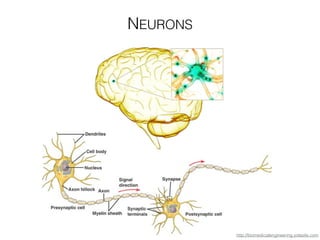
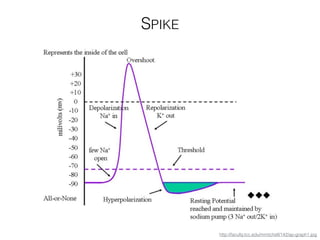
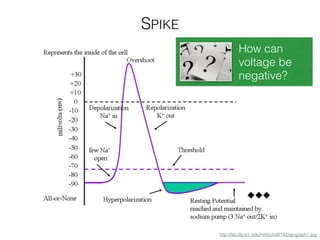
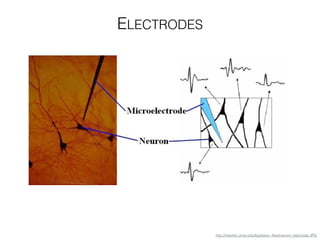
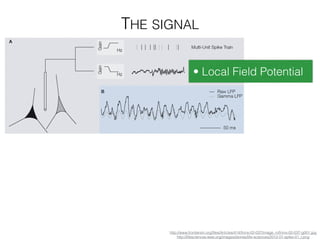
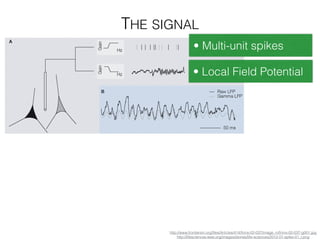
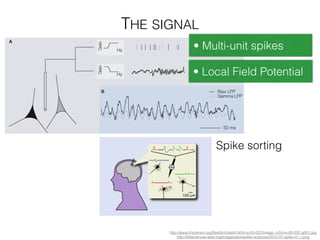
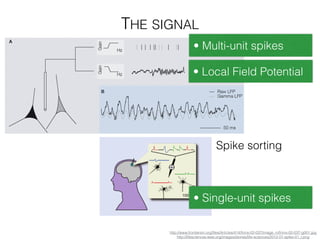
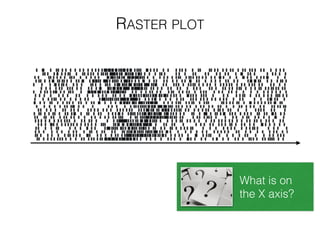
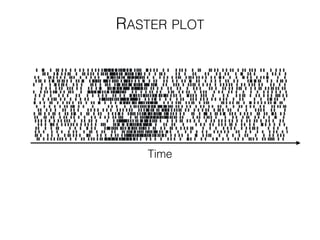
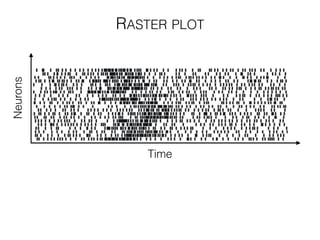
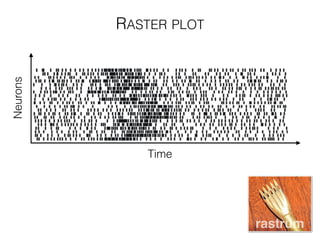
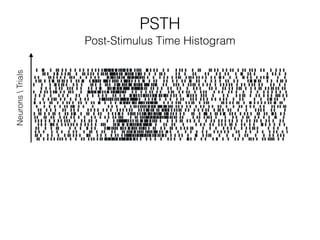
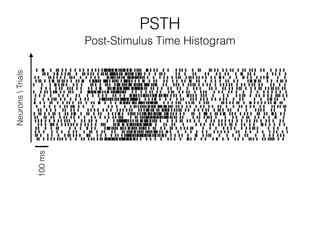
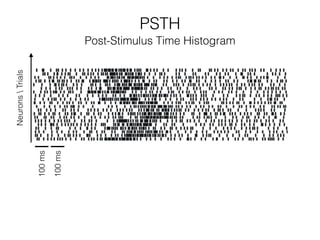
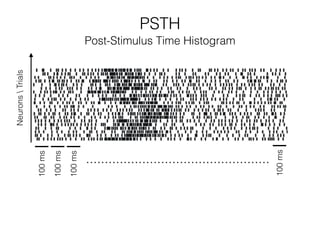
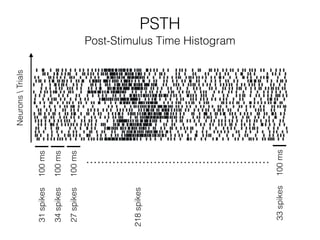
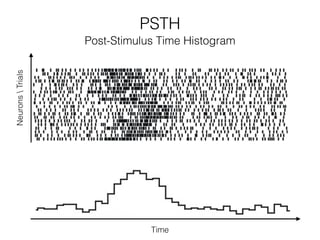
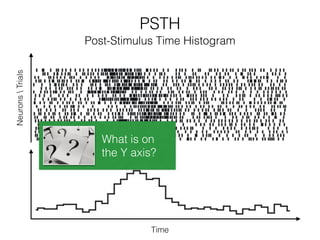
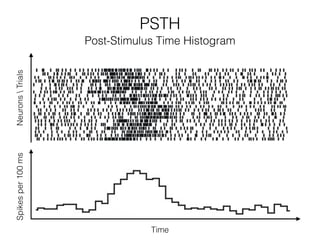
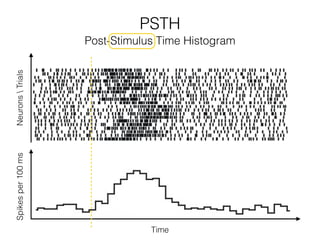
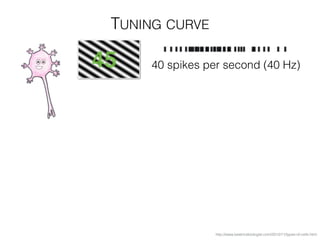
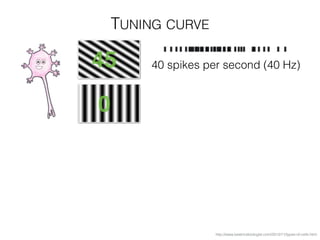
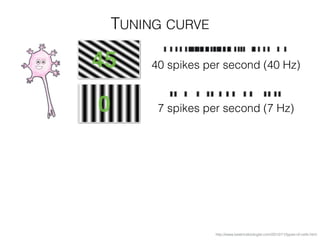
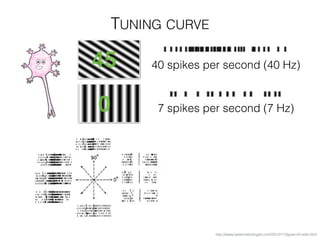
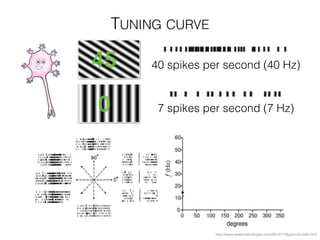
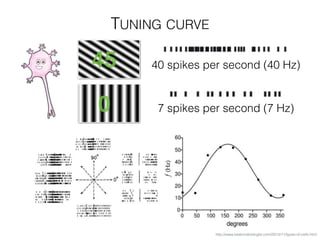
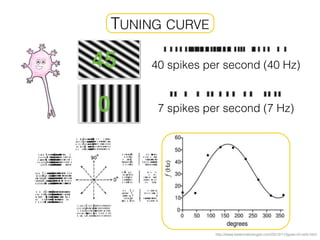
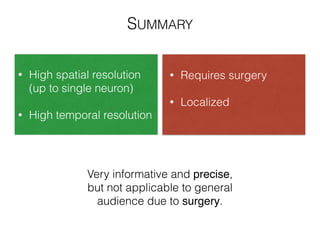
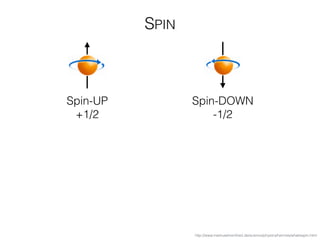
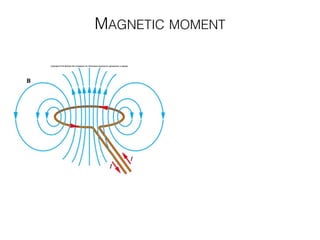
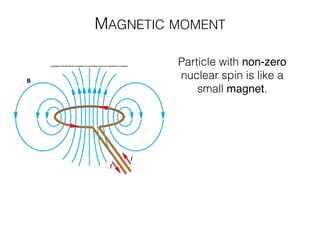
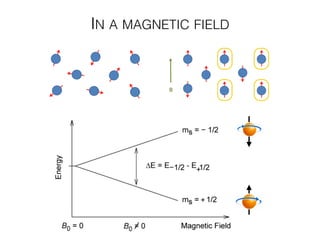
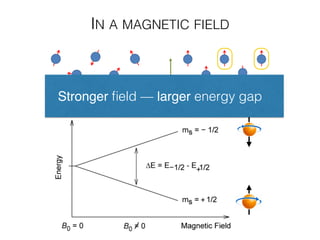
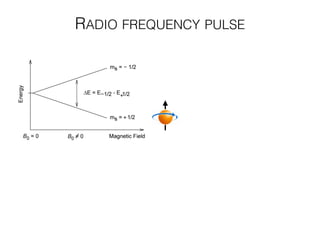
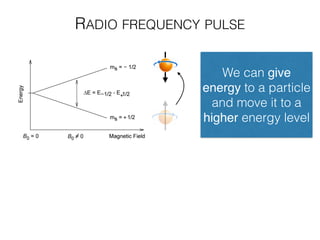
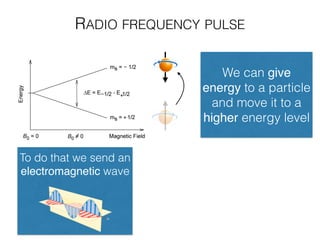
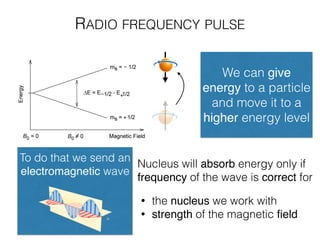
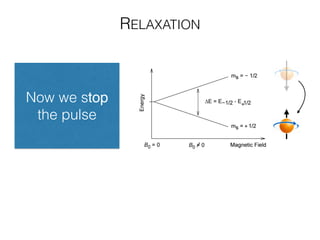
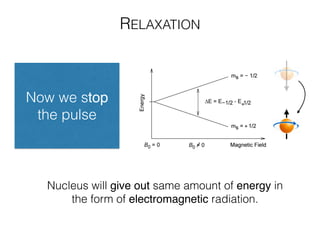
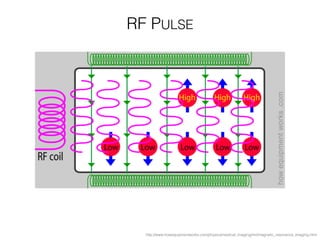
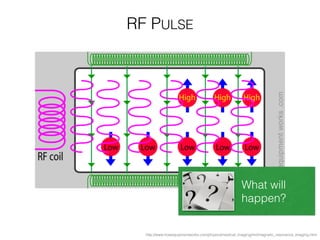
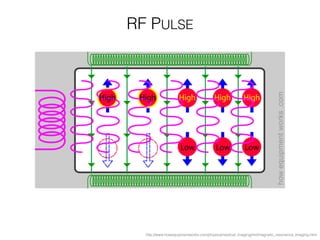
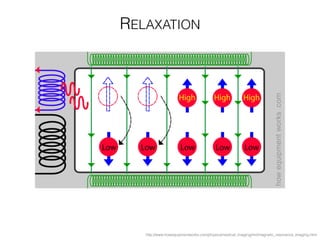
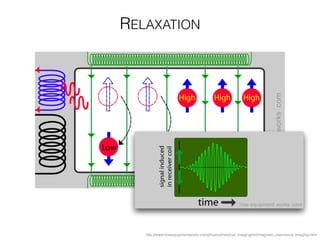
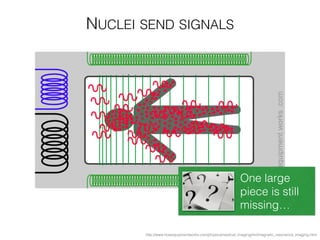
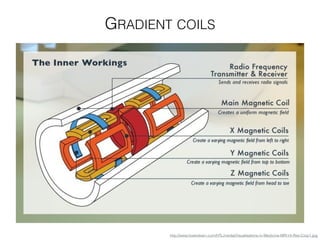
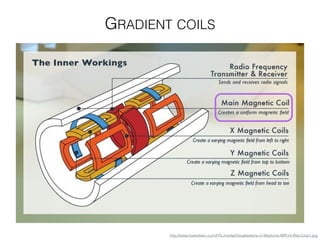
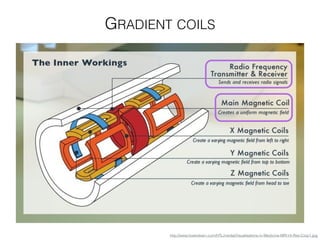
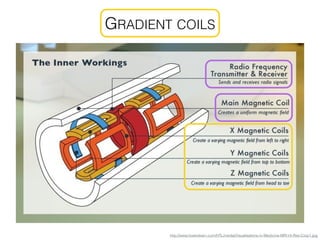
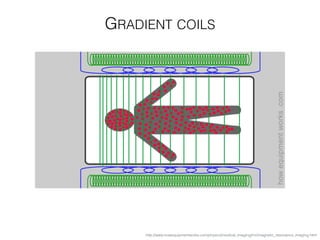
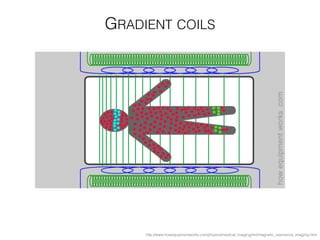
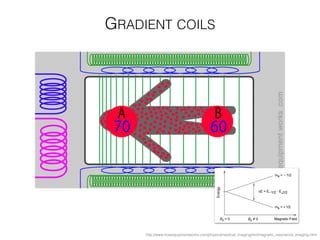
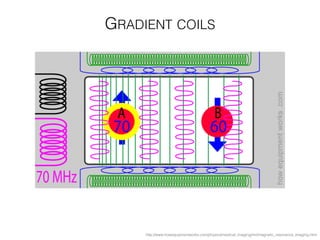
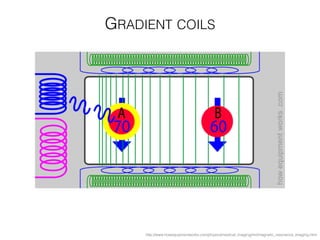
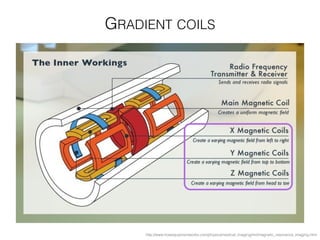
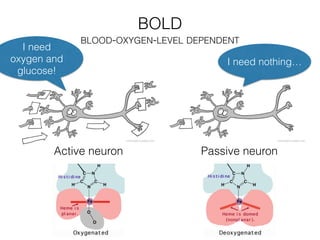
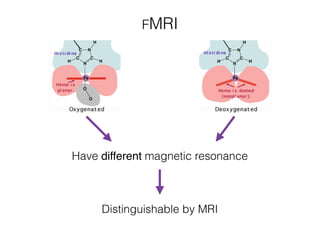
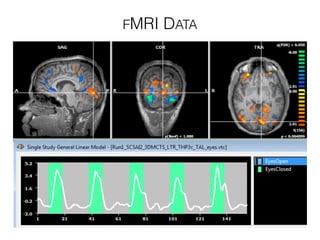
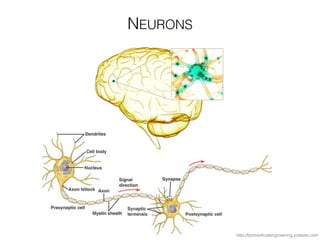
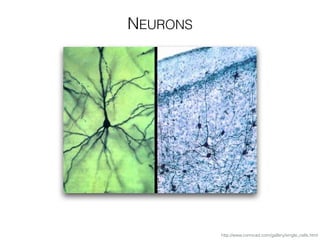
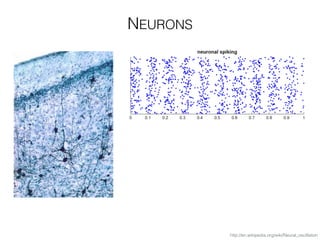
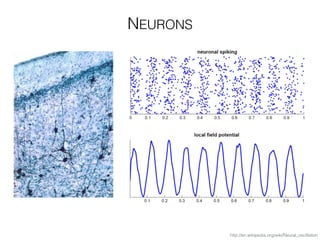
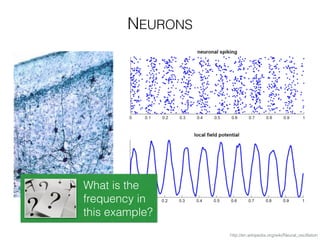
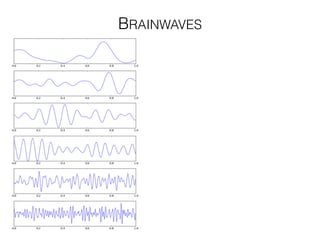
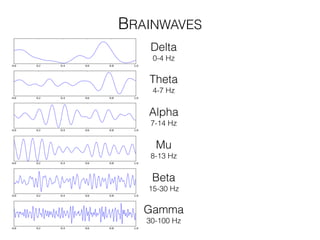
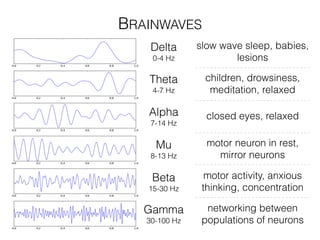
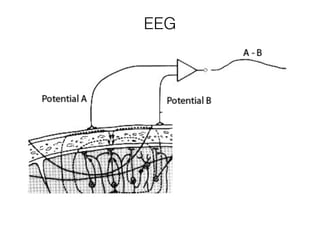
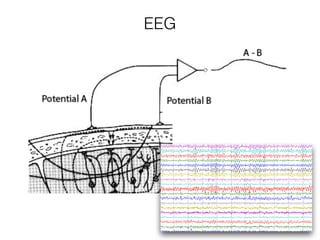
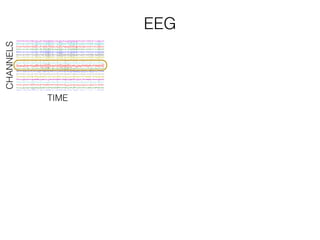
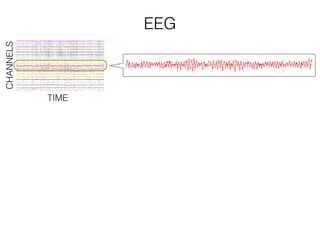
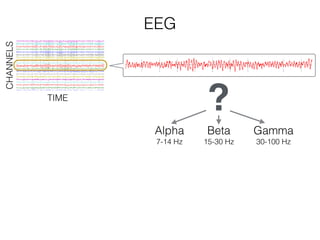
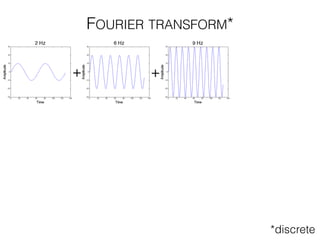
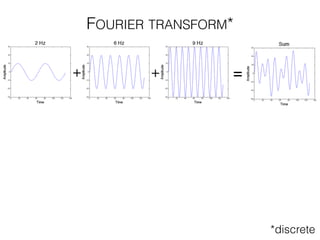
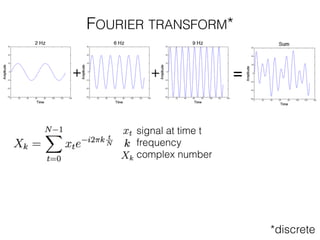
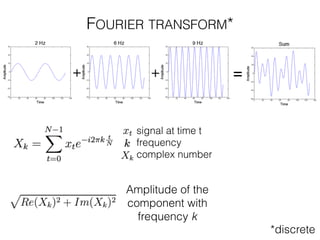
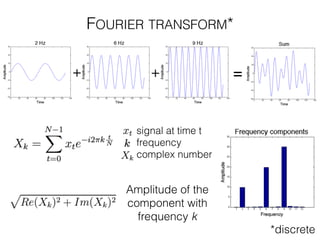
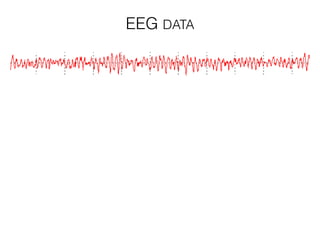
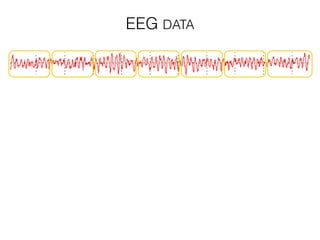
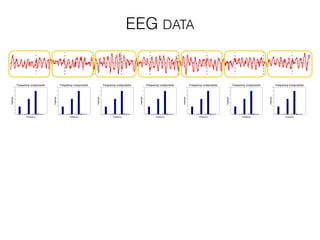
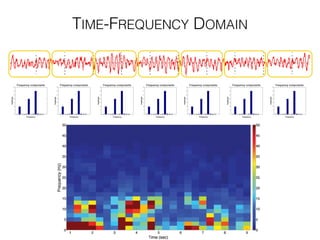
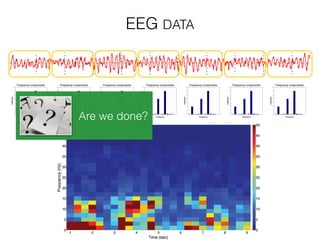
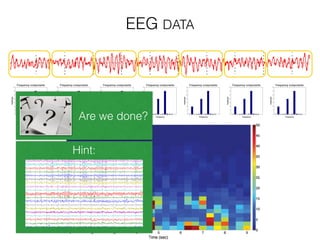
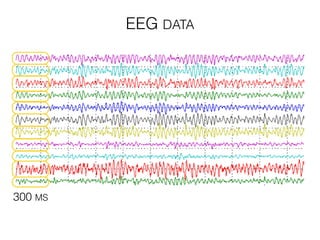
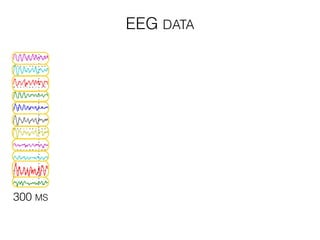
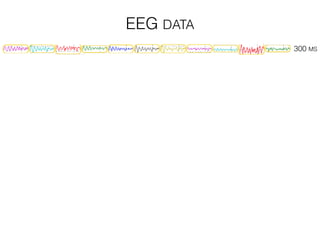
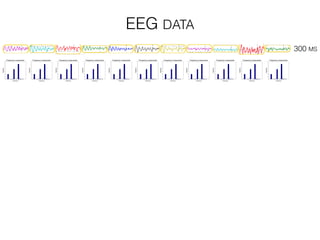
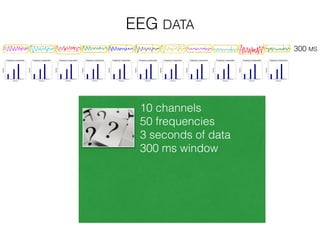
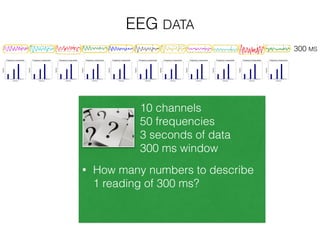
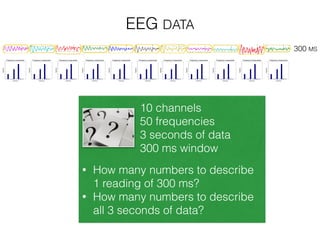
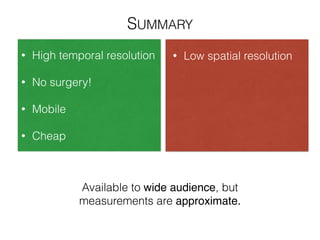
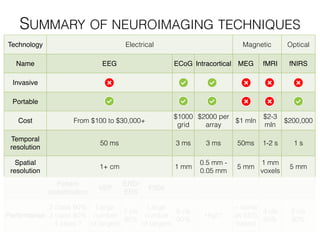
The document discusses various neuroimaging techniques, including intracortical neurons, fMRI, and EEG, highlighting their spatial and temporal resolution capabilities. It explains the underlying principles of each method, including their applications and limitations, such as the need for surgery in some cases and costs associated with the technologies. Overall, these techniques provide valuable insights into brain activity but vary significantly in their accessibility and the precision of the data obtained.