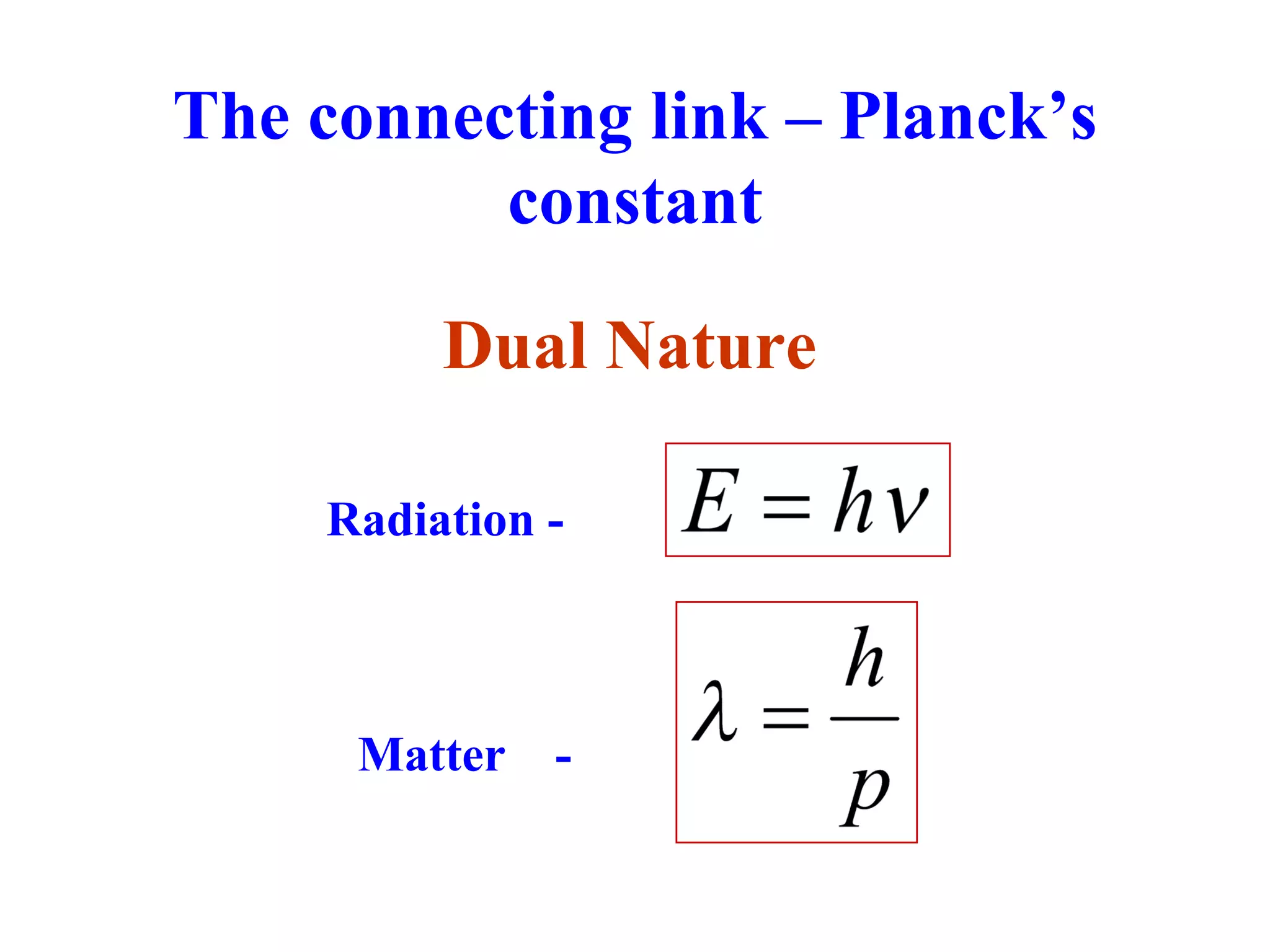
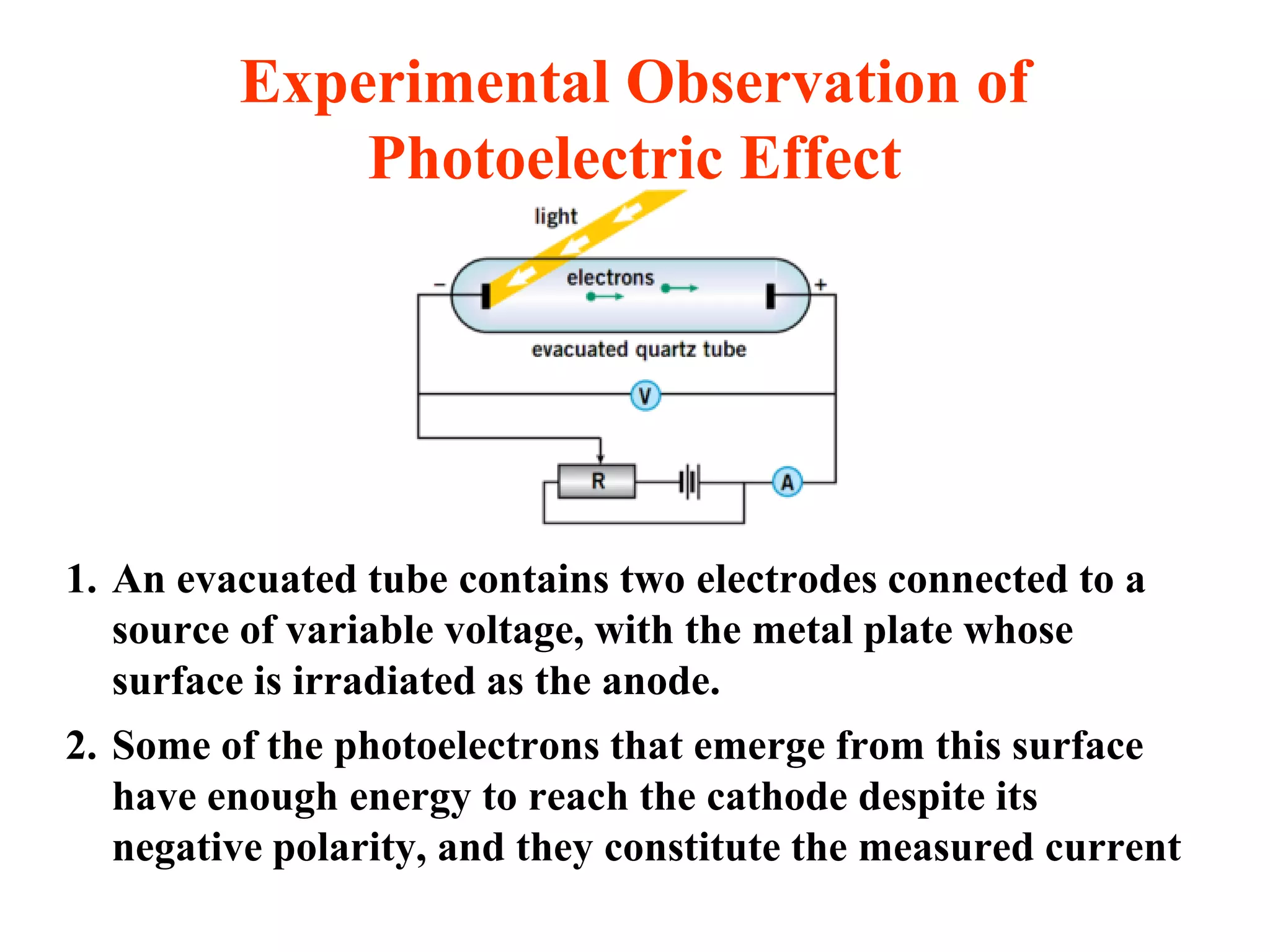
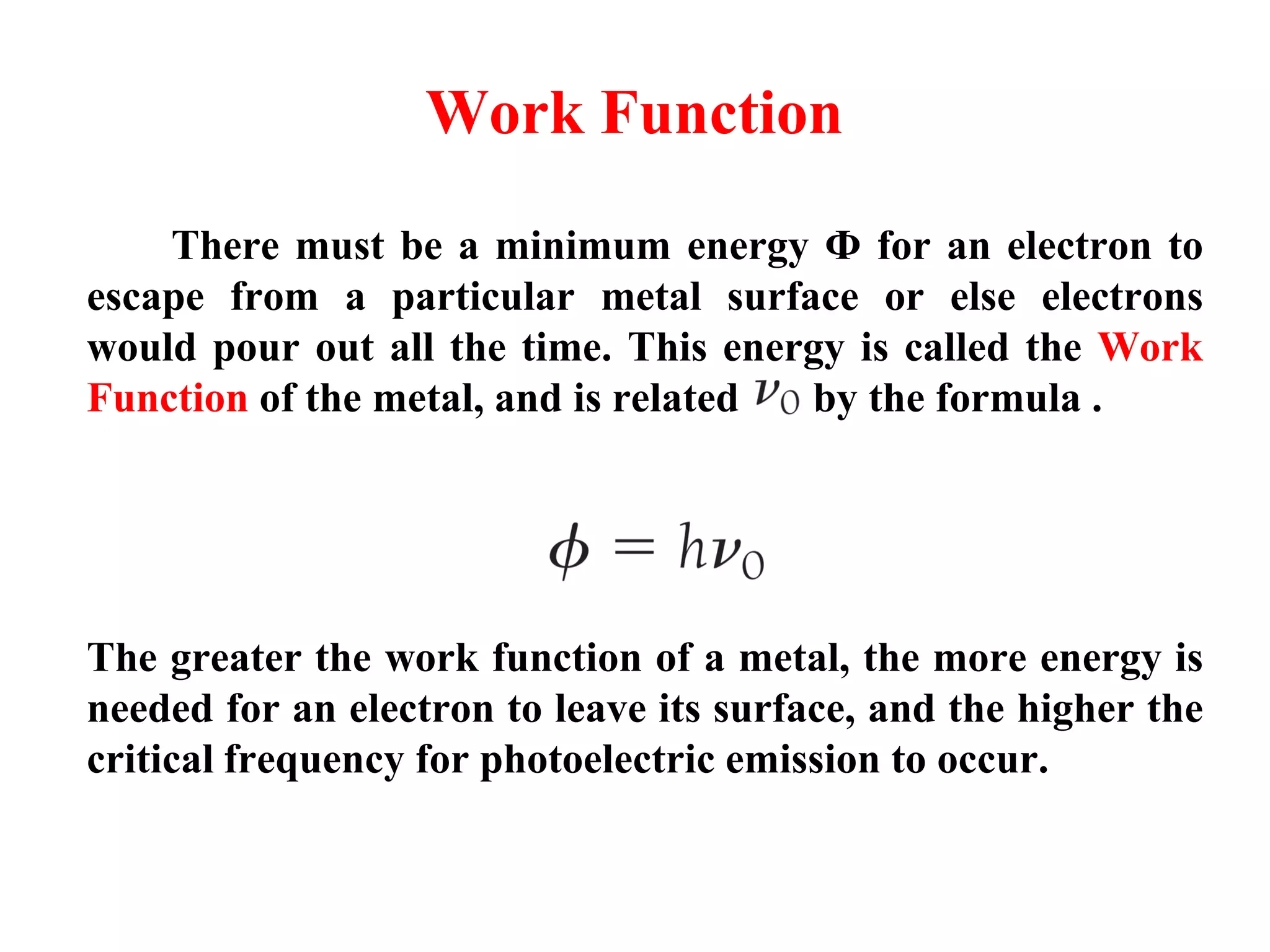
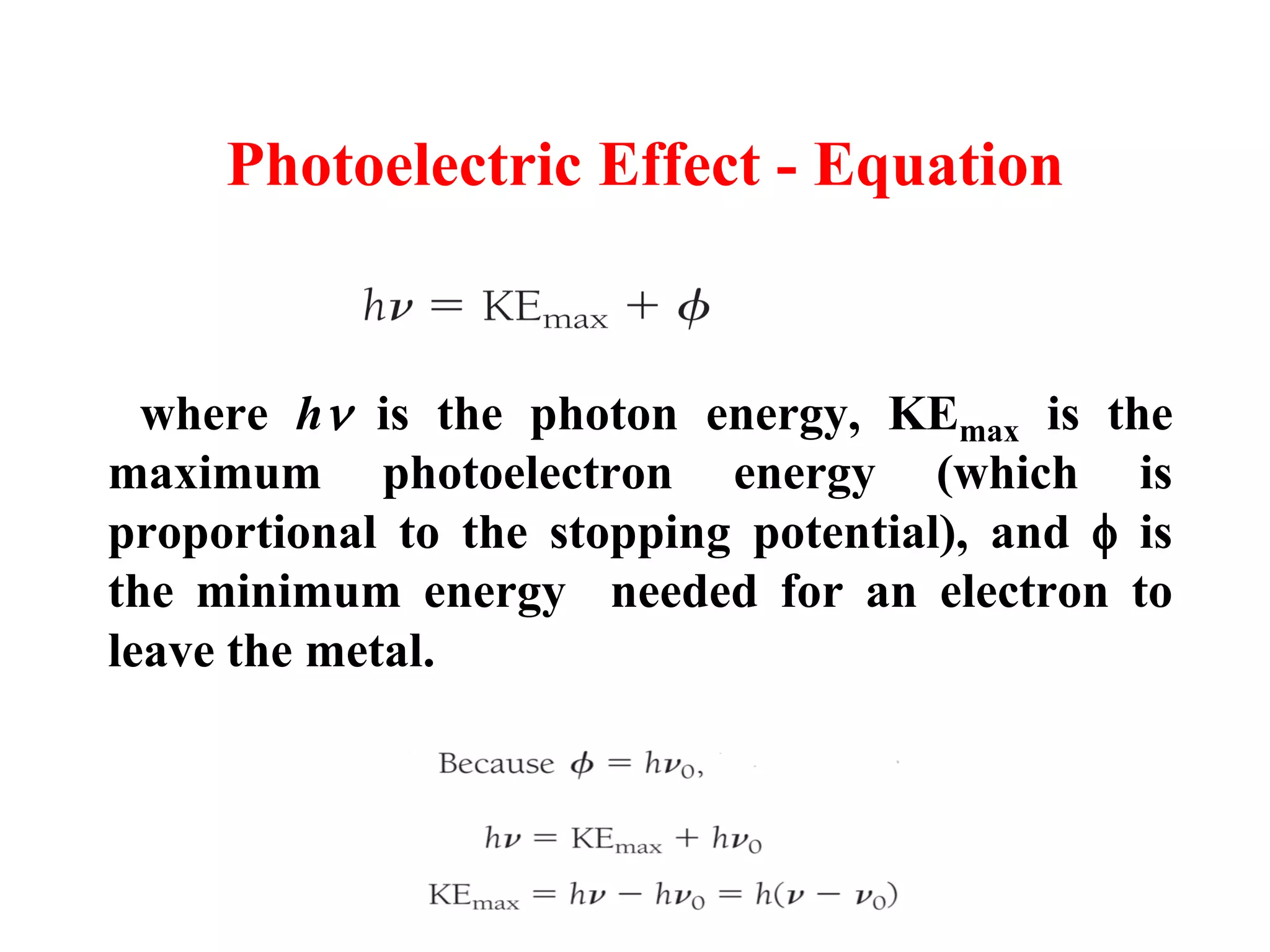
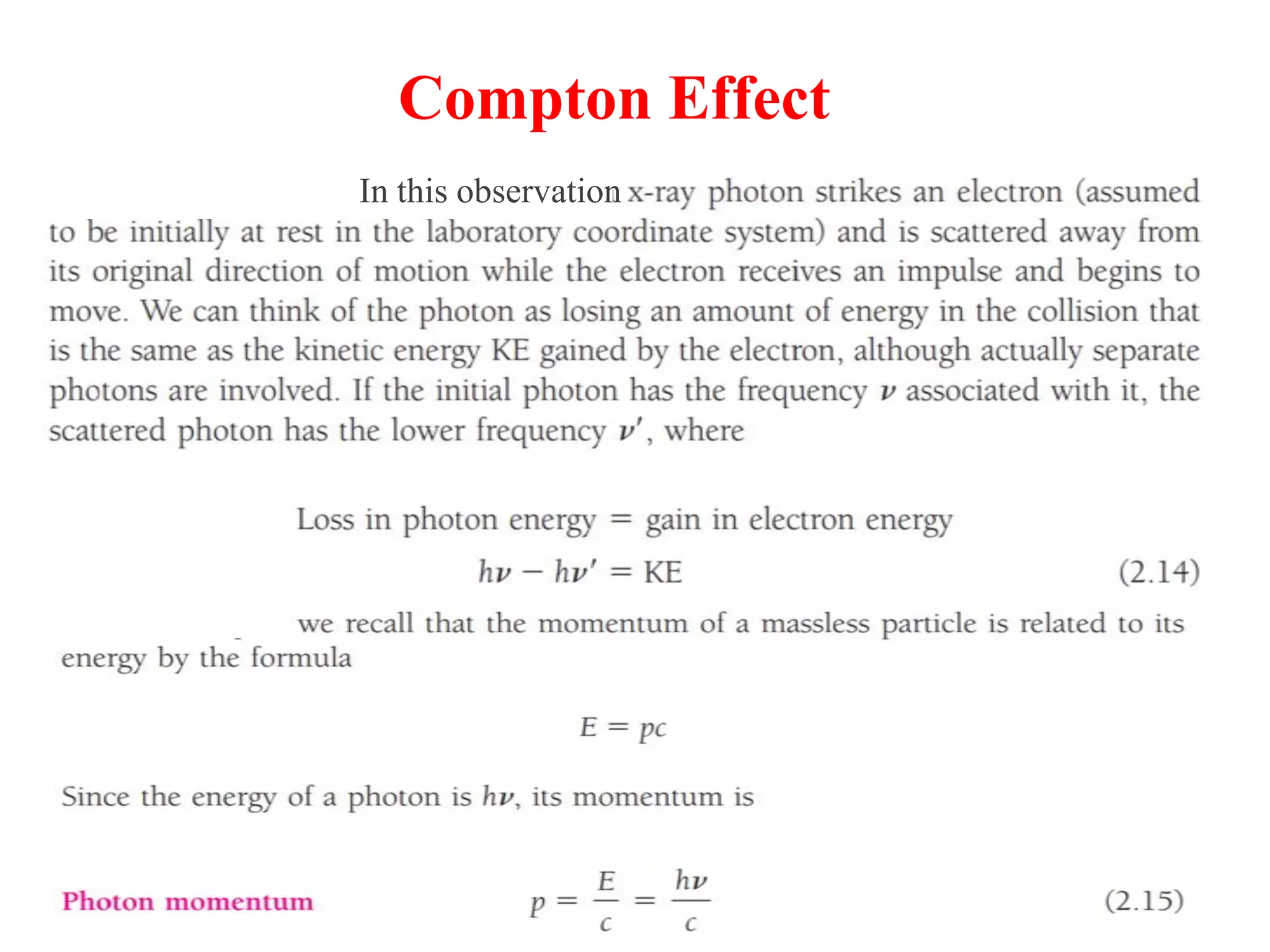
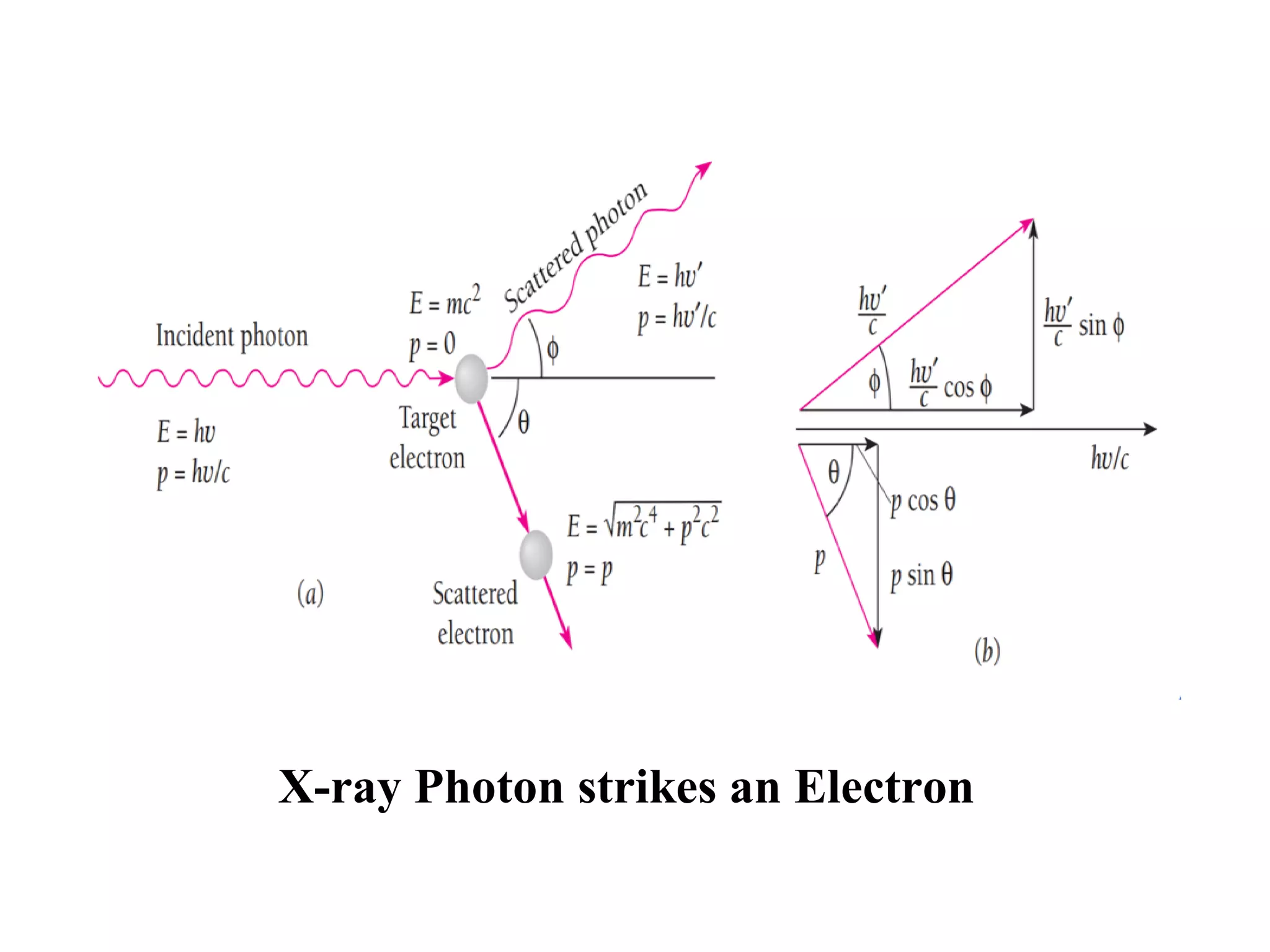
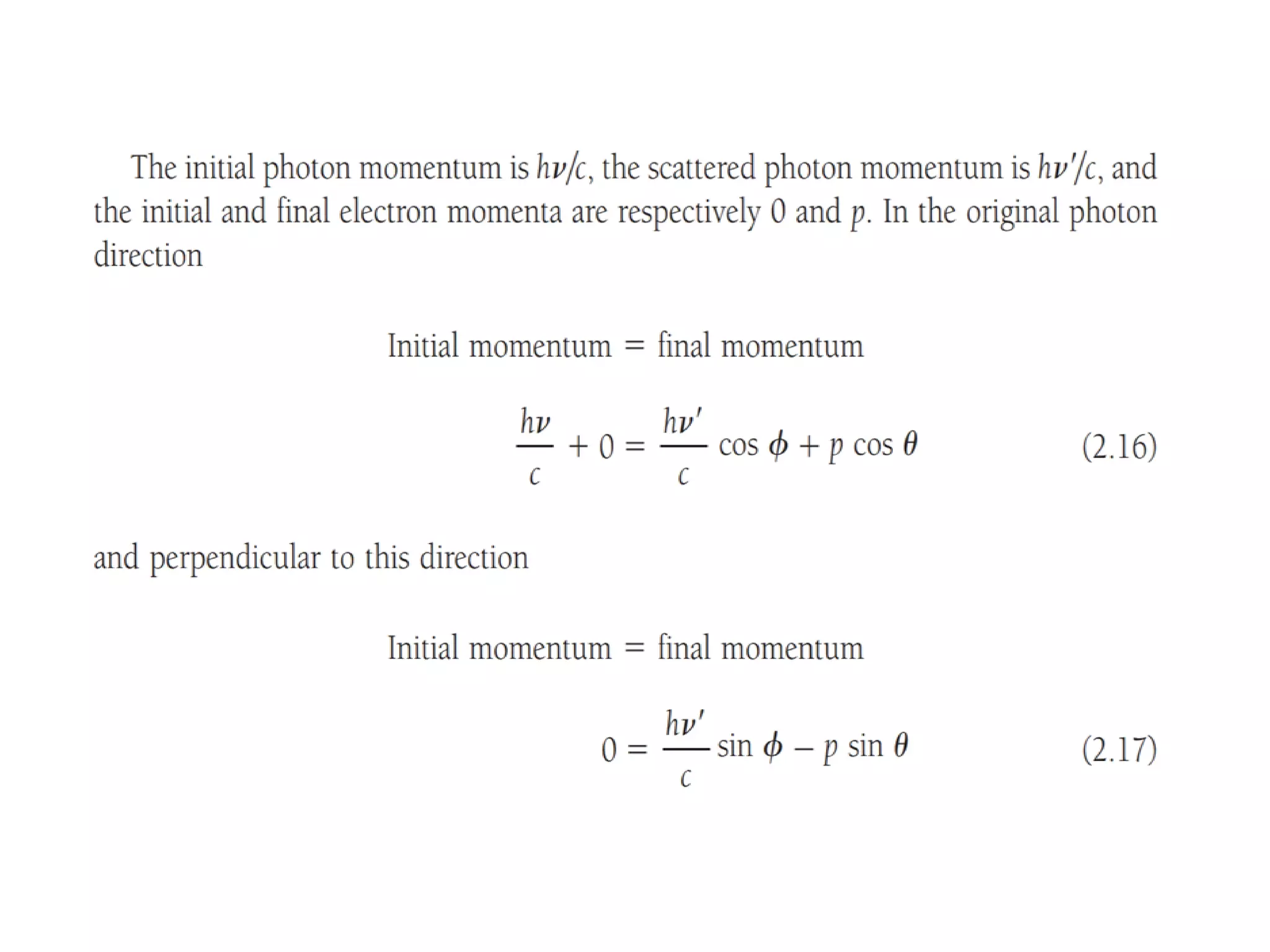
This document discusses the development of quantum mechanics. It summarizes that classical physics could not explain certain experimental observations, leading to quantum theory. Key events were Planck's blackbody radiation law, Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect using light quanta (photons), and Compton's discovery that photons transfer momentum to electrons. The photoelectric effect showed that light behaves as particles (photons), while the de Broglie hypothesis and Davisson-Germer experiment showed that electrons can behave as waves. This established the wave-particle duality of both light and matter.