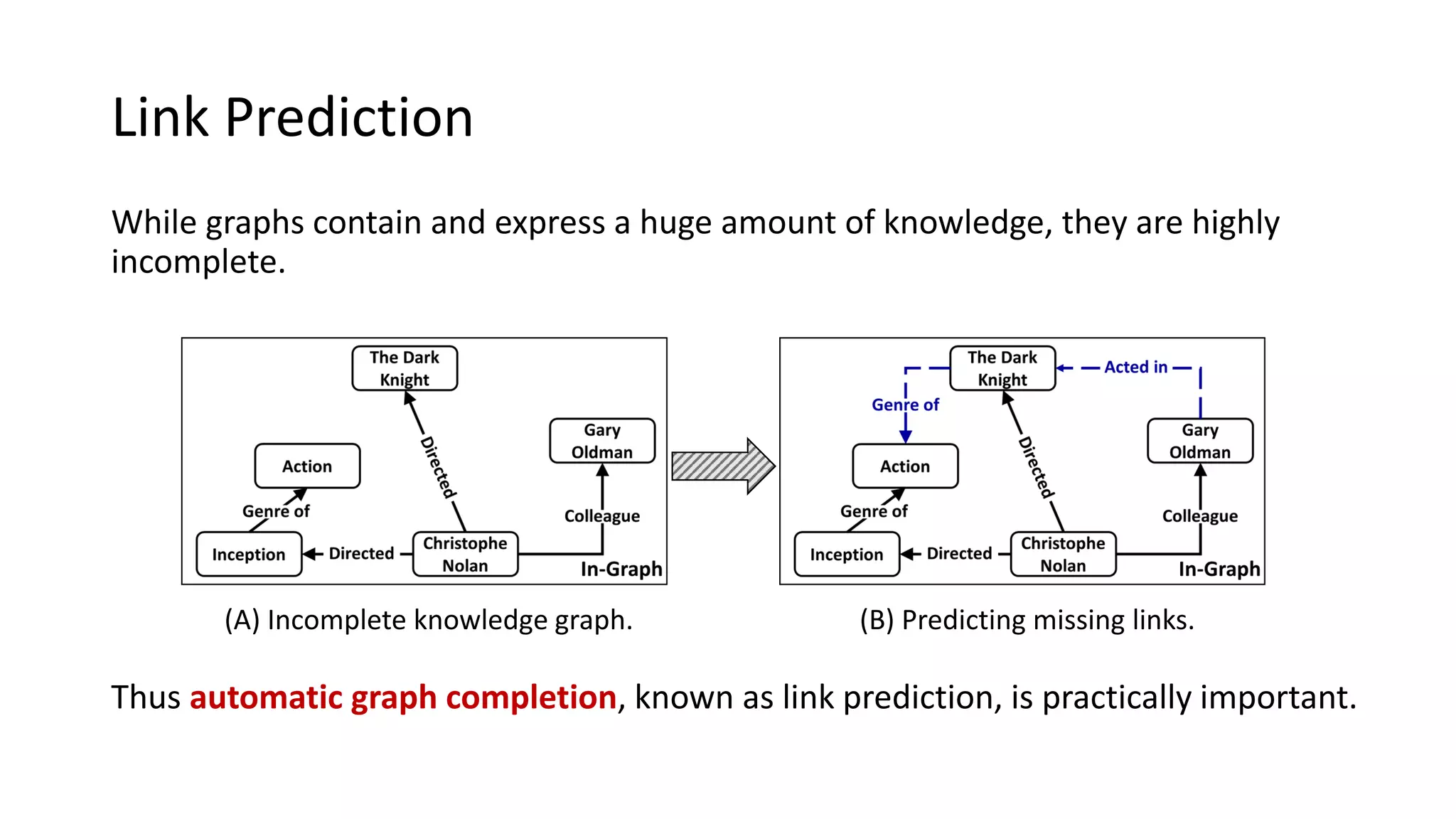
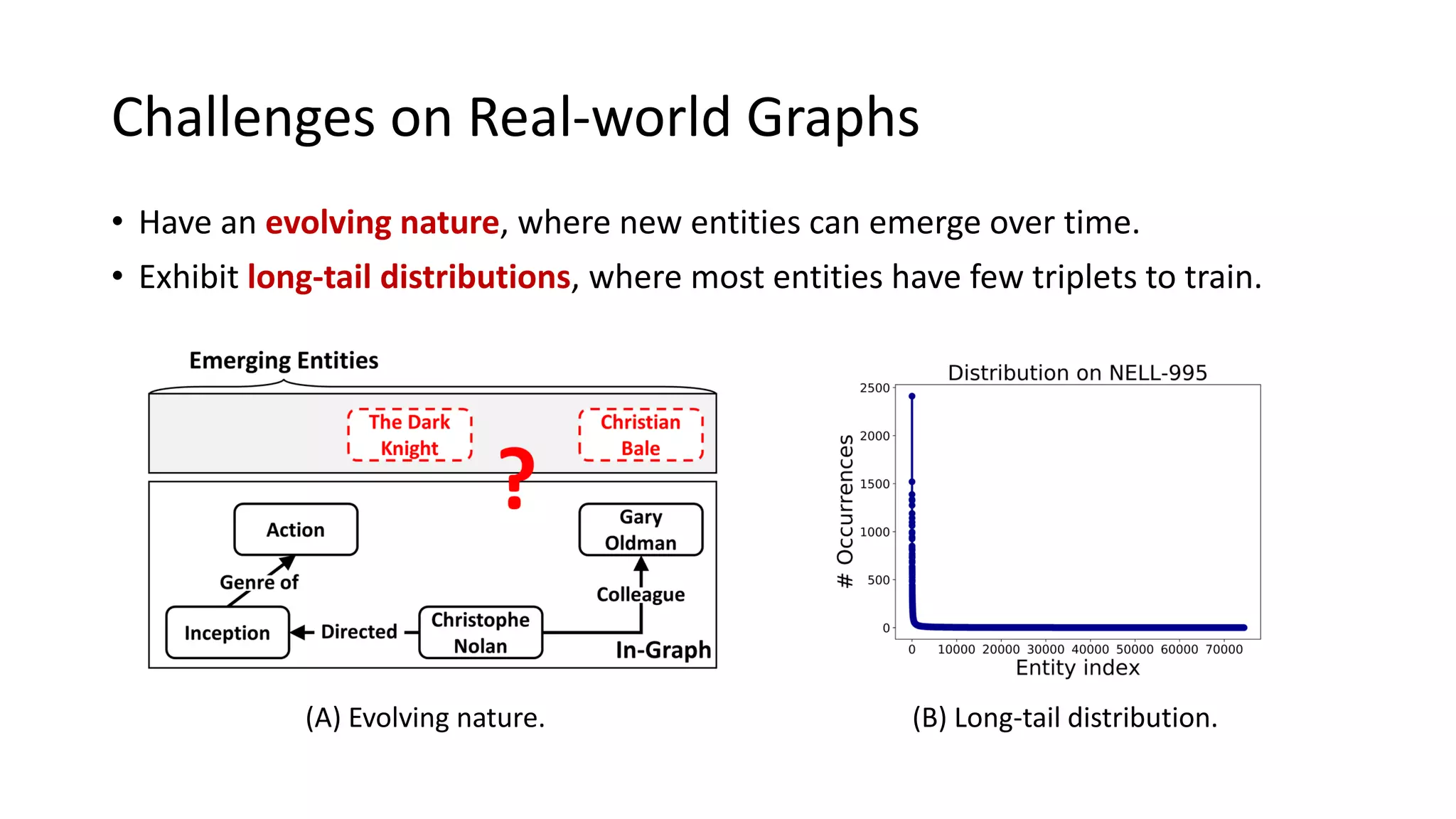
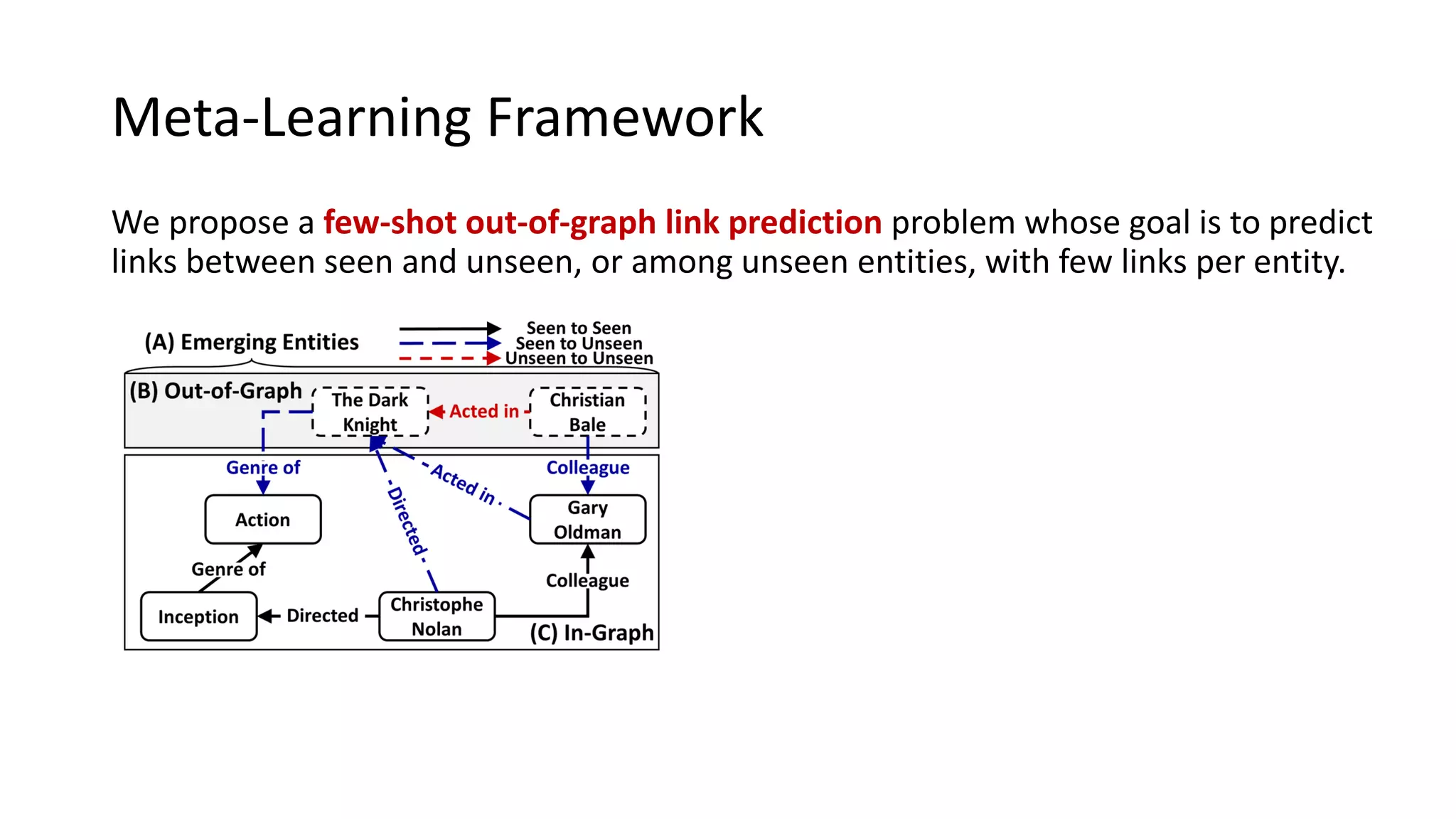
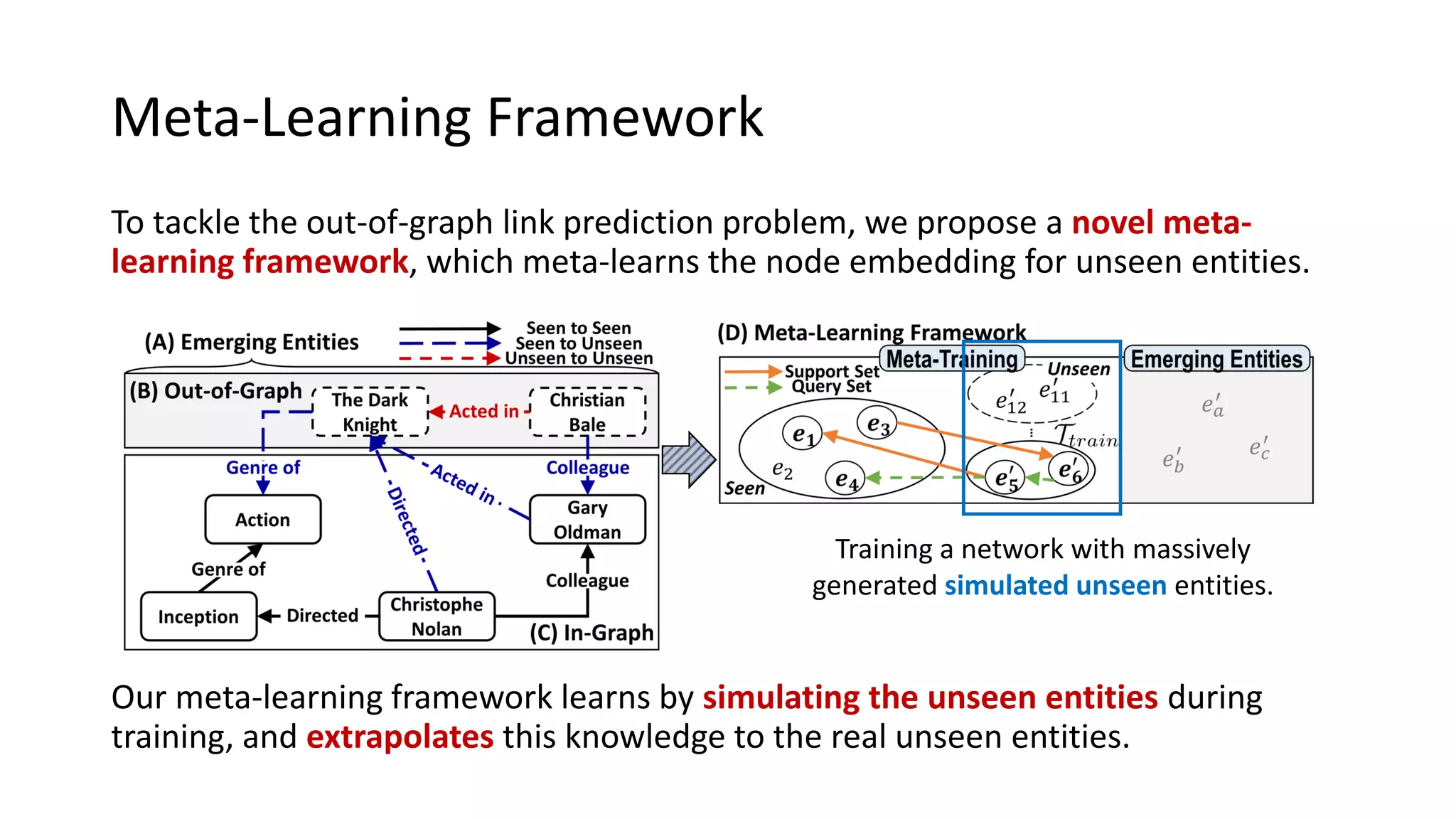
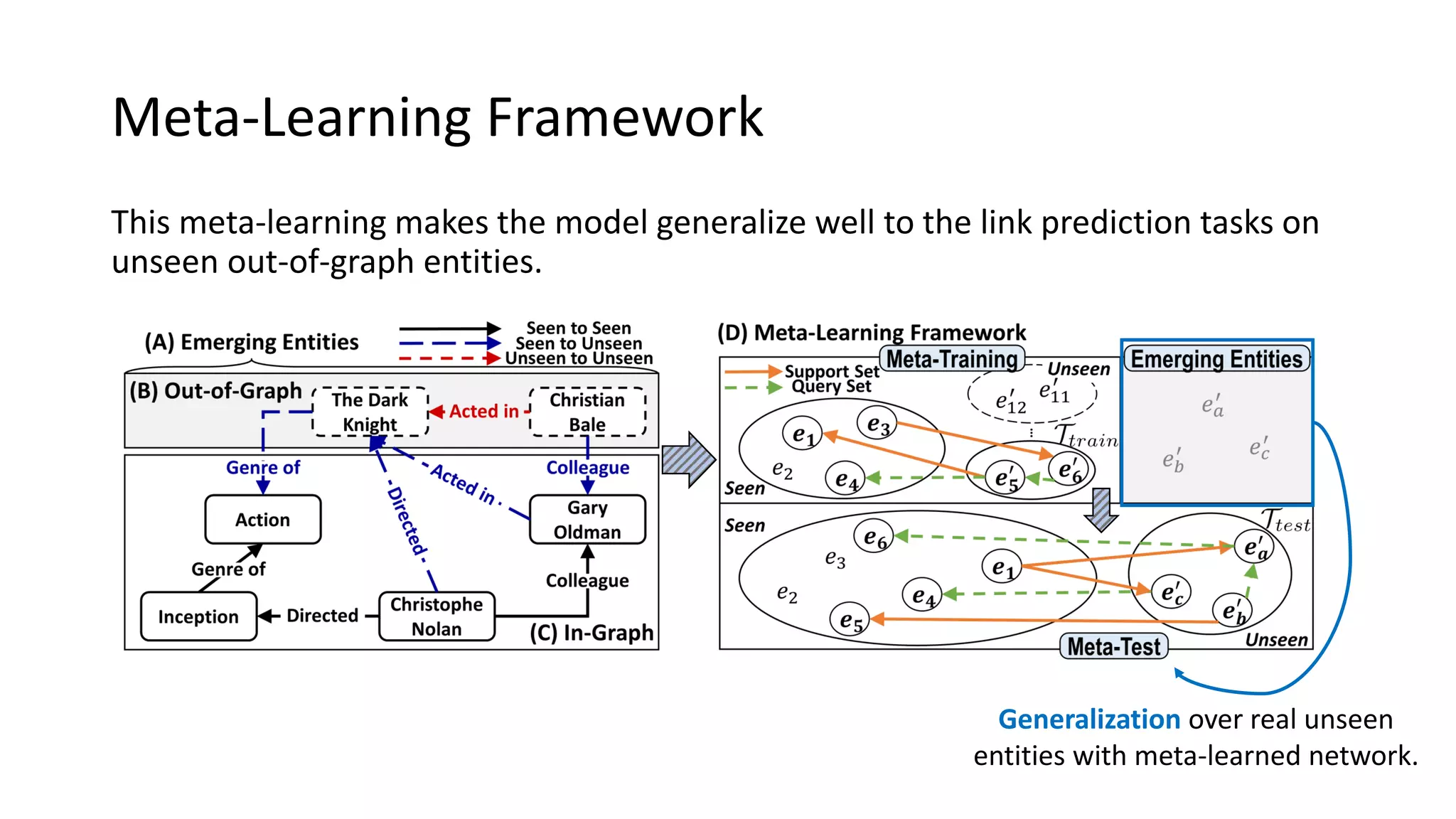
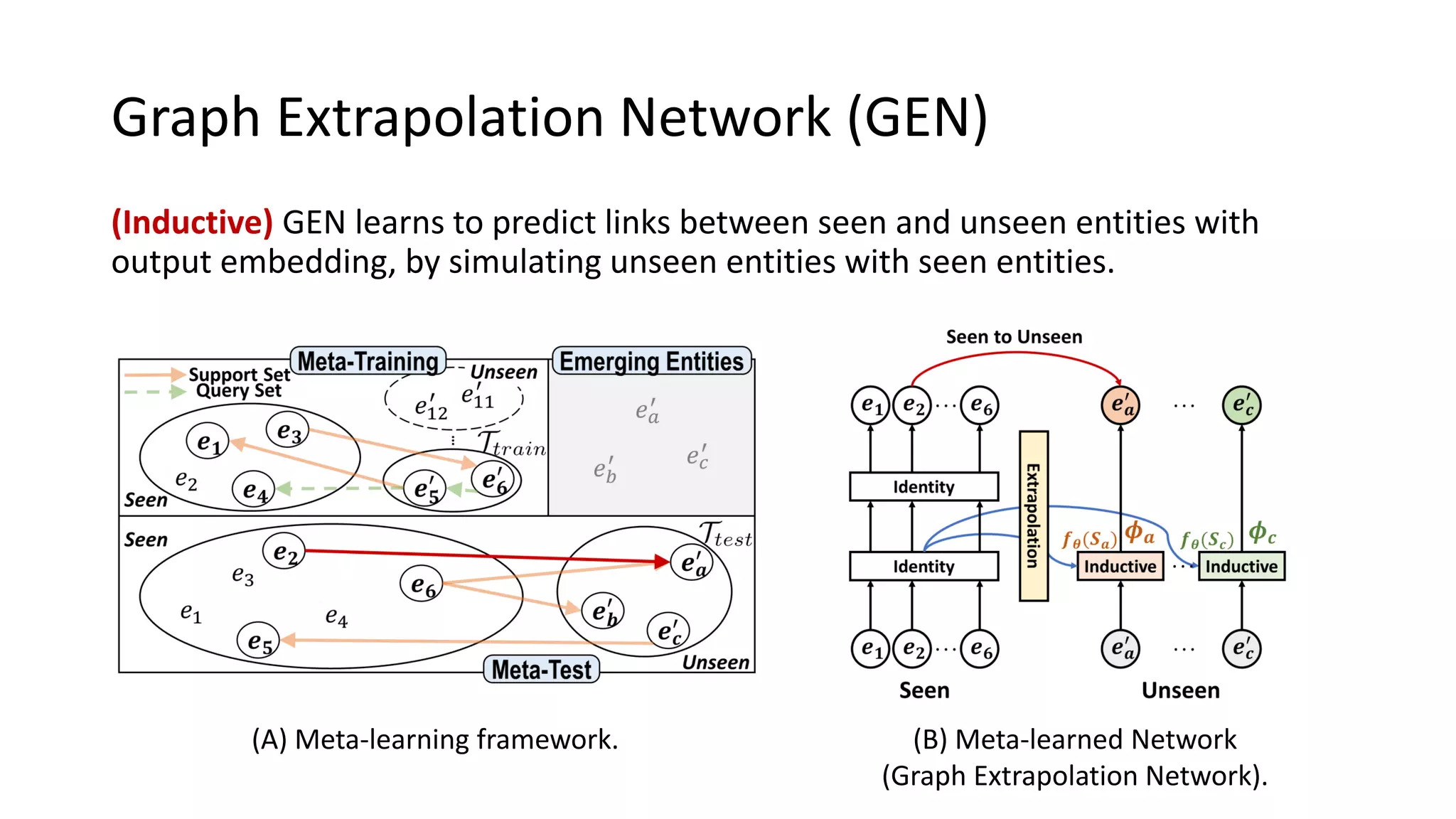
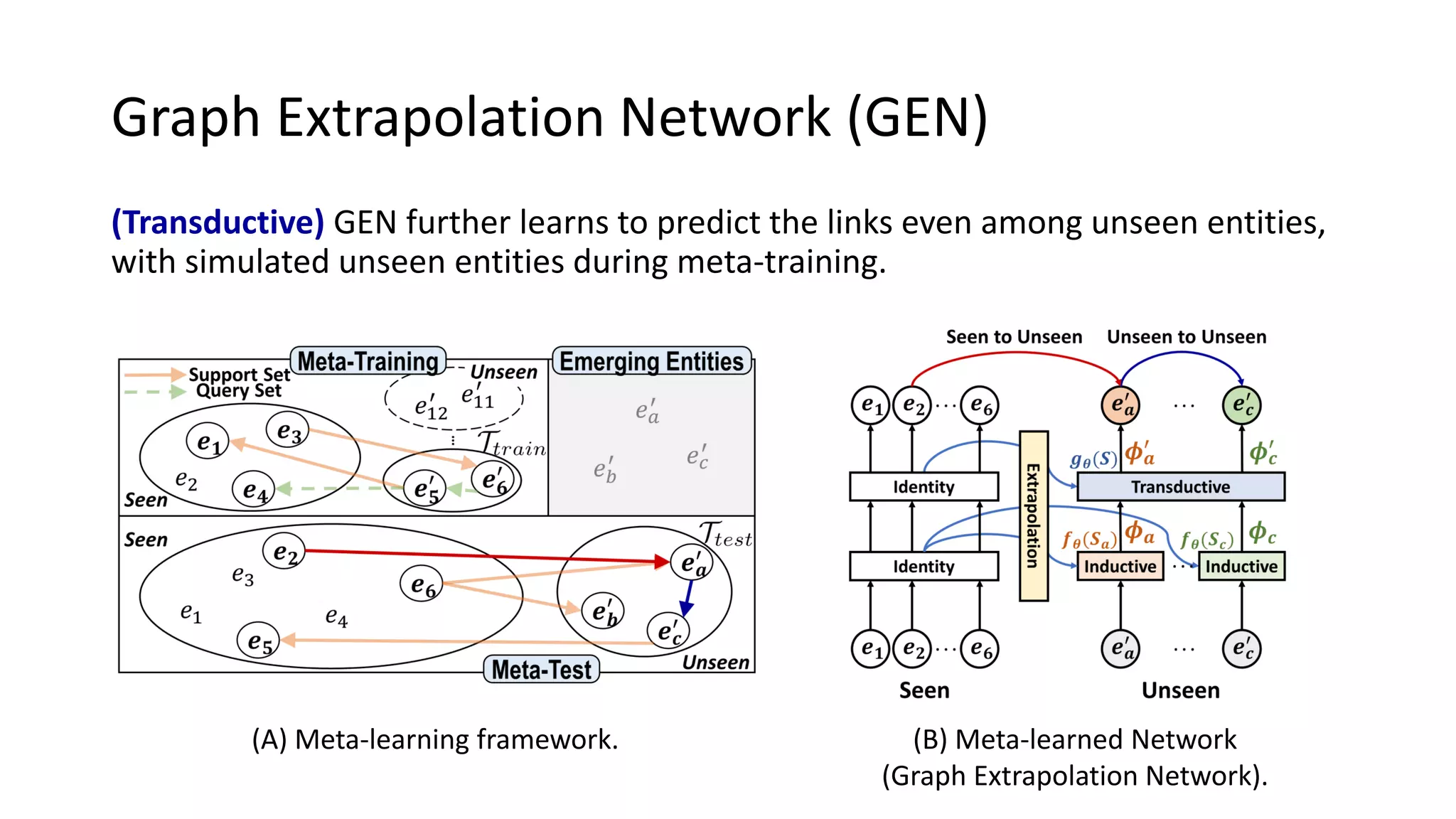
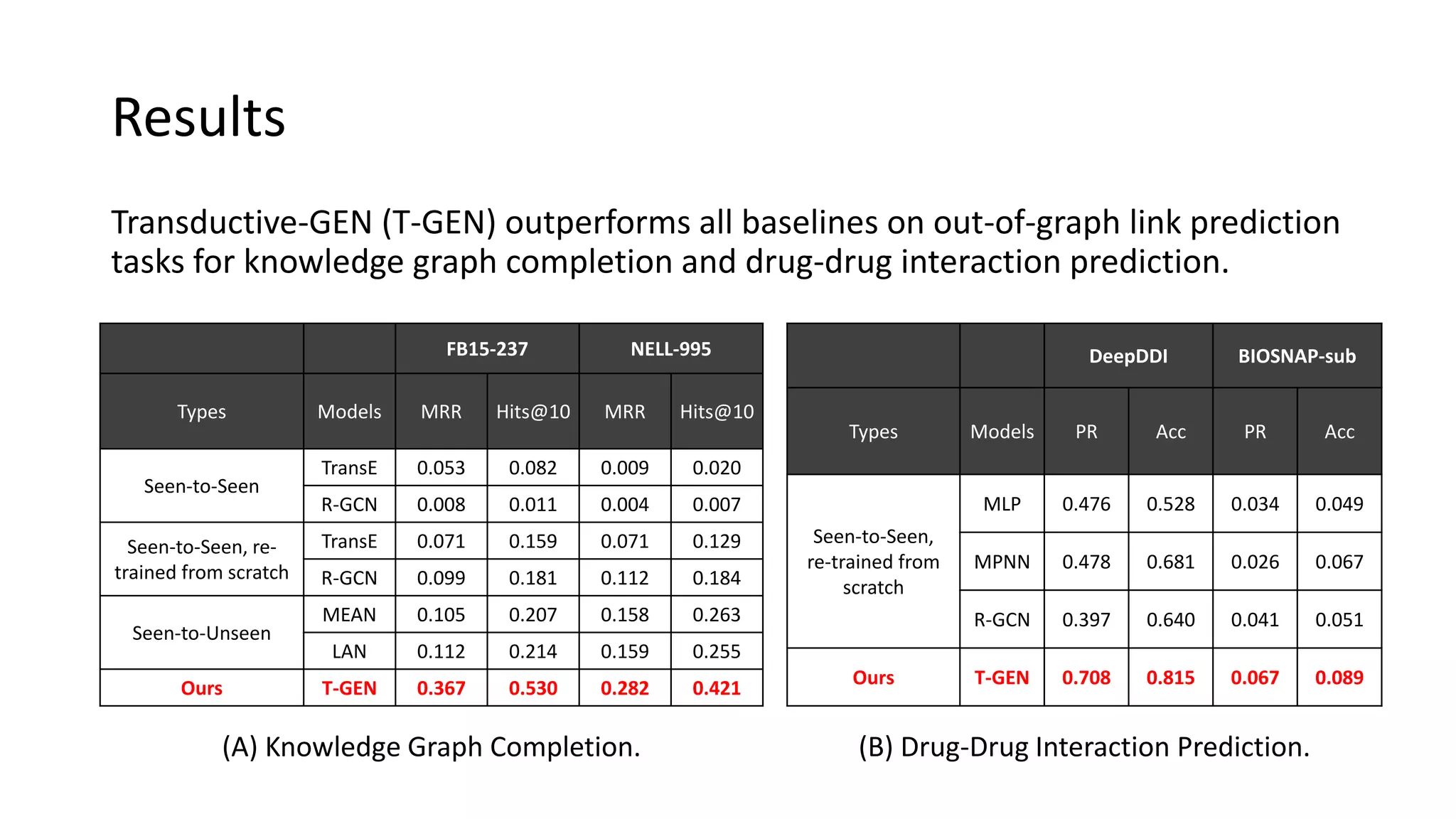
The document presents a novel meta-learning framework for few-shot out-of-graph link prediction, addressing the challenges of incomplete knowledge graphs and evolving entities. This approach, termed the Graph Extrapolation Network (GEN), effectively predicts links between seen and unseen entities, significantly outperforming existing baselines in knowledge graph completion and drug-drug interaction tasks. The framework learns from simulated unseen entities to improve generalization in link prediction tasks.

![Results
Why does GEN generalize well to link prediction with out-of-graph entities?
This is because GEN embeds the unseen entities on the manifold of seen entities,
while baselines embeds the unseen entities off-manifold.
(A) Seen-to-Unseen Baseline
(LAN [Wang et al.]).
(B) Seen-to-Seen Baseline, retrained
from scratch (TransE [Bordes et al.]).
(C) Ours (T-GEN).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/learningtoextrapolateknowledgetransductivefew-shotout-of-graphlinkprediction-201226020847/75/Learning-to-Extrapolate-Knowledge-Transductive-Few-shot-Out-of-Graph-Link-Prediction-10-2048.jpg)
