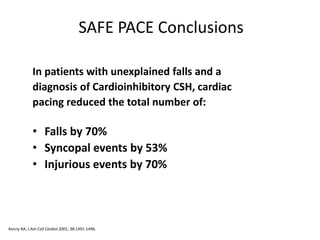
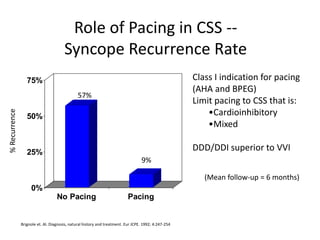
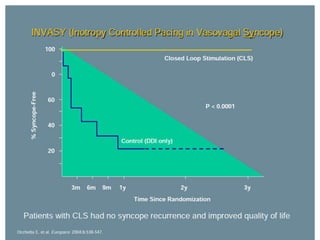
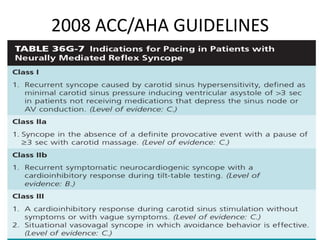
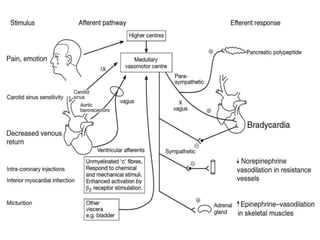
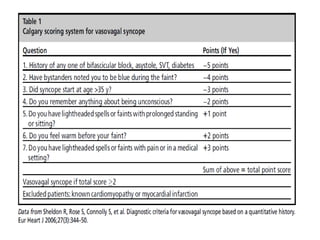
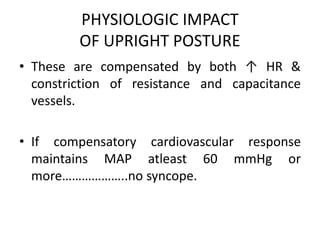
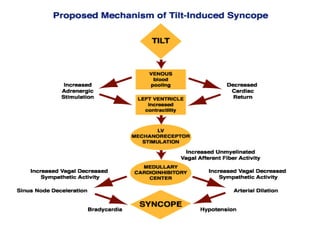
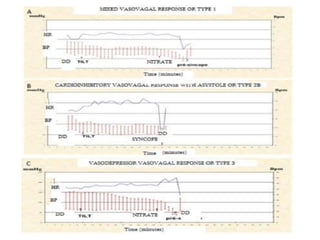
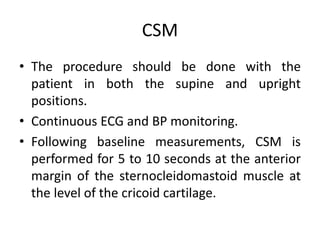
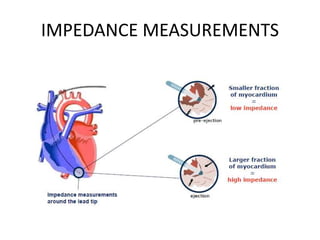
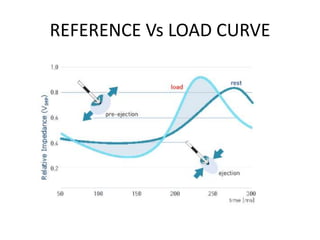
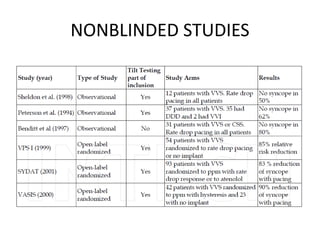
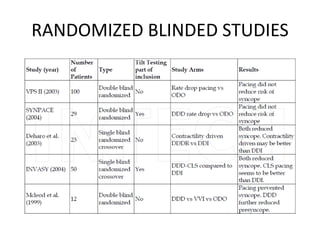
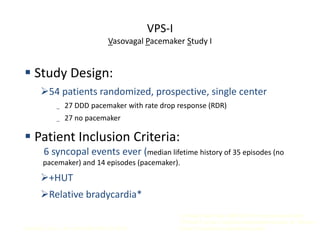
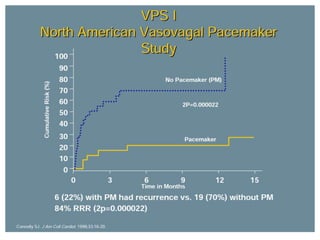
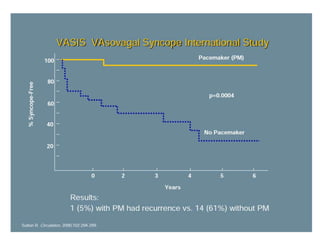
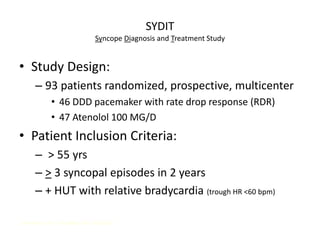
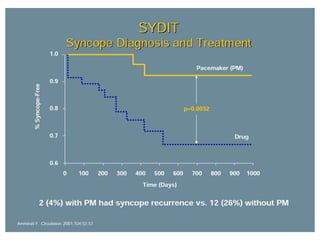
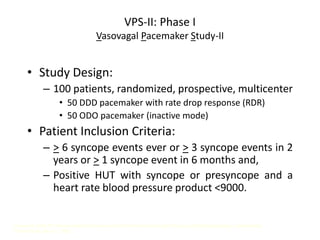
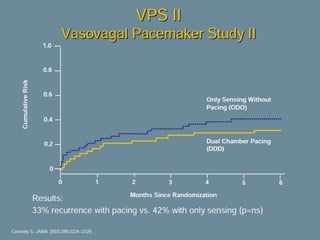
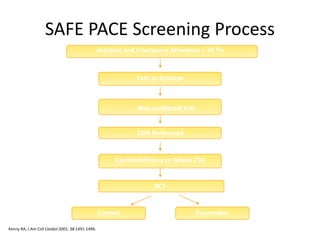
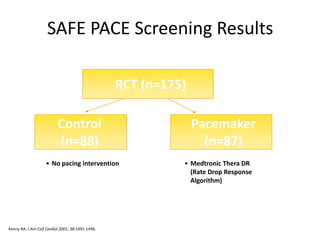
This document discusses neurocardiogenic syncope, specifically vasovagal syncope (VVS). It covers the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of VVS. Regarding diagnosis, it discusses head-up tilt table testing (HUTT) and implantable loop recorders (ILRs). While HUTT can help diagnose susceptibility to neurally-mediated syncope, its sensitivity, specificity, and prognostic value are limited. ILRs provide reproducible diagnostic information during spontaneous spells. Treatment focuses on non-pharmacological measures like education, salt/water intake, orthostatic training, and counterpressure maneuvers.


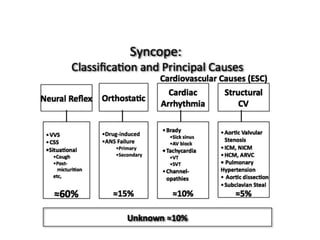




























































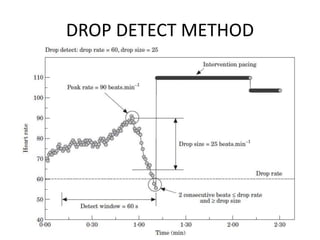
















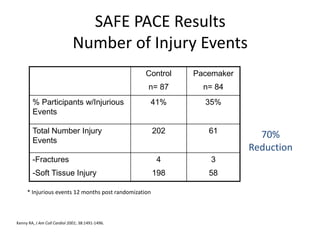
![SAFE PACE Results
Number of Falls
Control
n=87
Pacemaker
n=84
% Participants
w/Falls
60% 58%
Total Number of
Falls*
699 216
Mean Number of
Falls**
9.3 4.1
* Falls during 12 months post randomization
** Crude adjustment calculation
Kenny RA, J Am Coll Cardiol 2001; 38:1491-1496.
70%
Reduction
[OR 0.42; 95%
CI: 0.23, 0.75]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ncsyncopeppt-160920015810/85/NEUROCARDIOGENIC-SYNCOPE-ppt-113-320.jpg)
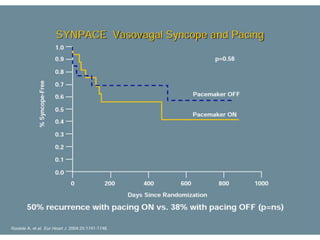
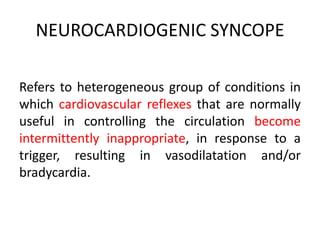
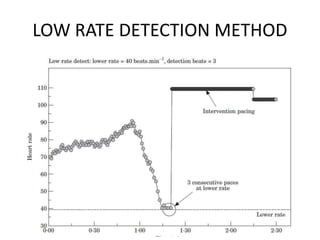
![Control
N=87
Pacemaker
N=84
% Participants
w/Syncopal Events
22% 11%
Total Number of
Syncopal Events
47 22
Mean Number Syncopal
Events
1.14 0.20
SAFE PACE Results
Number of Syncopal Episodes
50%
Reduction
[OR 0.53; 95%
CI 0.23; 1.20 ns]
* Syncopal events 12 months past randomization
** Crude adjustment calculation
Kenny RA, J Am Coll Cardiol 2001; 38:000-000.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ncsyncopeppt-160920015810/85/NEUROCARDIOGENIC-SYNCOPE-ppt-114-320.jpg)