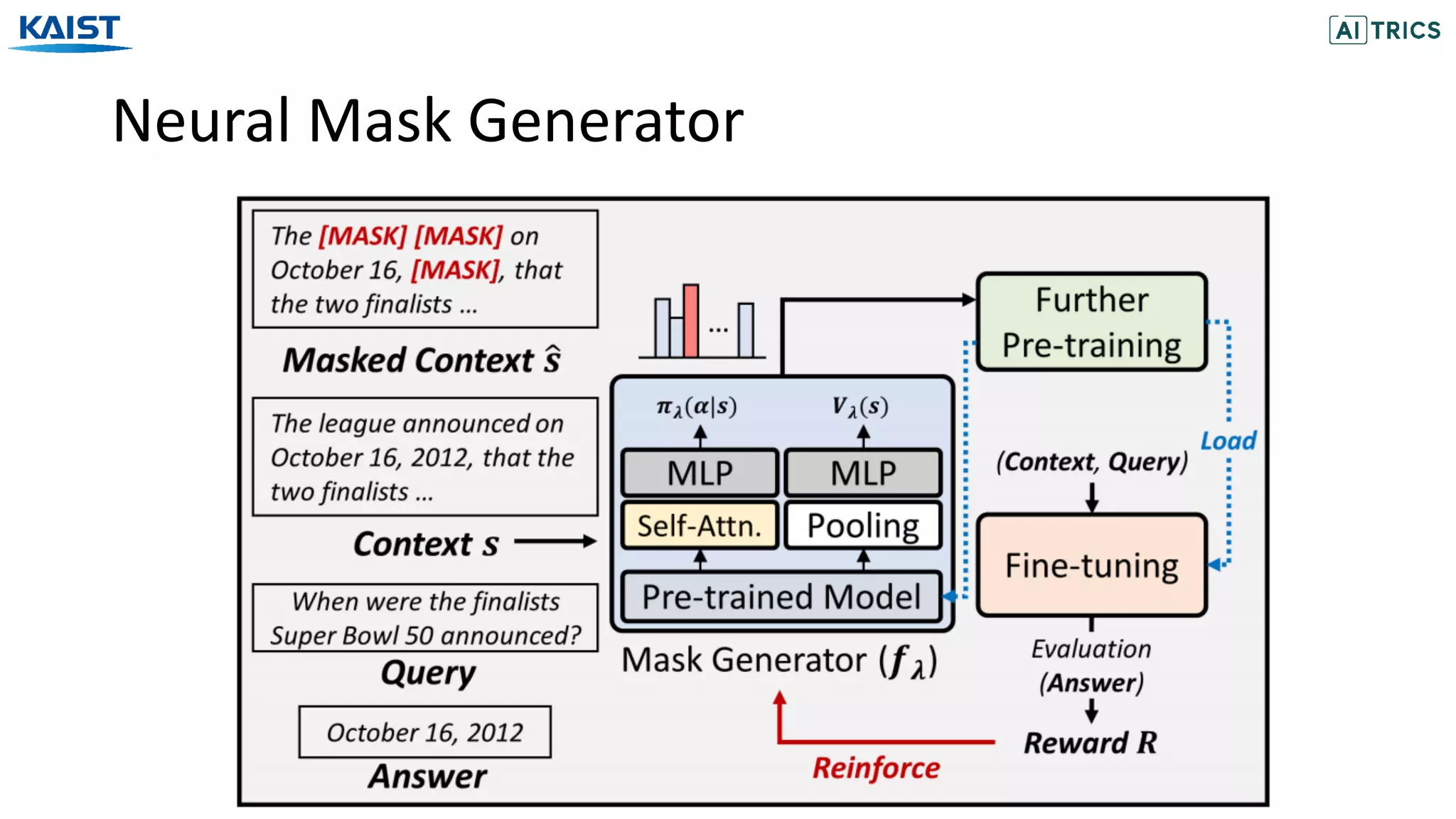
The document discusses the Neural Mask Generator (NMG), which is designed to generate adaptive word maskings for language model adaptation, leveraging a bi-level meta-learning framework and reinforcement learning. It addresses the need for effective masking policies in pre-trained language models, demonstrating through experiments that NMG achieves better or comparable performance than existing heuristic masking strategies across various natural language understanding tasks. The research proposes a methodology for optimizing masking policies to enhance domain-specific language model adaptation.

![Background
The recent success of neural language model is based on the scheme of
pre-train once, and fine-tune everywhere.
[Devlin et al. 19] BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding, NAACL 2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralmaskgeneratorlearningtogenerateadaptivewordmaskingsforlanguagemodeladaptation-201113072119/75/Neural-Mask-Generator-Learning-to-Generate-Adaptive-Word-Maskings-for-Language-Model-Adaptation-2-2048.jpg)
![Background
Recent Language Models (LM) are pre-trained on large and heterogeneous
dataset.
General Dataset
(e.g. Wikipedia)
Specific-Domain
Dataset
Further
Pre-training
[Beltagy et al. 19] SciBERT: A Pretrained Language Model for Scientific Text, EMNLP 2019.
[Lee et al. 20] BioBERT: a pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining, Bioinformatics 2020.
[Gururangan et al. 20] Don’t stop Pre-training: Adapt Language Models to Domains and Tasks, ACL 2020.
Some works propose further pre-training for LM adaptation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralmaskgeneratorlearningtogenerateadaptivewordmaskingsforlanguagemodeladaptation-201113072119/75/Neural-Mask-Generator-Learning-to-Generate-Adaptive-Word-Maskings-for-Language-Model-Adaptation-3-2048.jpg)
![Background
Masked Language Models (MLMs) objective has shown to be effective
for language model pre-training.
A myocardial infarction,
also known as a [MASK]
attack, occurs when blo
od flow decreases.
A myocardial infarction,
also known as a heart
attack, occurs when bl
ood flow decreases.
[Original] [Model Input] [Model Output]
heart
[Devlin et al. 19] BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding, NAACL 2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralmaskgeneratorlearningtogenerateadaptivewordmaskingsforlanguagemodeladaptation-201113072119/75/Neural-Mask-Generator-Learning-to-Generate-Adaptive-Word-Maskings-for-Language-Model-Adaptation-4-2048.jpg)
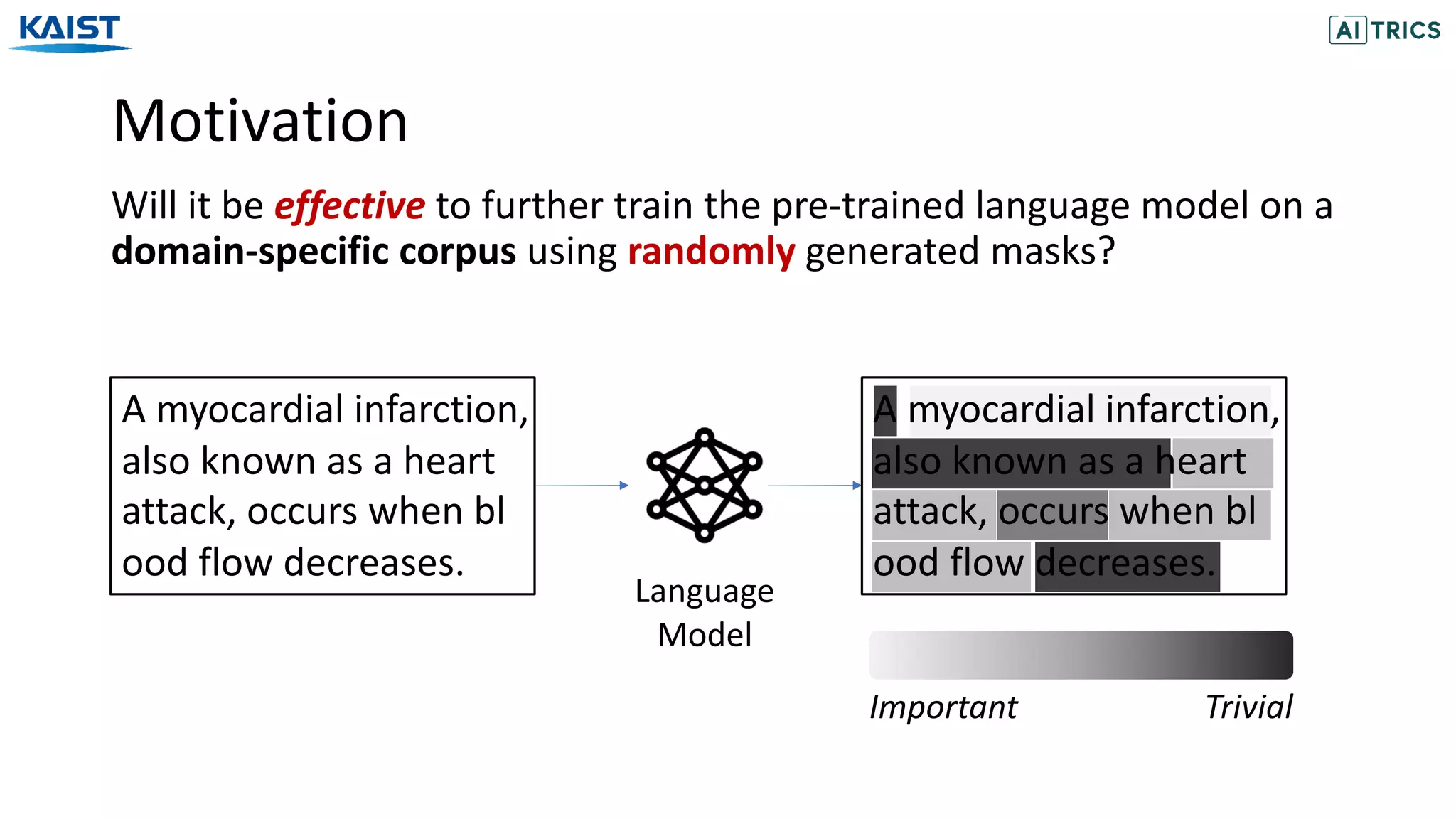
![Motivation
Although several heuristic masking policies have been proposed, none
of them is clearly superior over others.
A myo ##car ##dial in ##farc ##tion occurs when blood flow ....Original:
A [MASK] [MASK] [MASK] in ##farc ##tion occurs when blood flow ...Whole-word:
Span: A myo ##car ##dial in ##farc [MASK] [MASK] [MASK] blood flow ...
A myo [MASK] ##dial [MASK] ##farc ##tion occurs when [MASK] flow ...Random:
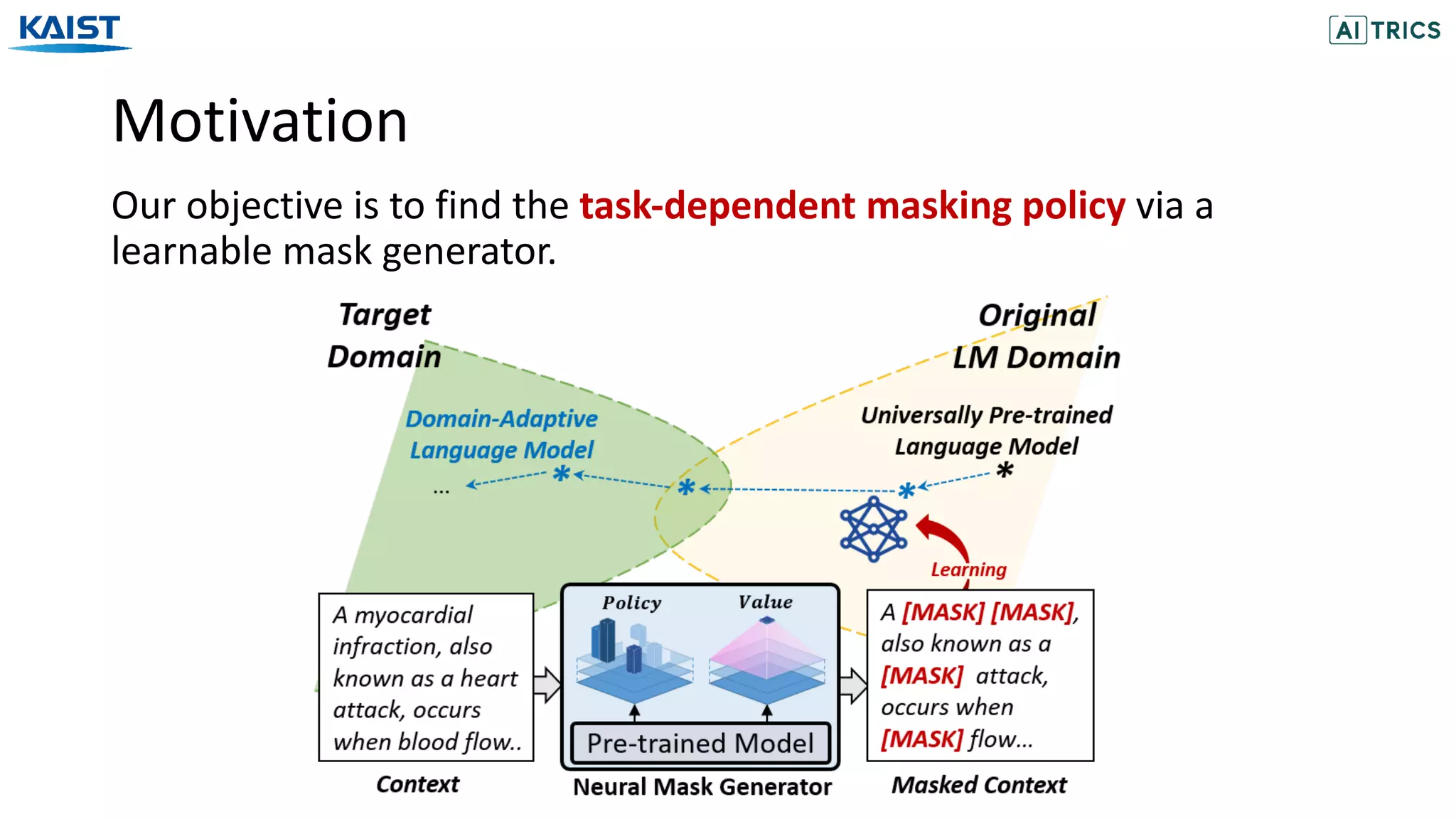
In this work, we propose to generate the masks adaptively for the
given domain, by learning the optimal masking policy.
[Joshi et al. 20] SpanBERT: Improving Pre-training by Representing and Predicting Spans, TACL 2020.
[Sun et al. 19] Enhanced Representation through Knowledge Integration, arXiv 2019.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralmaskgeneratorlearningtogenerateadaptivewordmaskingsforlanguagemodeladaptation-201113072119/75/Neural-Mask-Generator-Learning-to-Generate-Adaptive-Word-Maskings-for-Language-Model-Adaptation-6-2048.jpg)
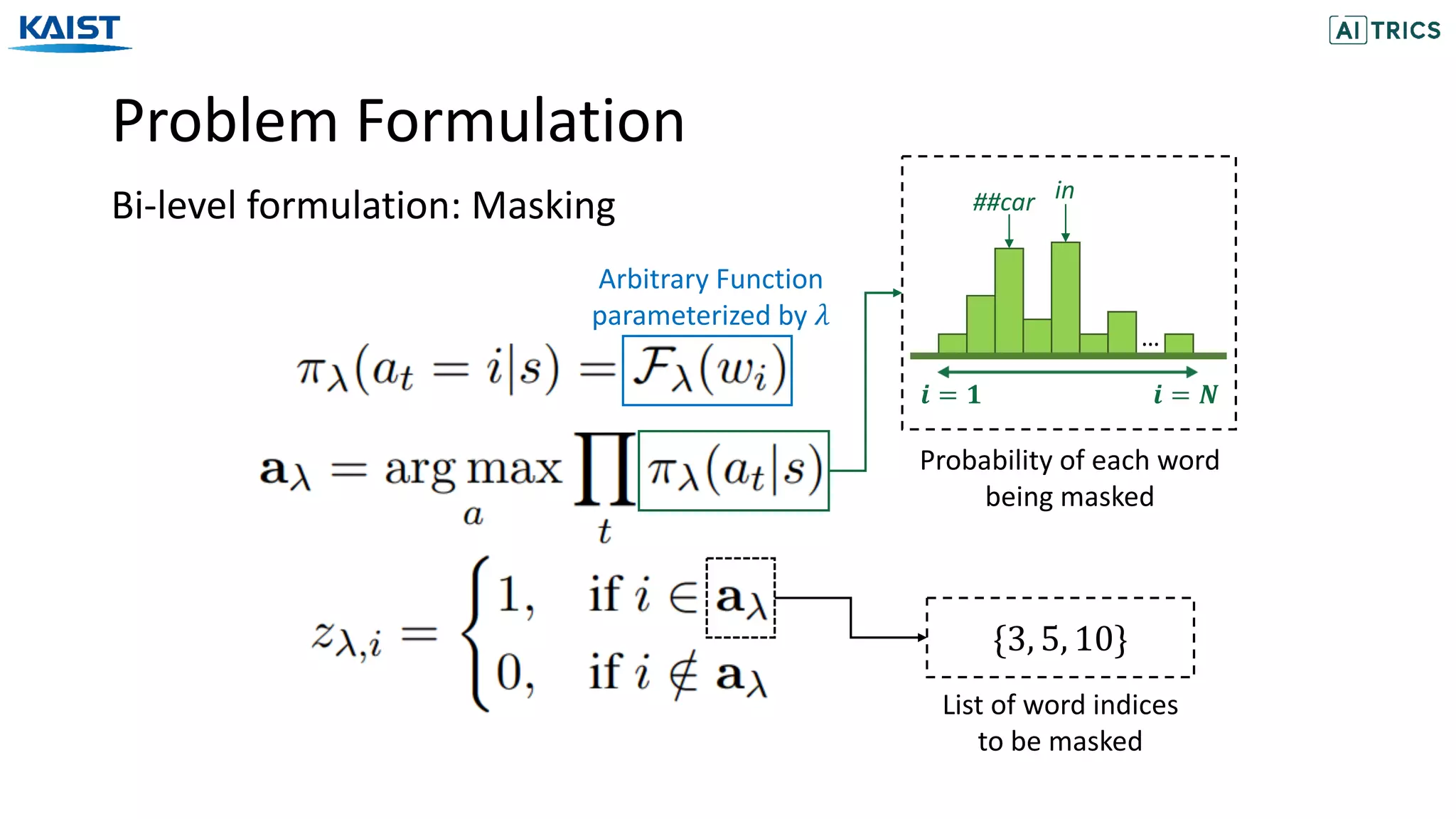
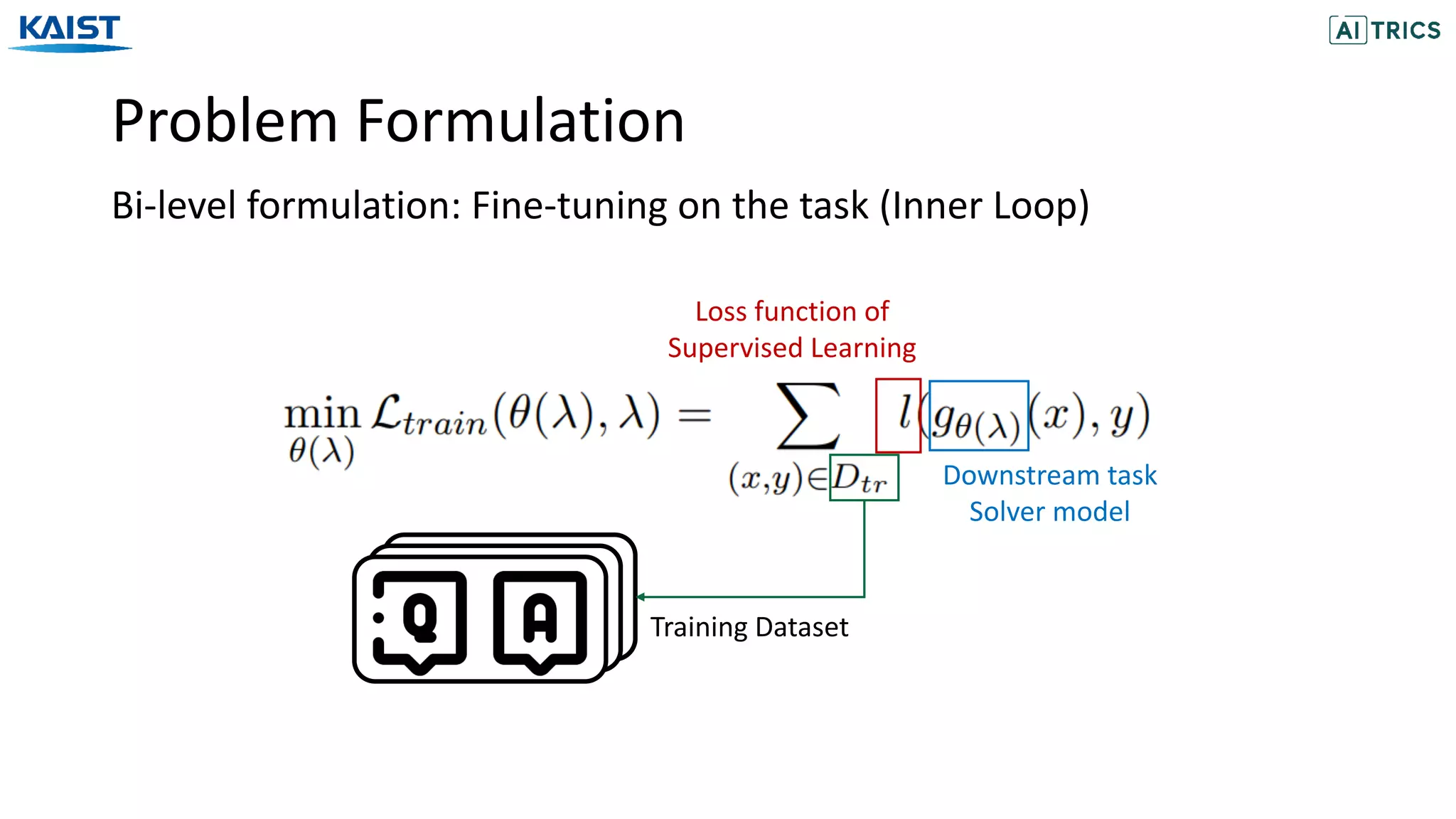
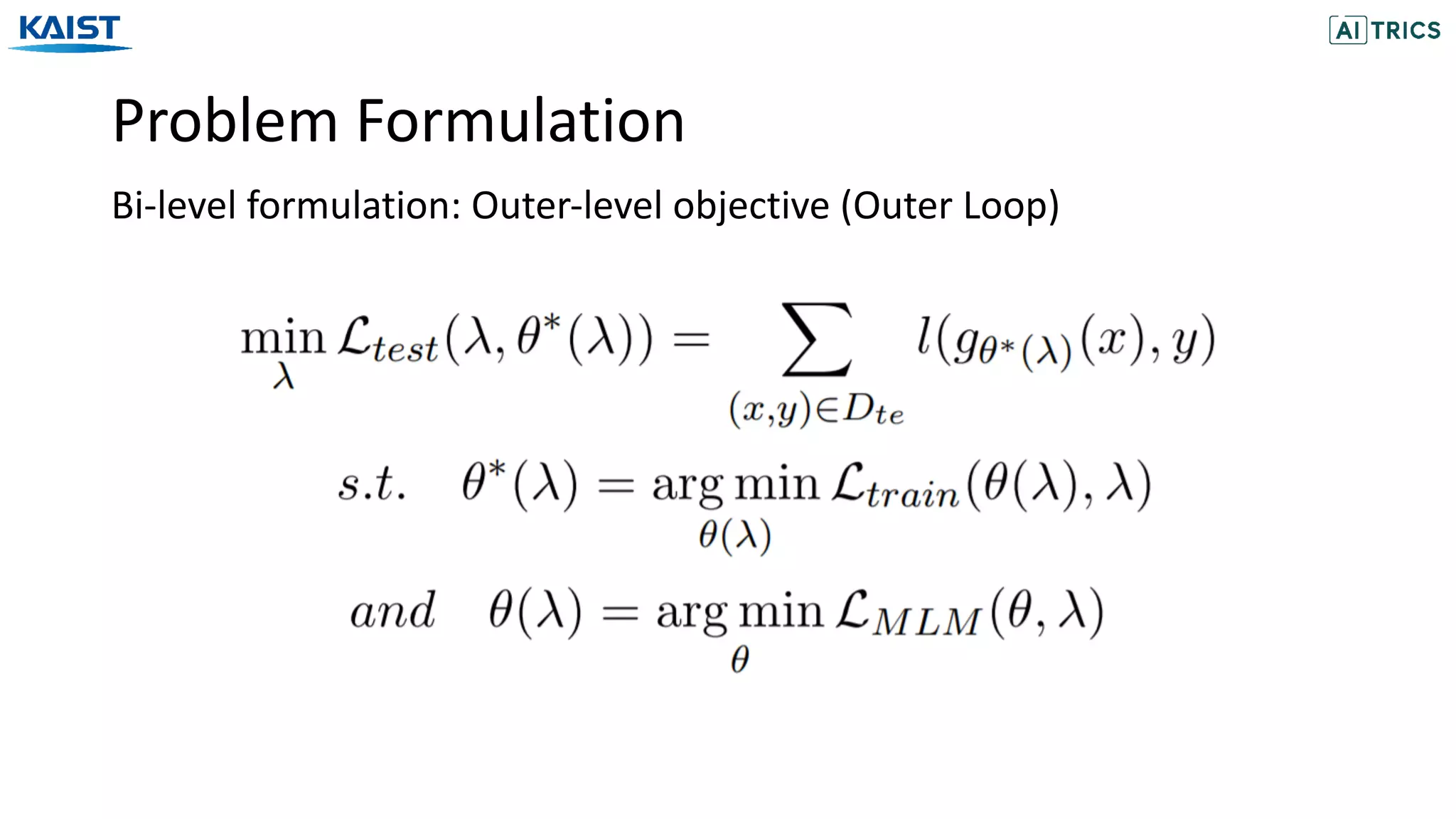
![Problem Formulation
Masked Language Model
Unannotated
Text corpus
[MASK]
Masked
Text corpus
Language Model
Parameters [MASK]
Original
Context
Masked
Context](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralmaskgeneratorlearningtogenerateadaptivewordmaskingsforlanguagemodeladaptation-201113072119/75/Neural-Mask-Generator-Learning-to-Generate-Adaptive-Word-Maskings-for-Language-Model-Adaptation-8-2048.jpg)
![Problem Formulation
Masked Language Model
A myo [MASK] ##dial [MASK]
##farc ##tion occurs when
[MASK] flow ...
Masked Context
A myo ##car ##dial in ##farc
##tion occurs when blood flo
w ...
Original Context
𝑤! = A
𝑤" = myo
𝑤# = ##car
𝑤$ = ##dial
𝑤% = in
𝑤& = ##farc
𝑤' = ##tion
…
Words (Tokens)
𝑧( = $
1,
0,
𝑖𝑓 𝑖-𝑡ℎ word is masked
𝑜𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑤𝑖𝑠𝑒](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralmaskgeneratorlearningtogenerateadaptivewordmaskingsforlanguagemodeladaptation-201113072119/75/Neural-Mask-Generator-Learning-to-Generate-Adaptive-Word-Maskings-for-Language-Model-Adaptation-9-2048.jpg)
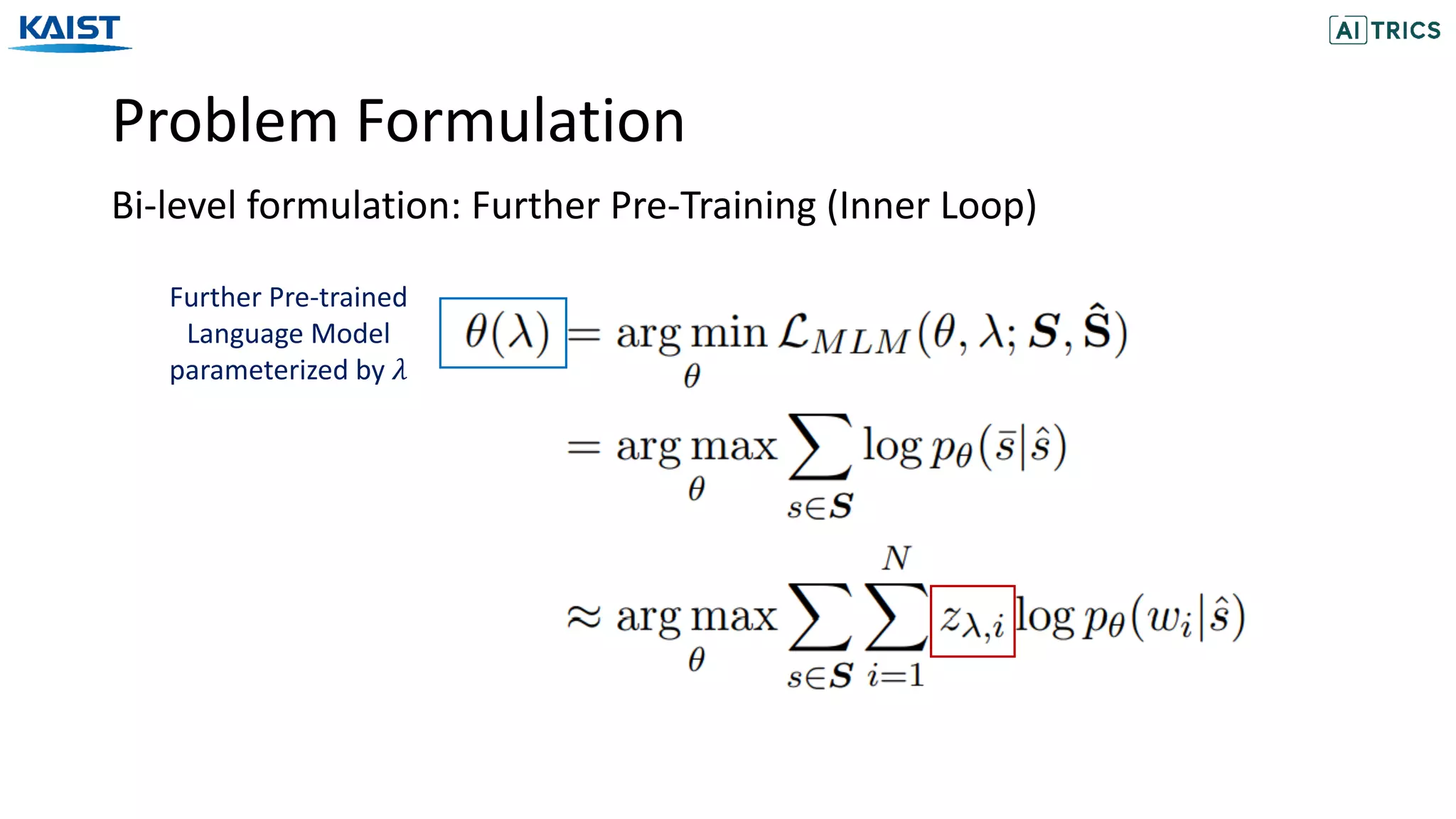
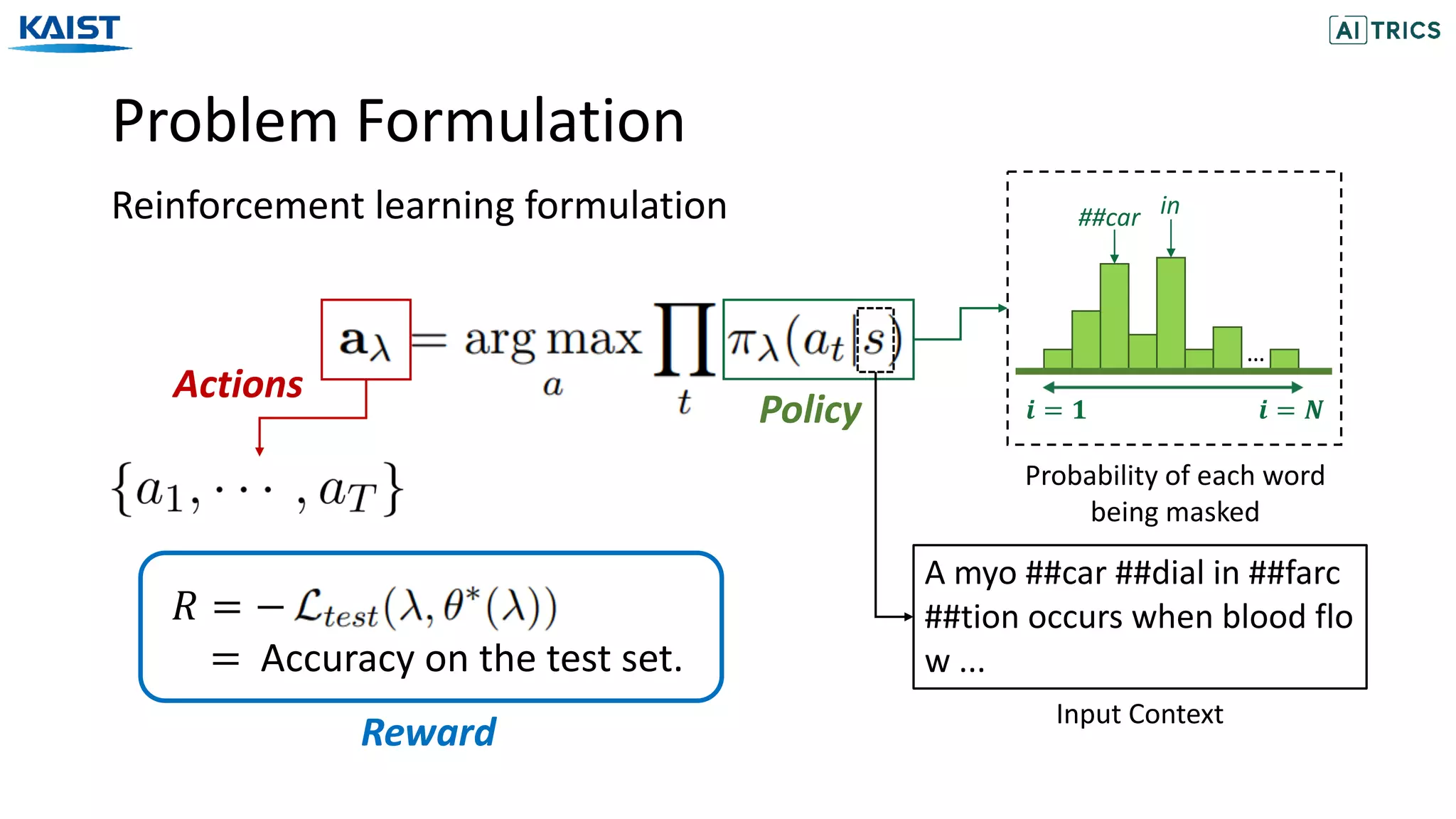
![Problem Formulation
Reinforcement learning formulation
The probability of
masking T tokens
Transition
Probability
The cat is cute .
The [MASK] is cute .
The [MASK] is [MASK] .
t=1
t=2
t=3
Example (MDP)
The cat is cute .
The [MASK] is [MASK] .
Example (Approximation)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralmaskgeneratorlearningtogenerateadaptivewordmaskingsforlanguagemodeladaptation-201113072119/75/Neural-Mask-Generator-Learning-to-Generate-Adaptive-Word-Maskings-for-Language-Model-Adaptation-15-2048.jpg)
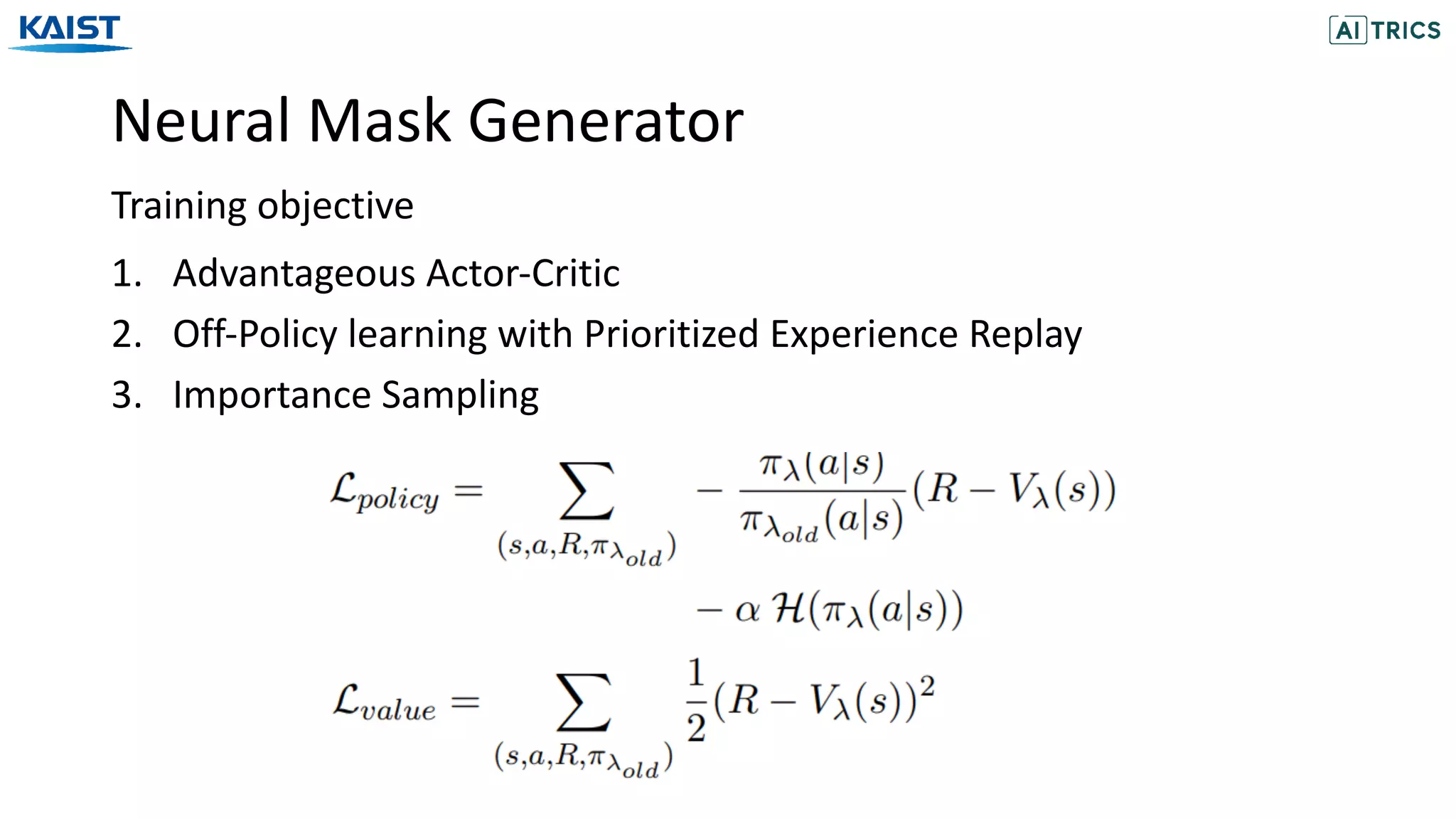
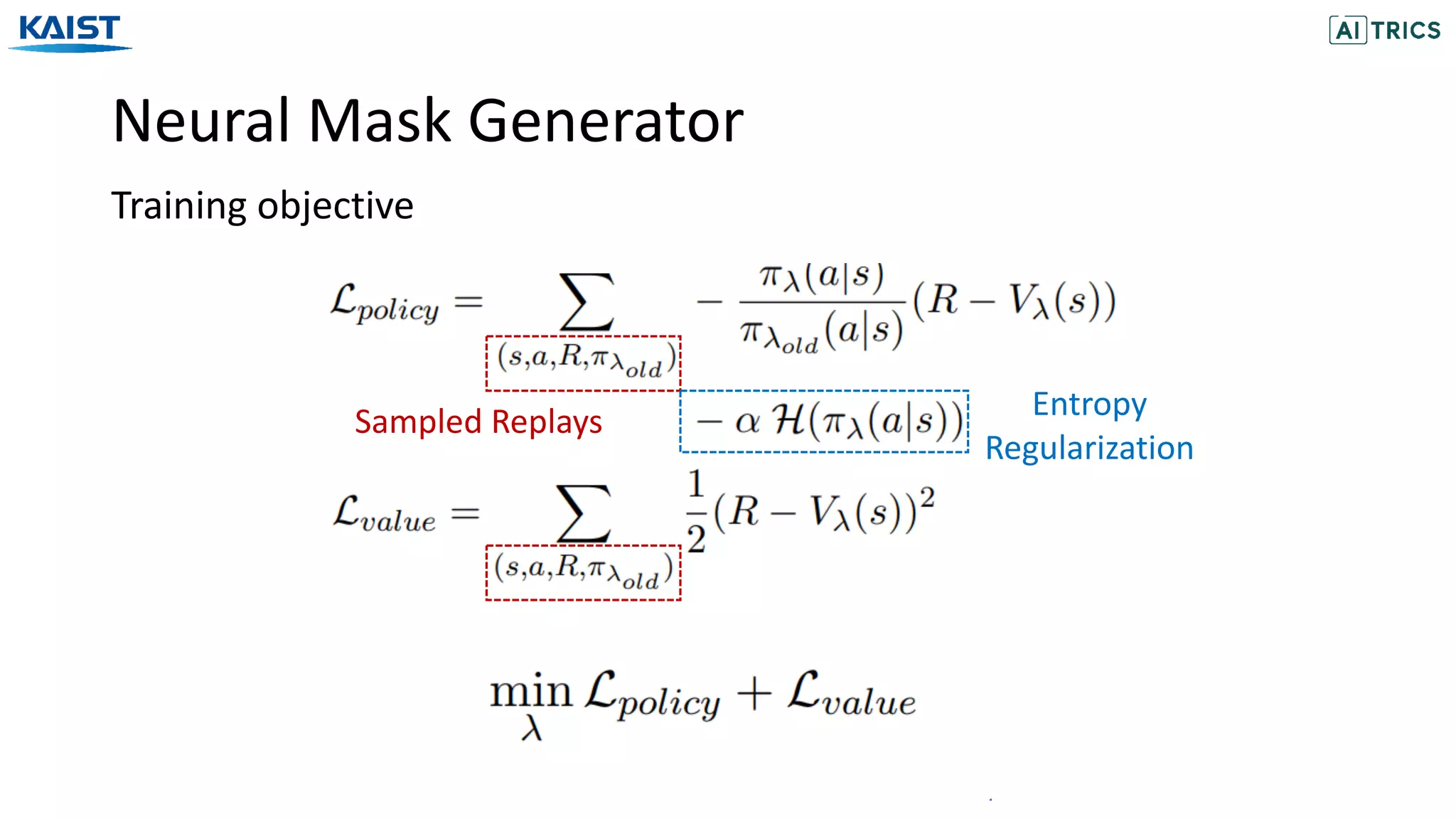
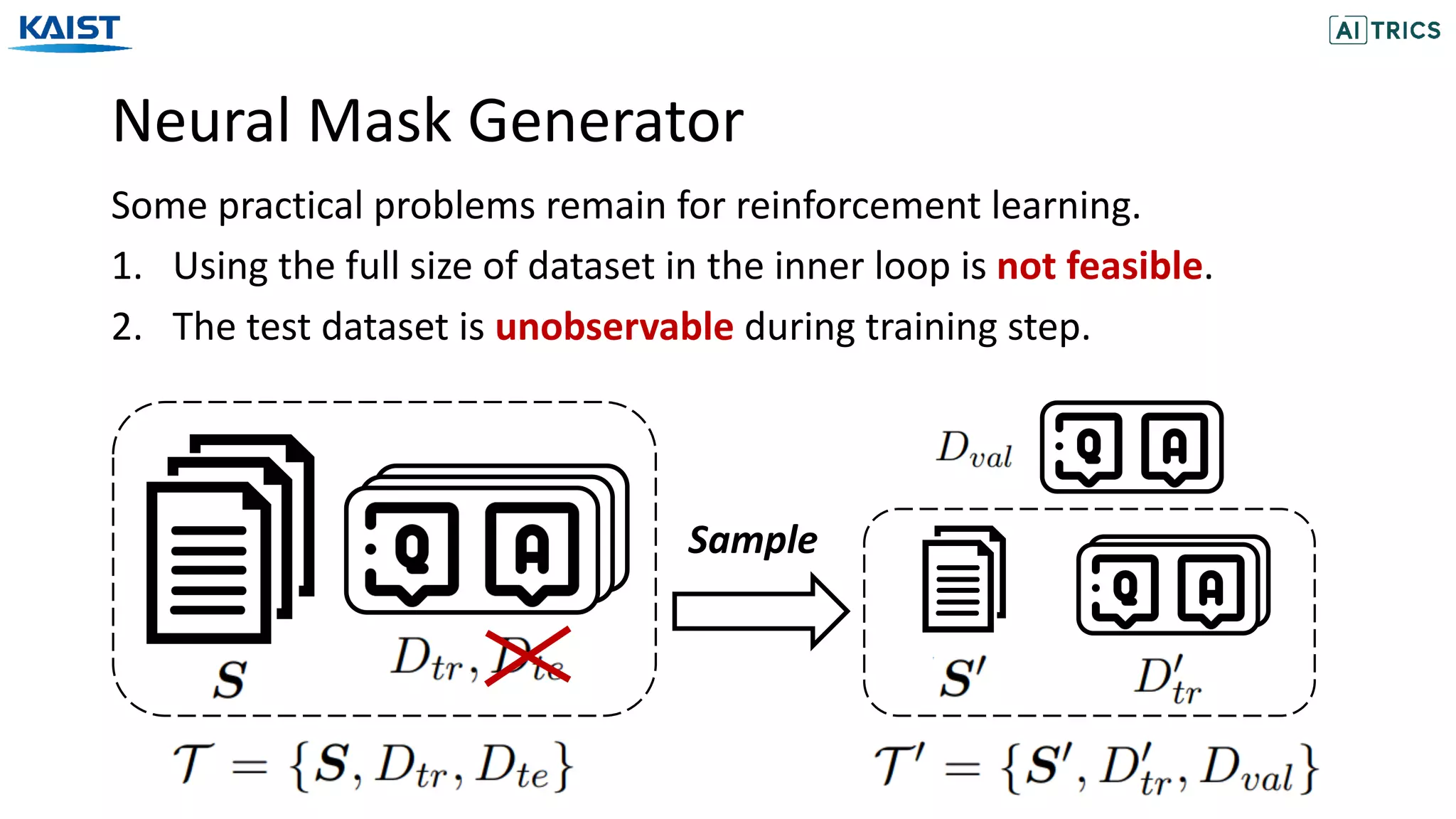
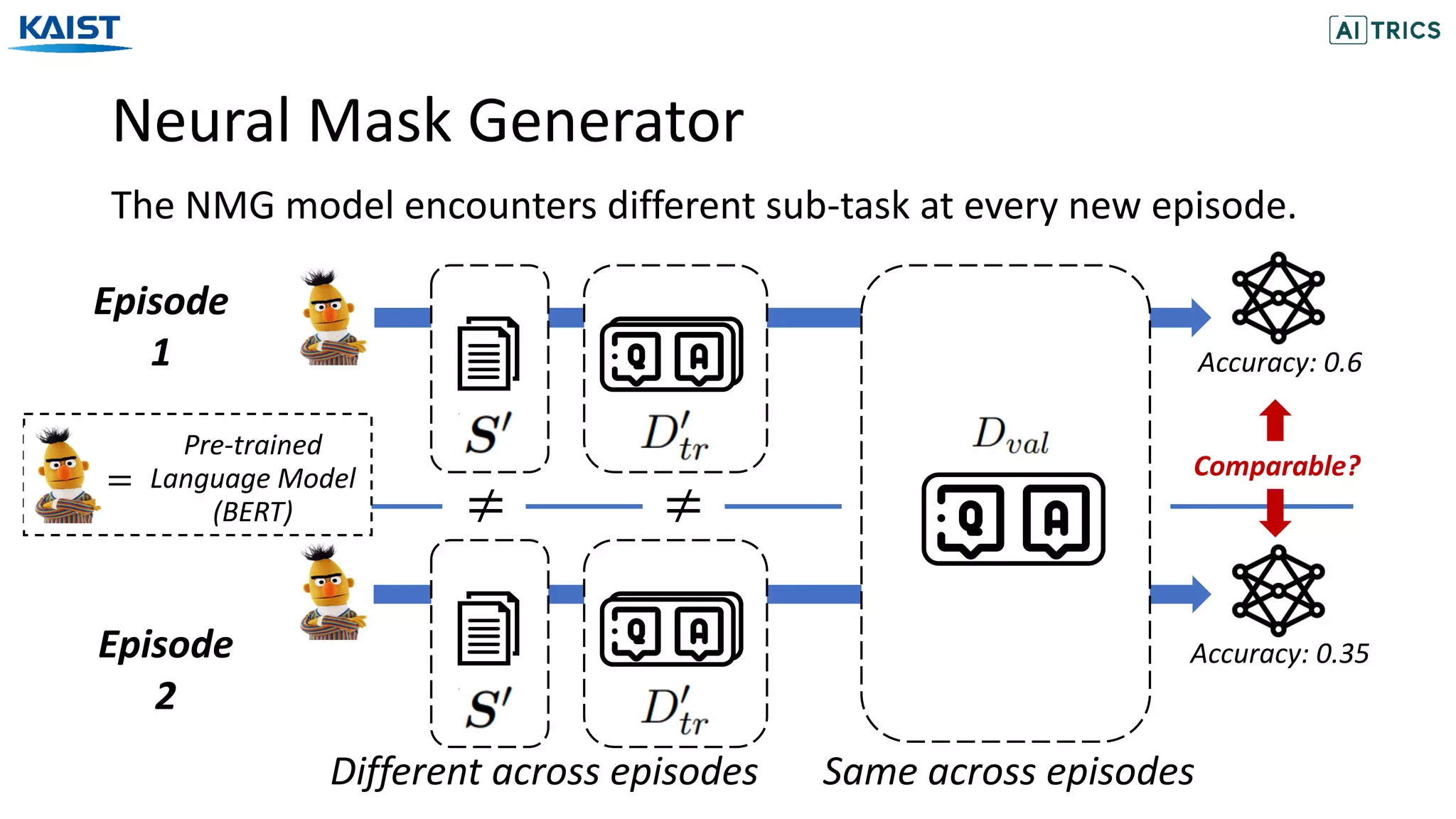
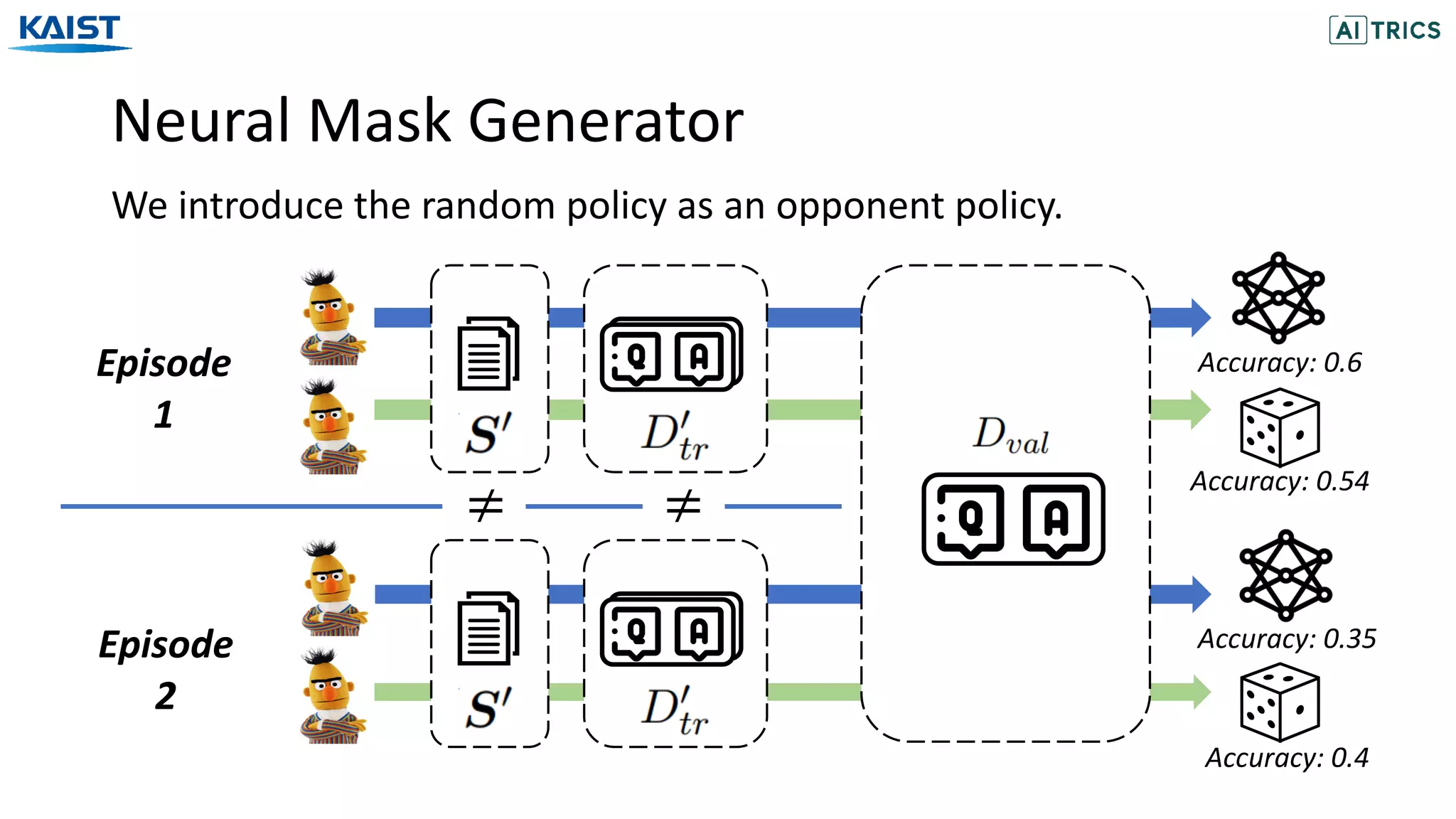
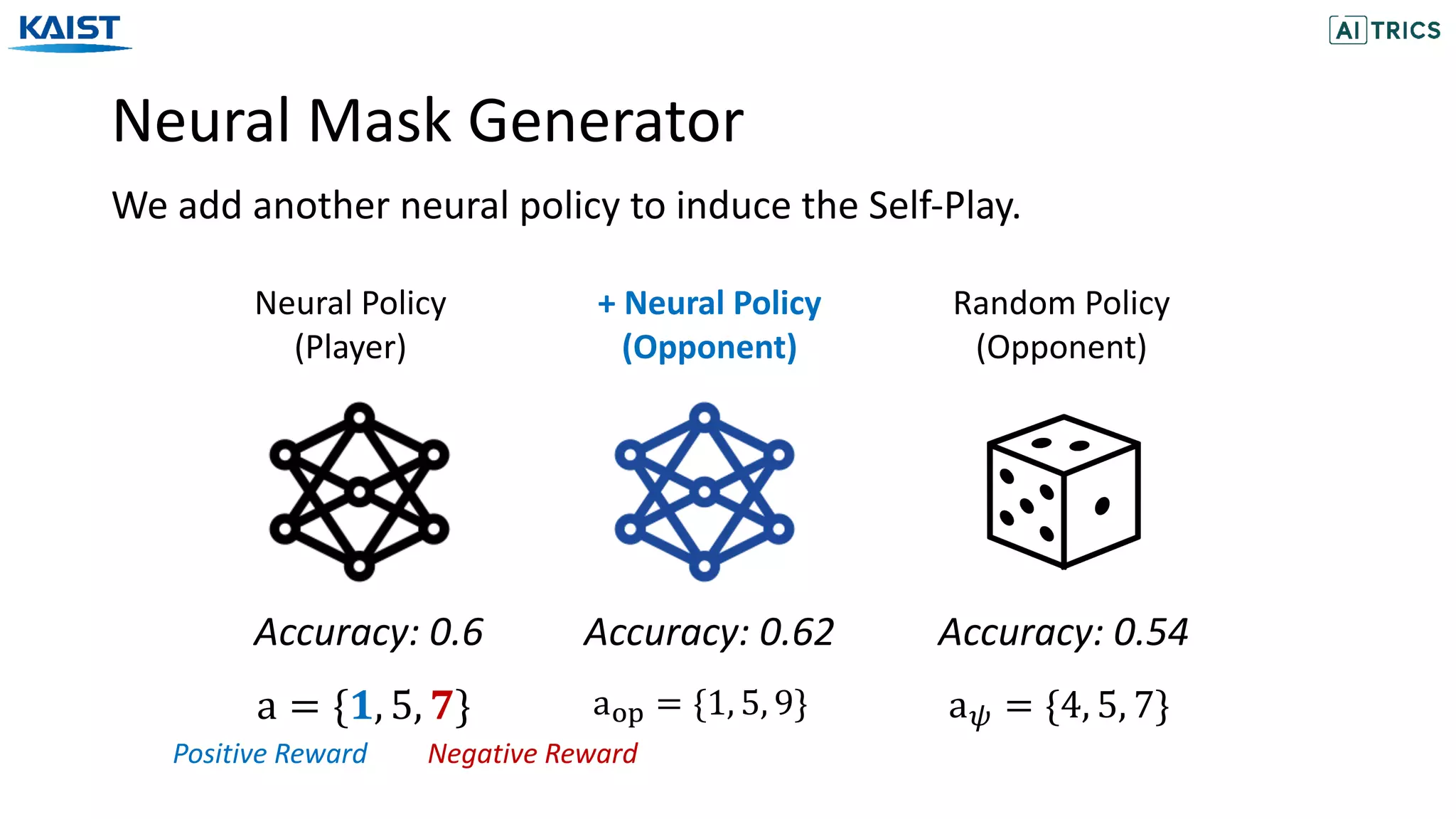
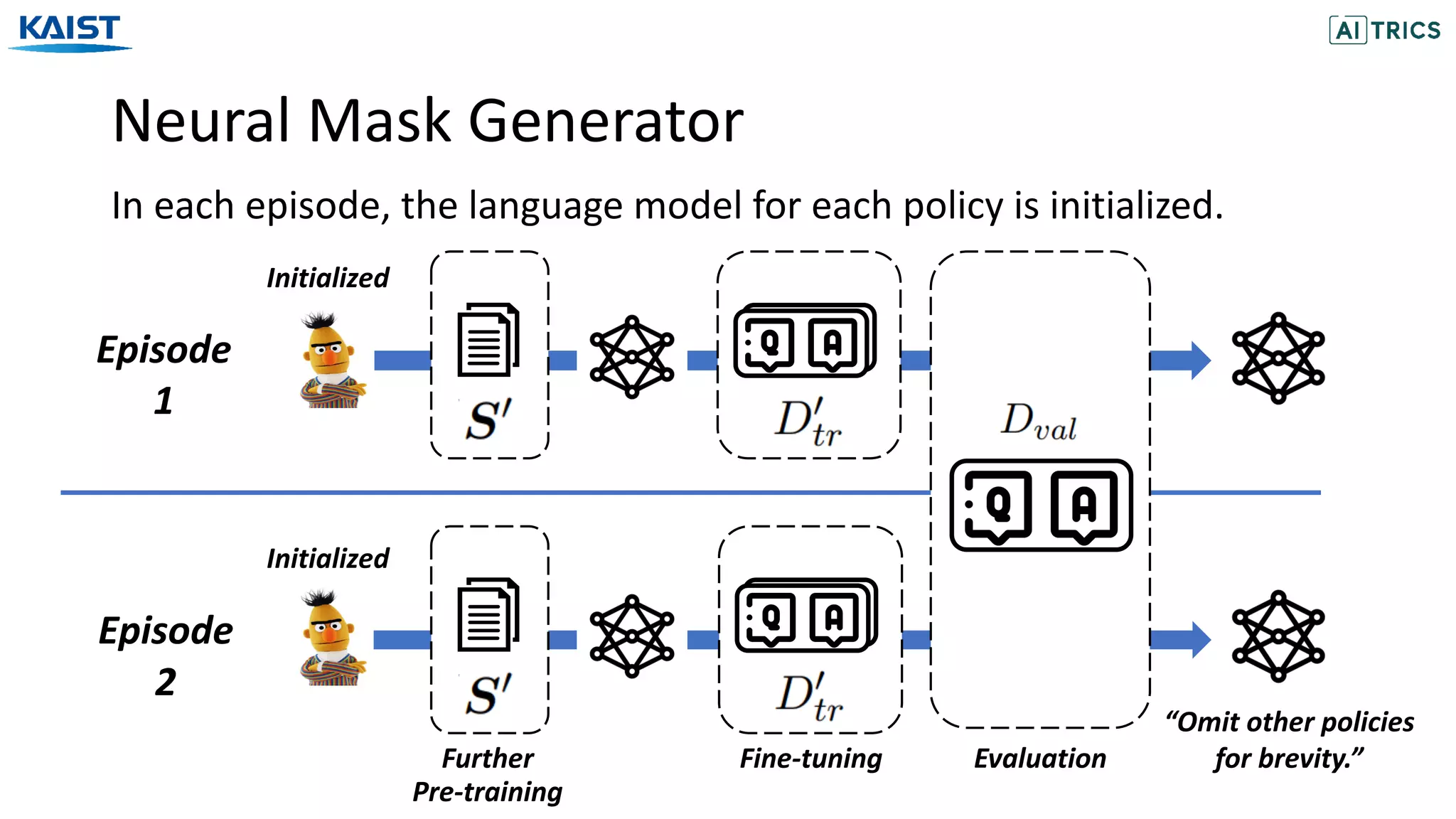
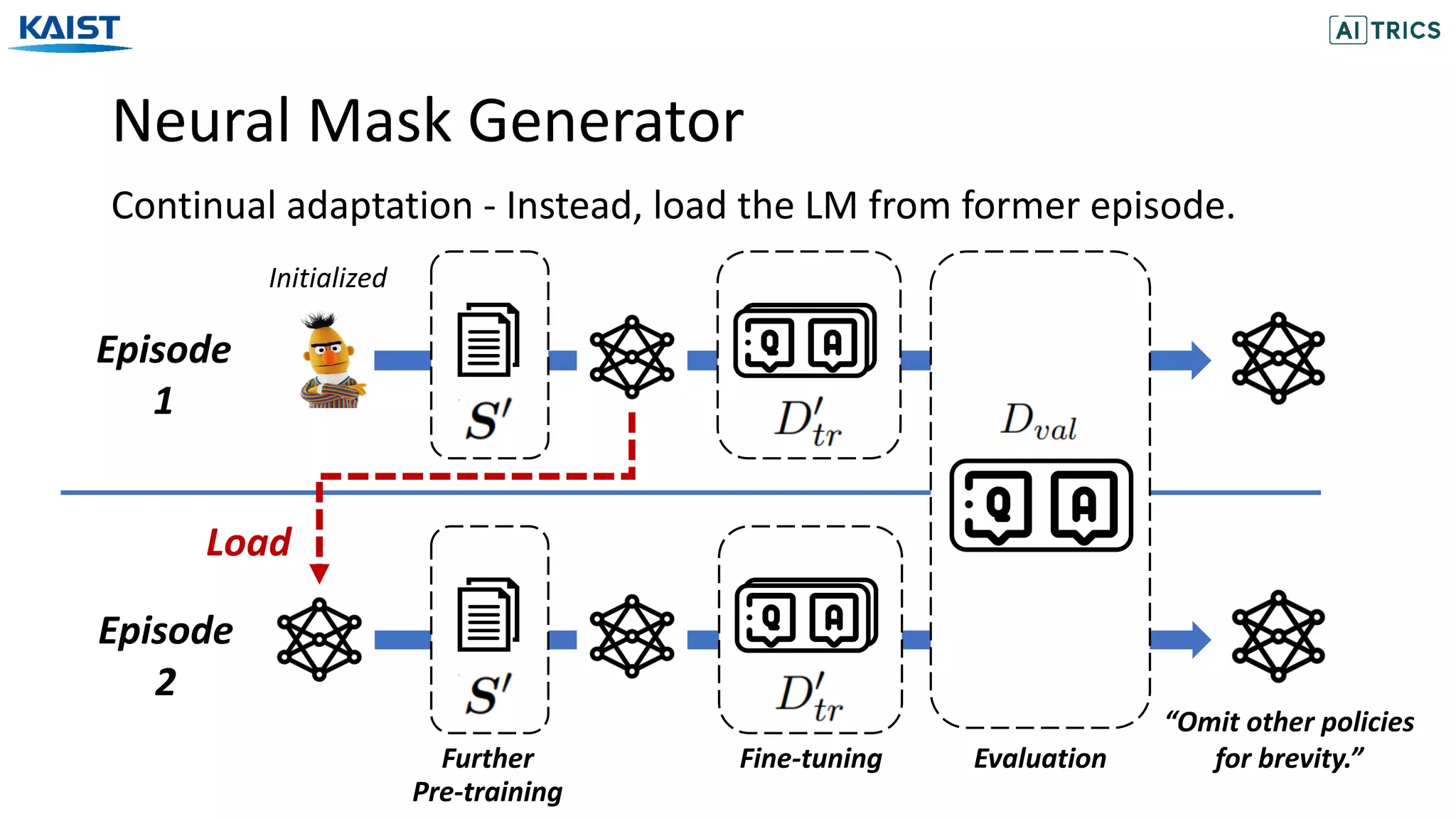
![Experiments
• No Pre-training
• Random Masking (Devlin et al. 19)
• Whole-Random Masking (Devlin et al. 19)
• Span-Random Masking (Joshi et al. 20)
• Entity-Random Masking (Sun et al. 19)
• Punctuation-Random Masking
Baselines
[Joshi et al. 20] SpanBERT: Improving Pre-training by Representing and Predicting Spans, TACL 2020.
[Sun et al. 19] Enhanced Representation through Knowledge Integration, arXiv 2019.
[Devlin et al. 19] BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding, NAACL 2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralmaskgeneratorlearningtogenerateadaptivewordmaskingsforlanguagemodeladaptation-201113072119/75/Neural-Mask-Generator-Learning-to-Generate-Adaptive-Word-Maskings-for-Language-Model-Adaptation-26-2048.jpg)
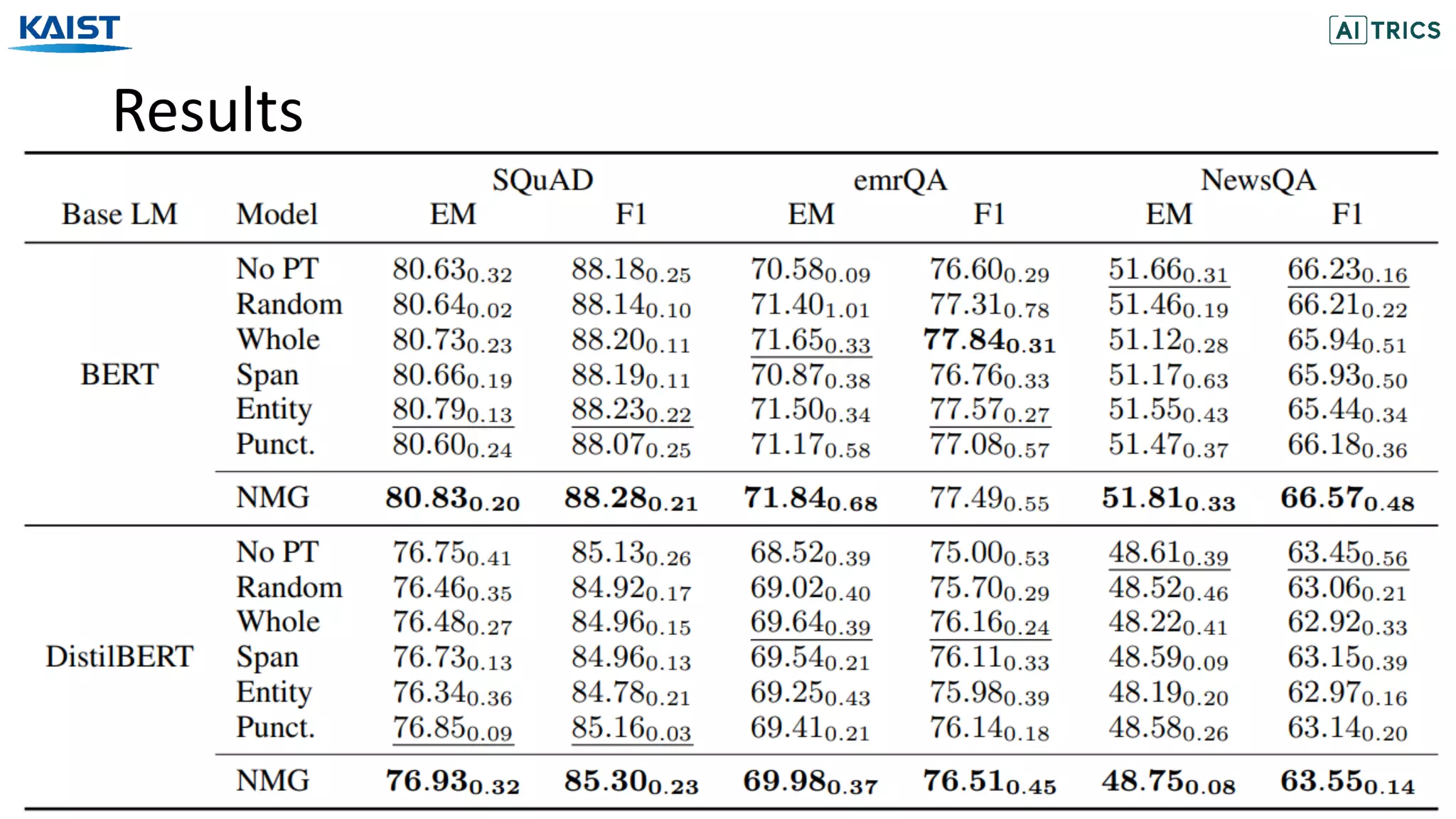
![[Text Classification Results] [Ablation Results]
Results](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralmaskgeneratorlearningtogenerateadaptivewordmaskingsforlanguagemodeladaptation-201113072119/75/Neural-Mask-Generator-Learning-to-Generate-Adaptive-Word-Maskings-for-Language-Model-Adaptation-28-2048.jpg)
![Analysis
[Example from NewsQA]
[Top6 Part-Of-Speech Tag of Masked Words on NewsQA]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neuralmaskgeneratorlearningtogenerateadaptivewordmaskingsforlanguagemodeladaptation-201113072119/75/Neural-Mask-Generator-Learning-to-Generate-Adaptive-Word-Maskings-for-Language-Model-Adaptation-29-2048.jpg)

