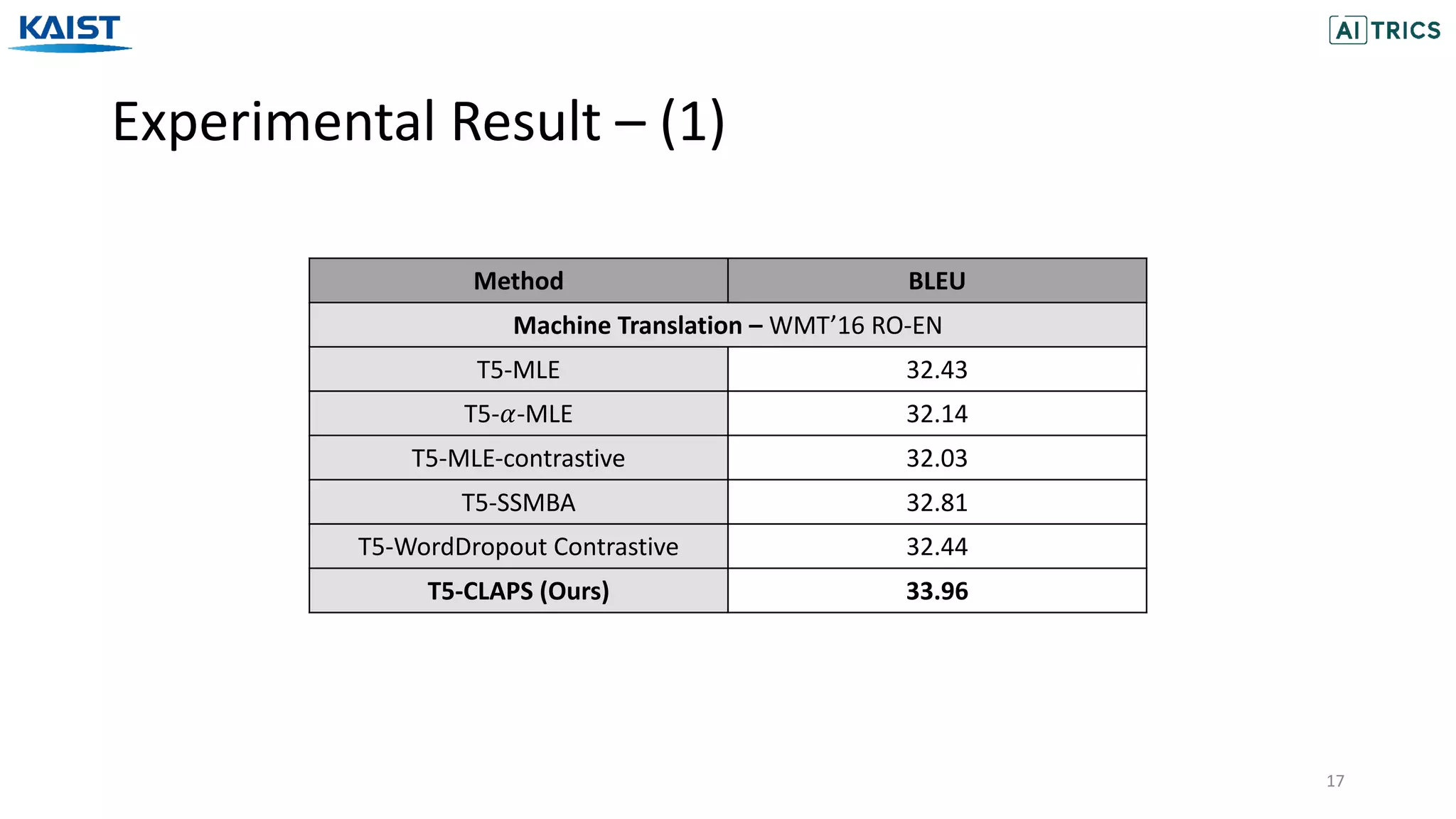
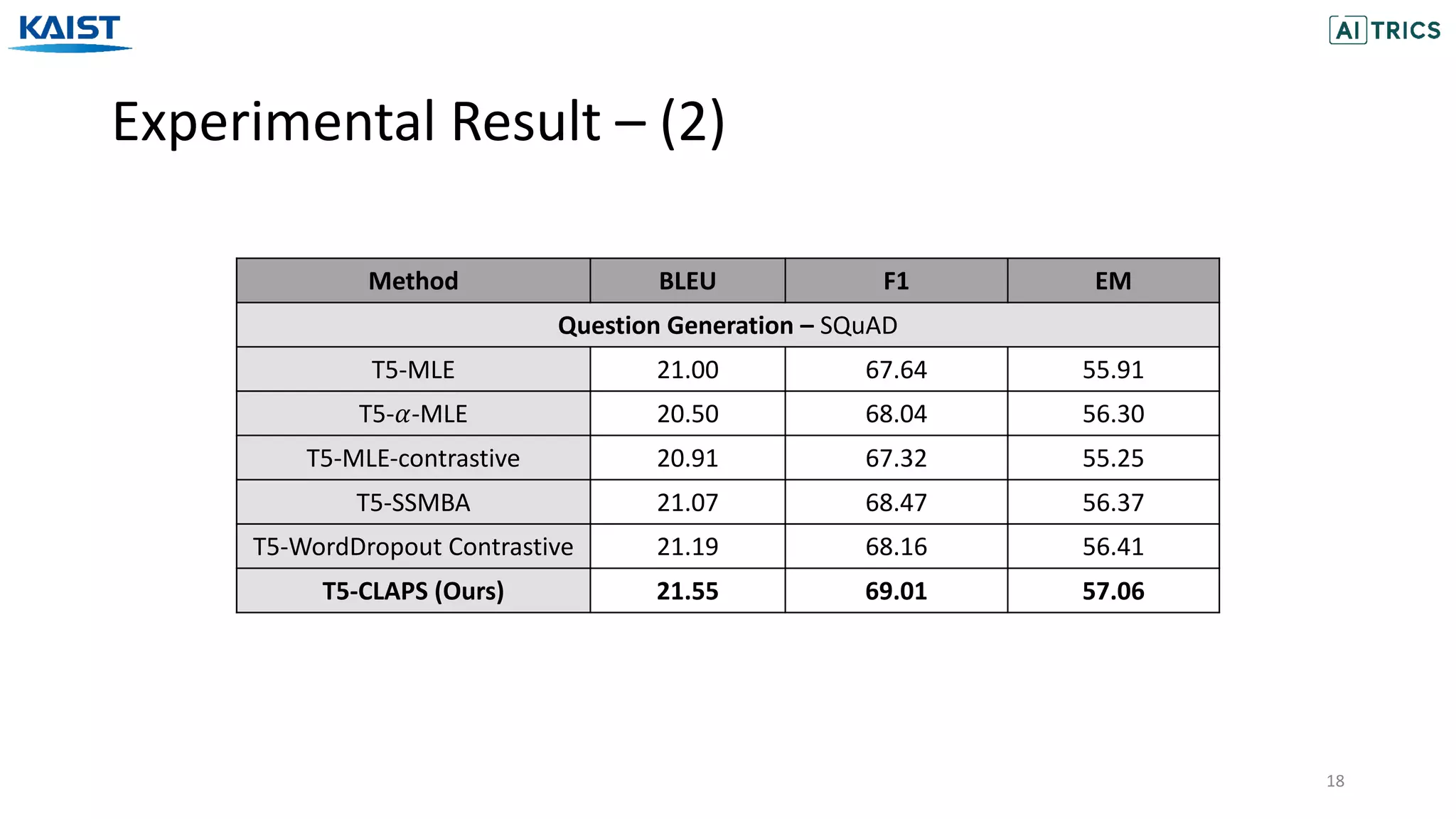
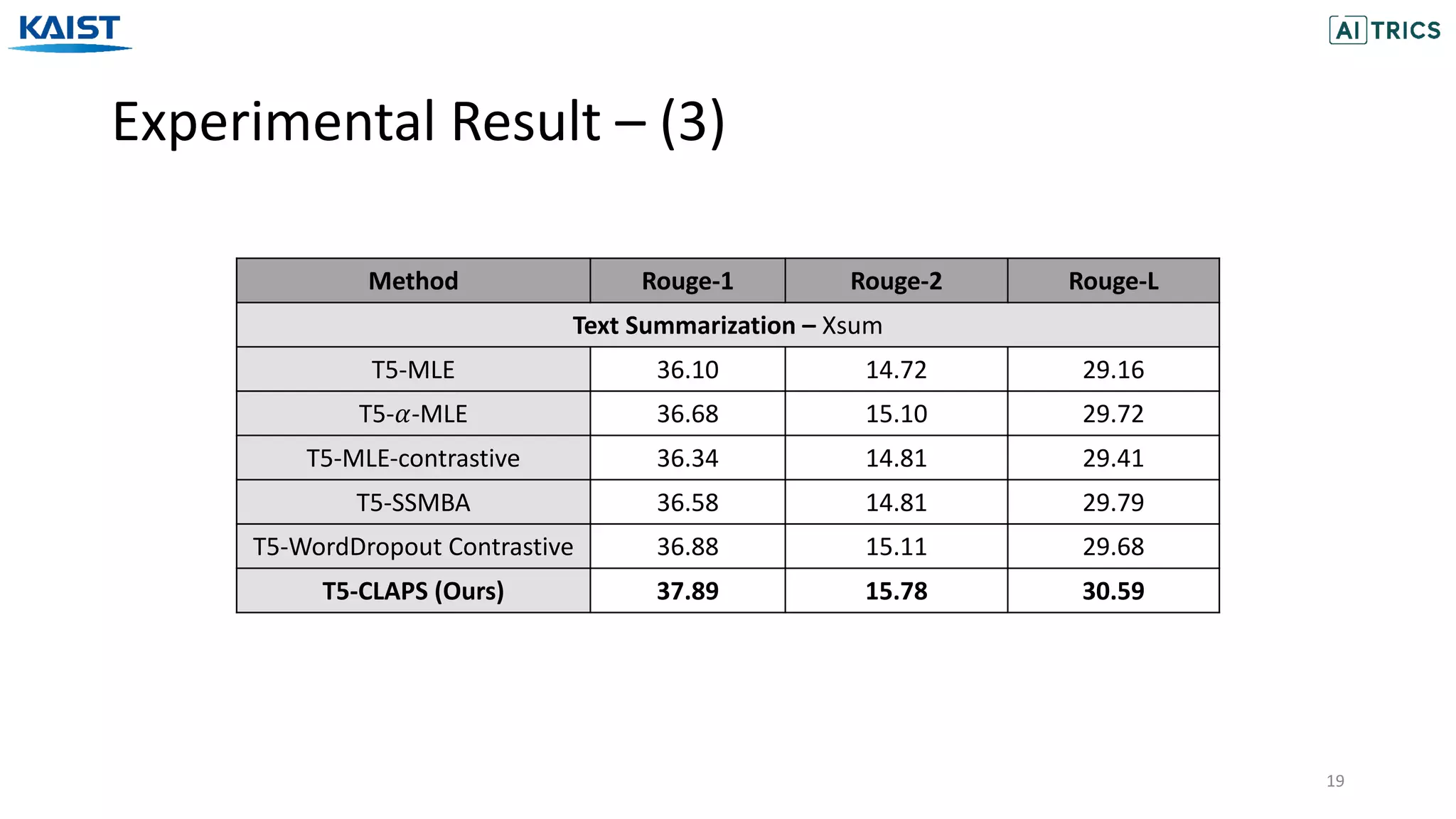
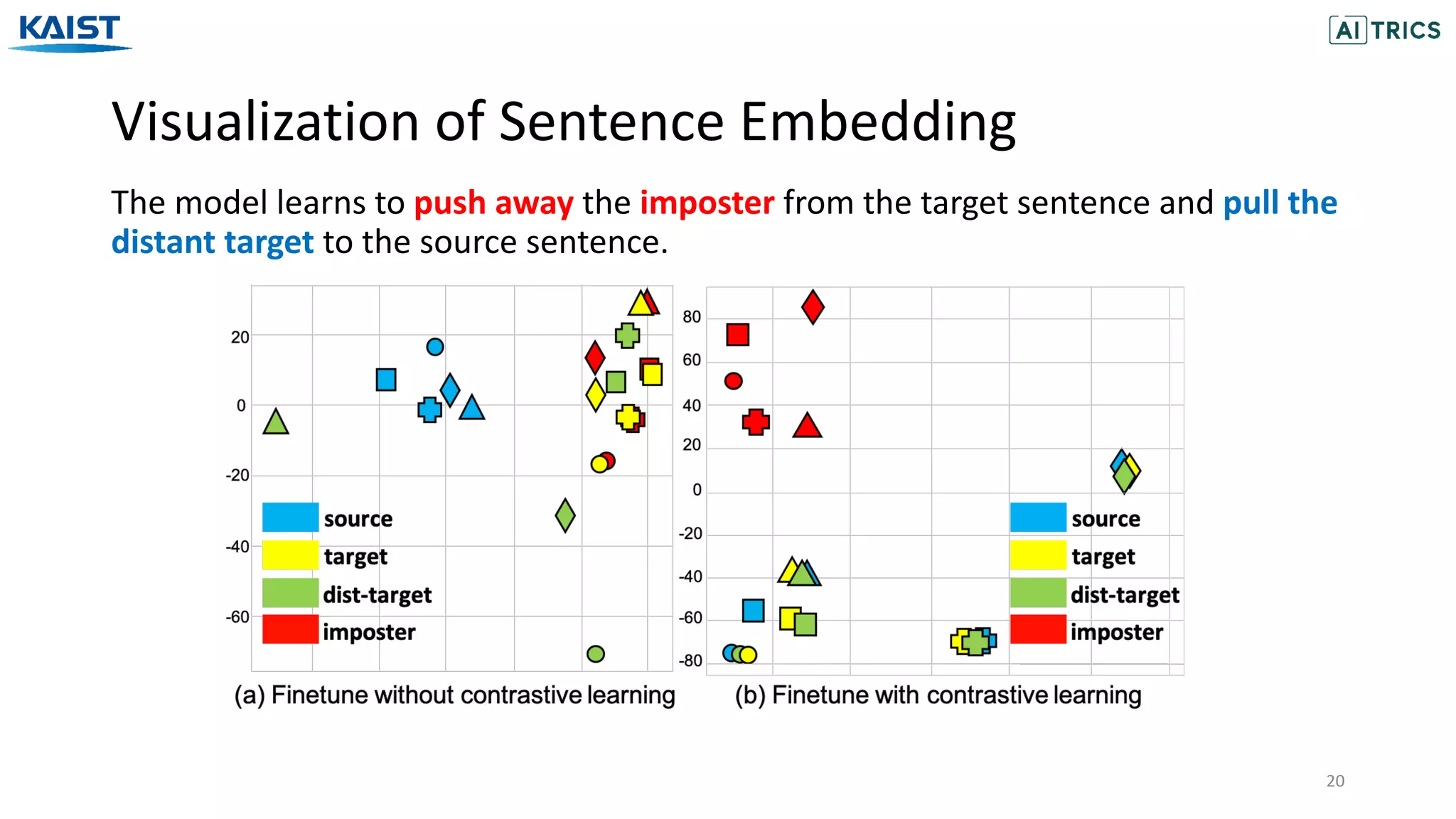
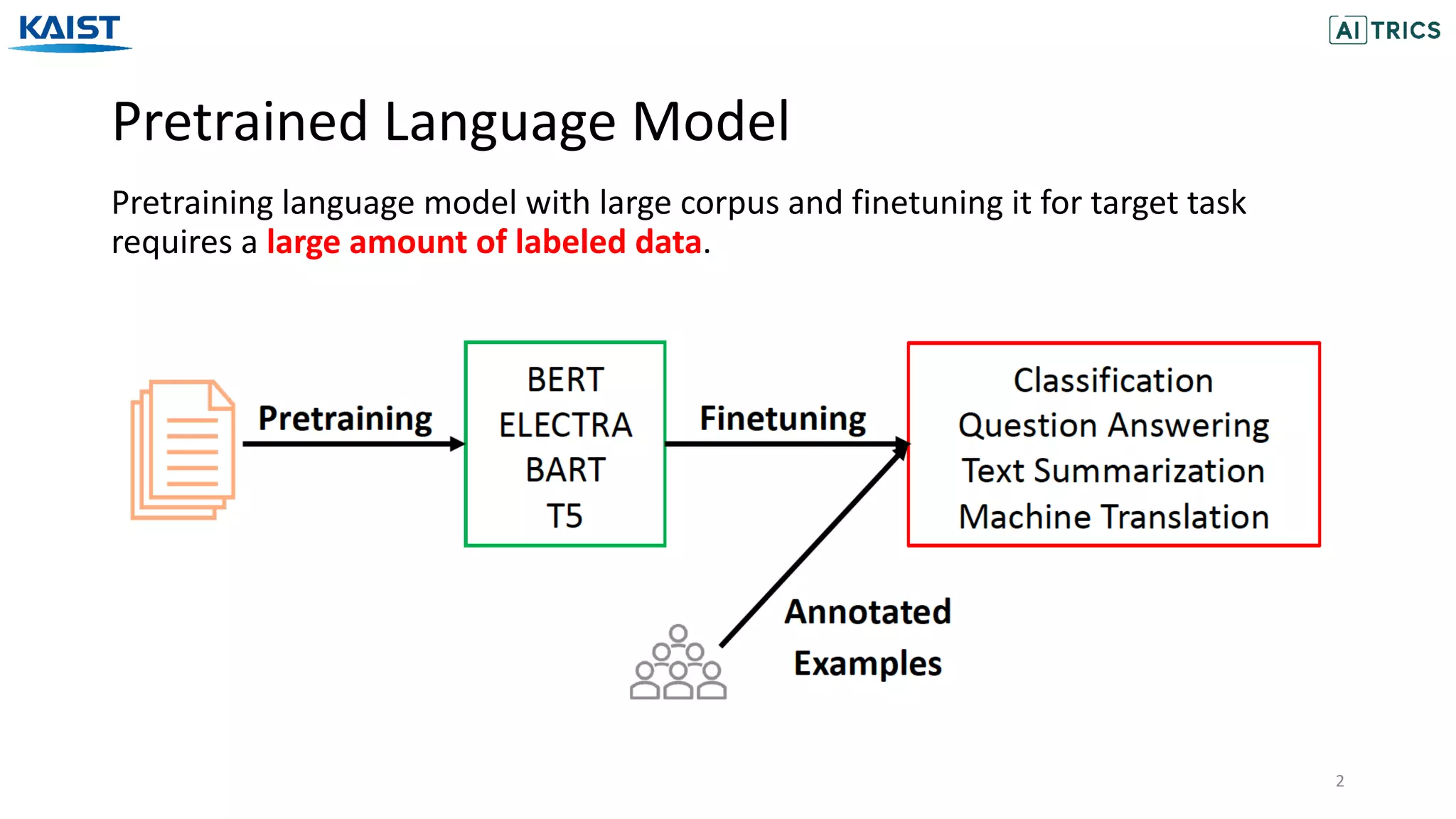
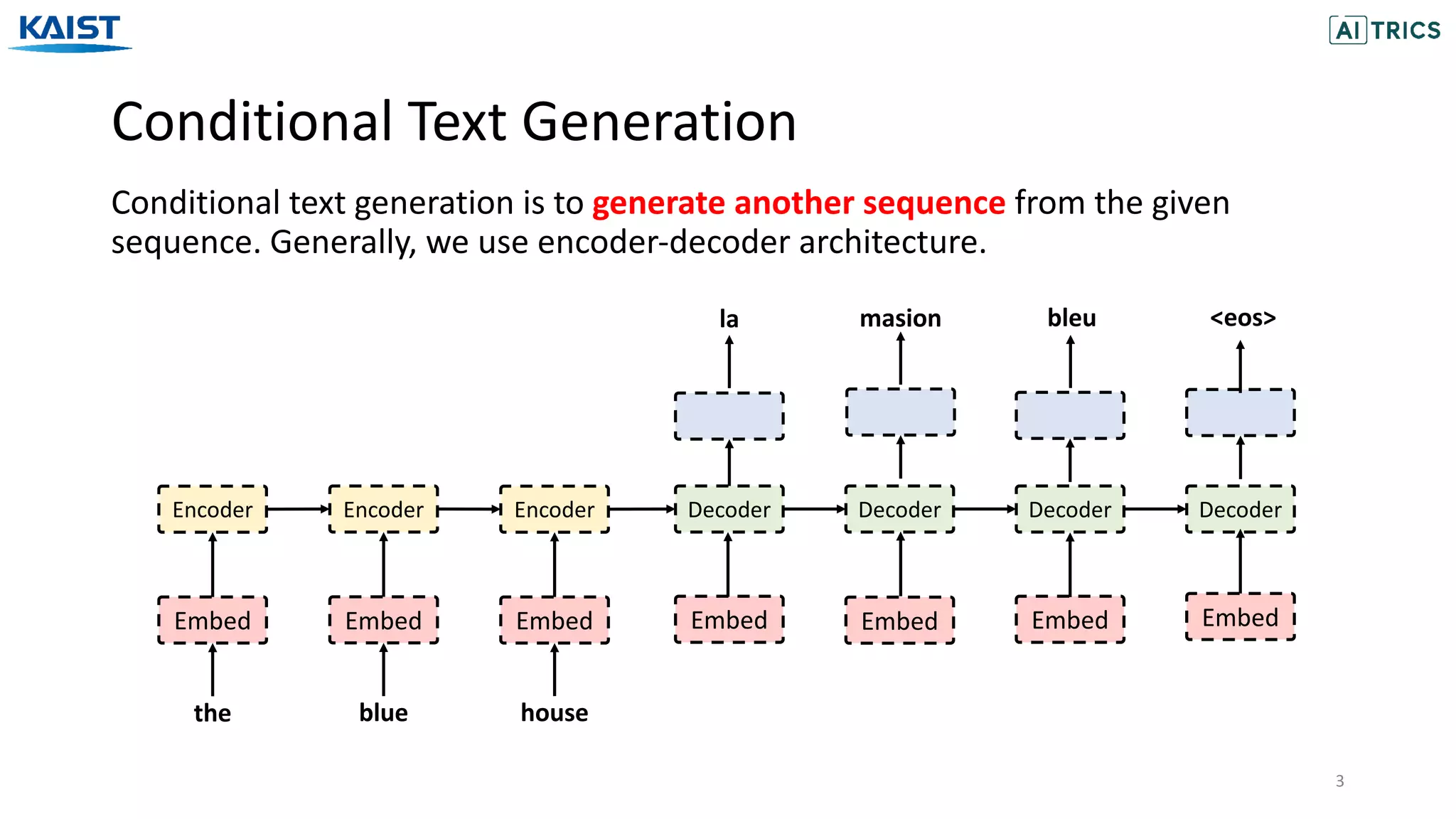
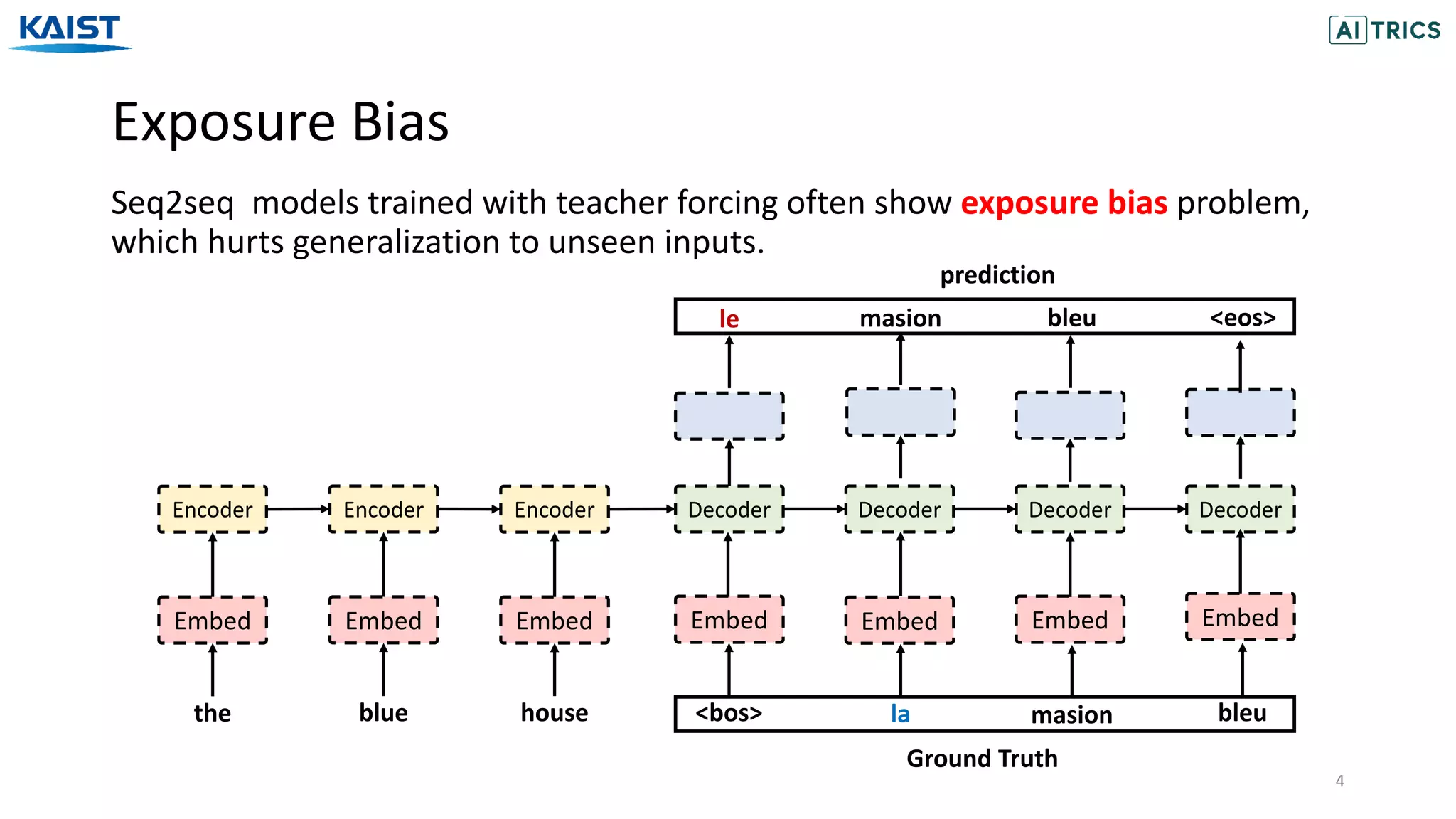
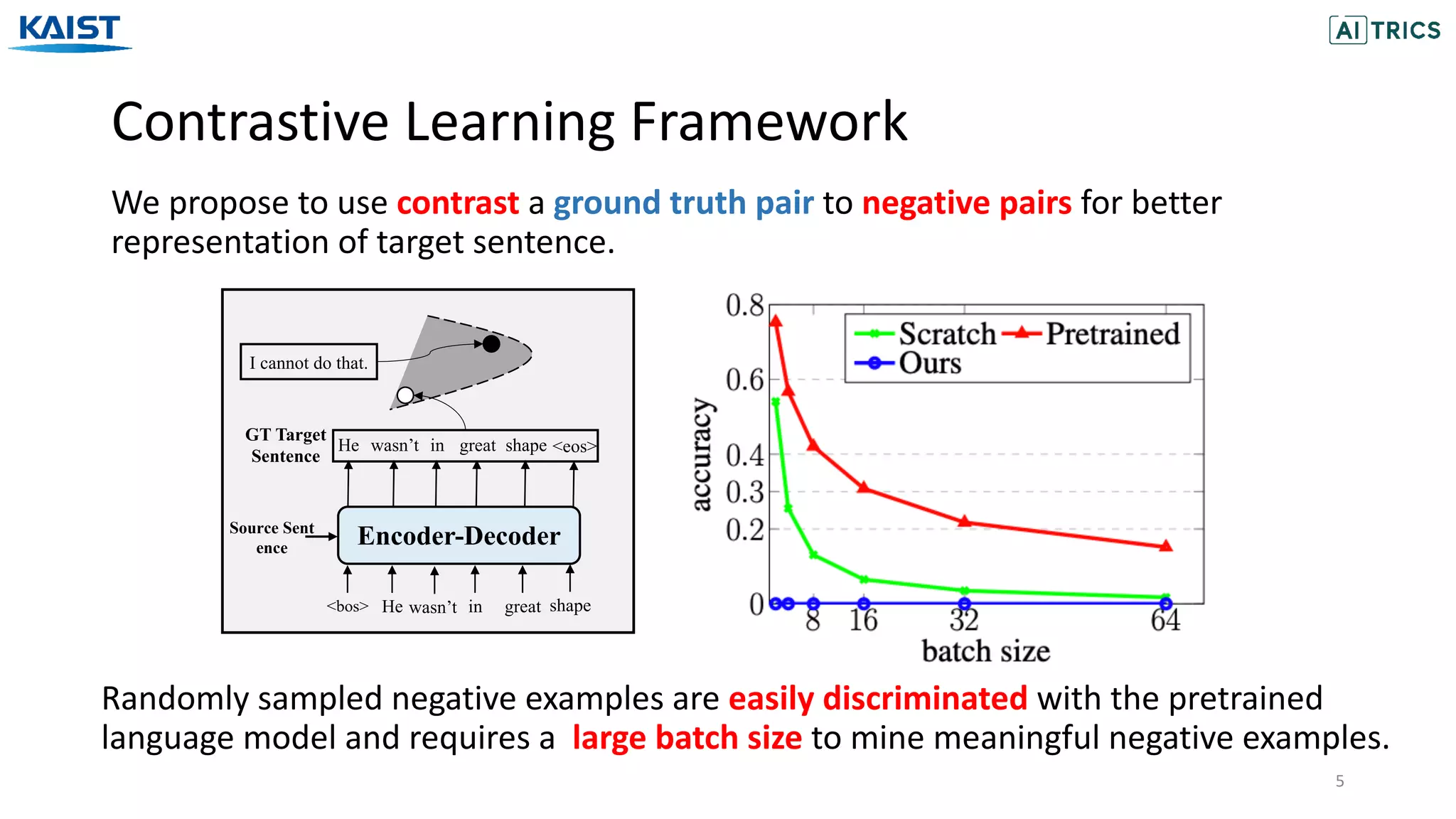
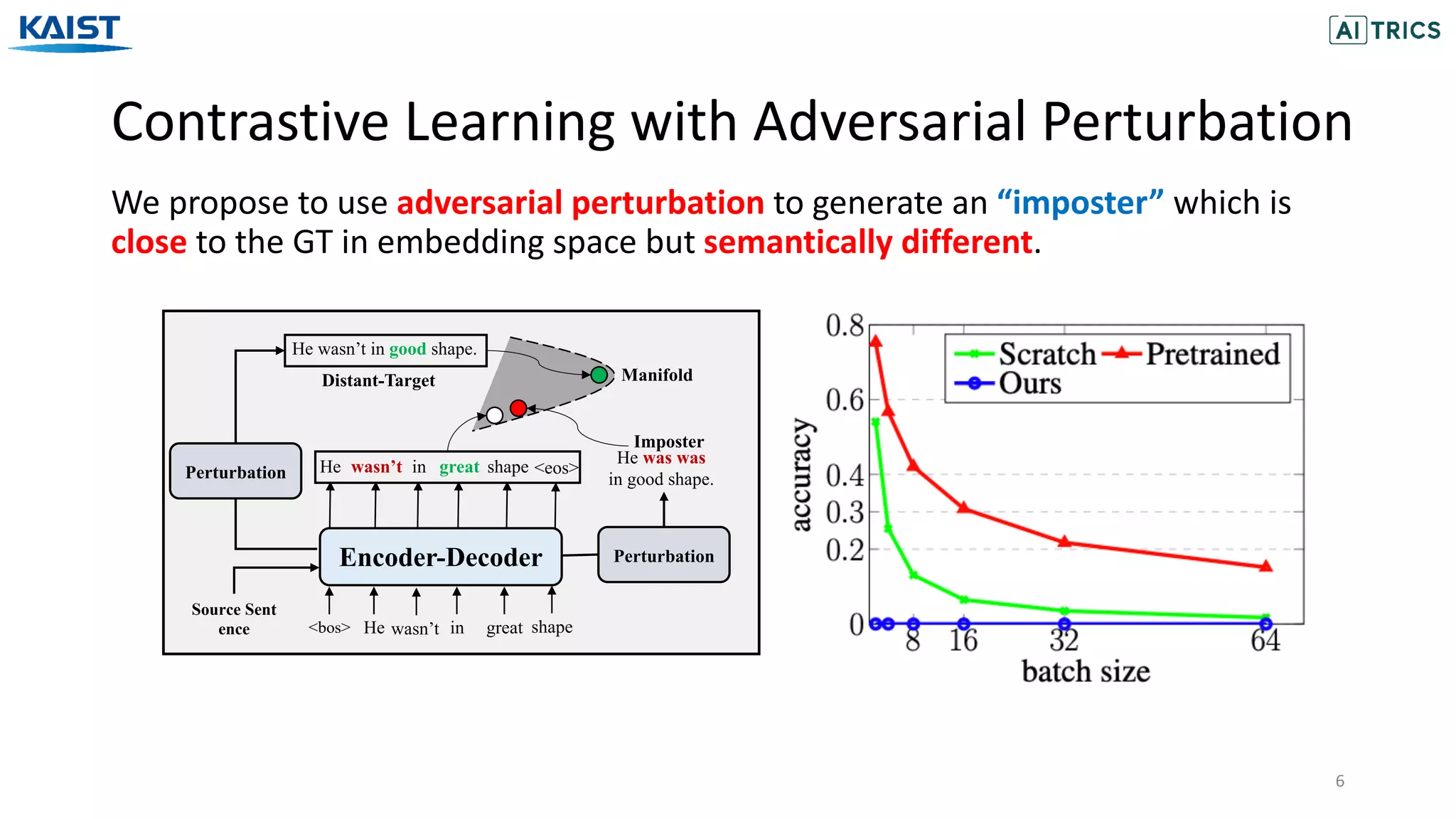
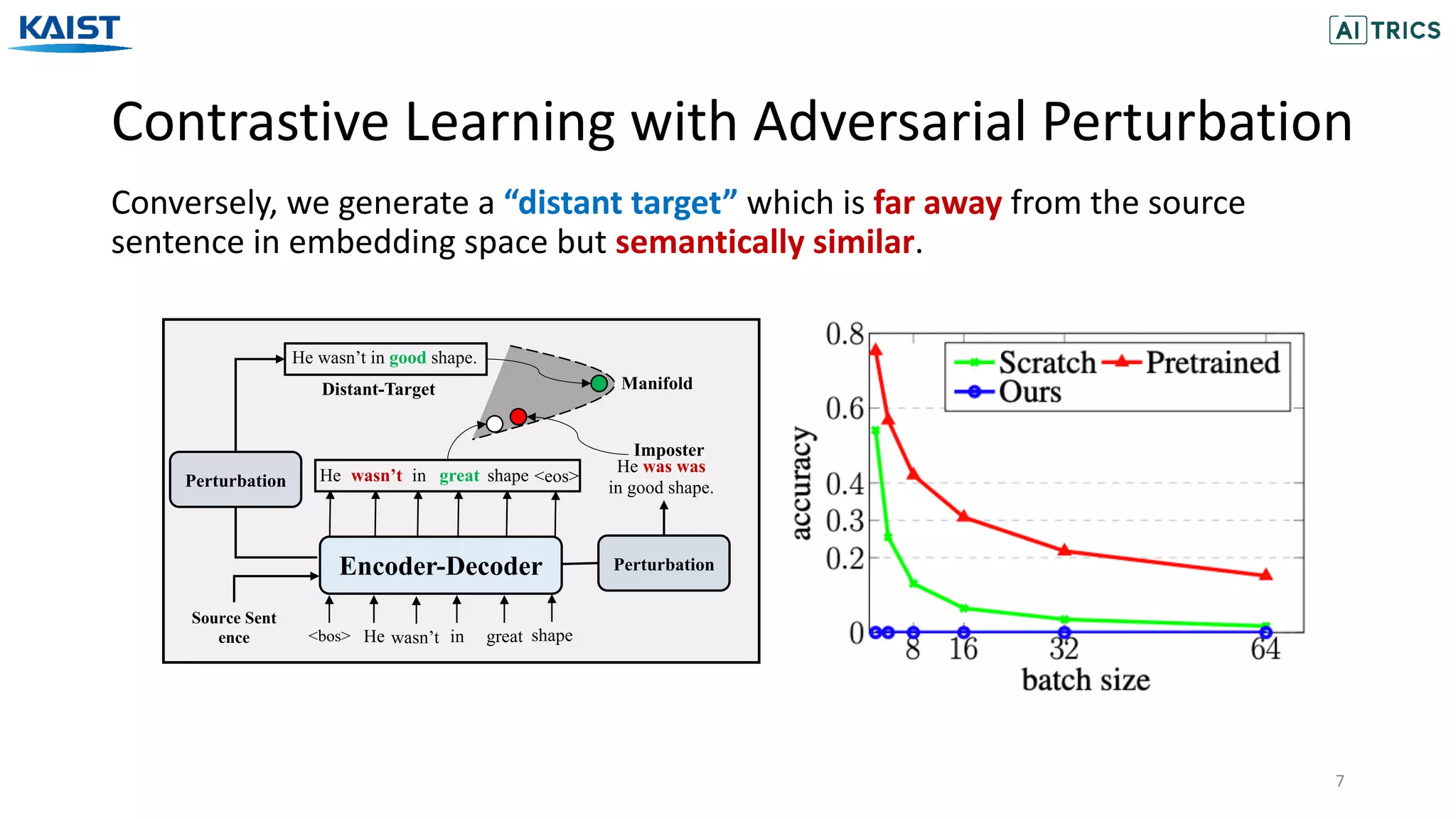
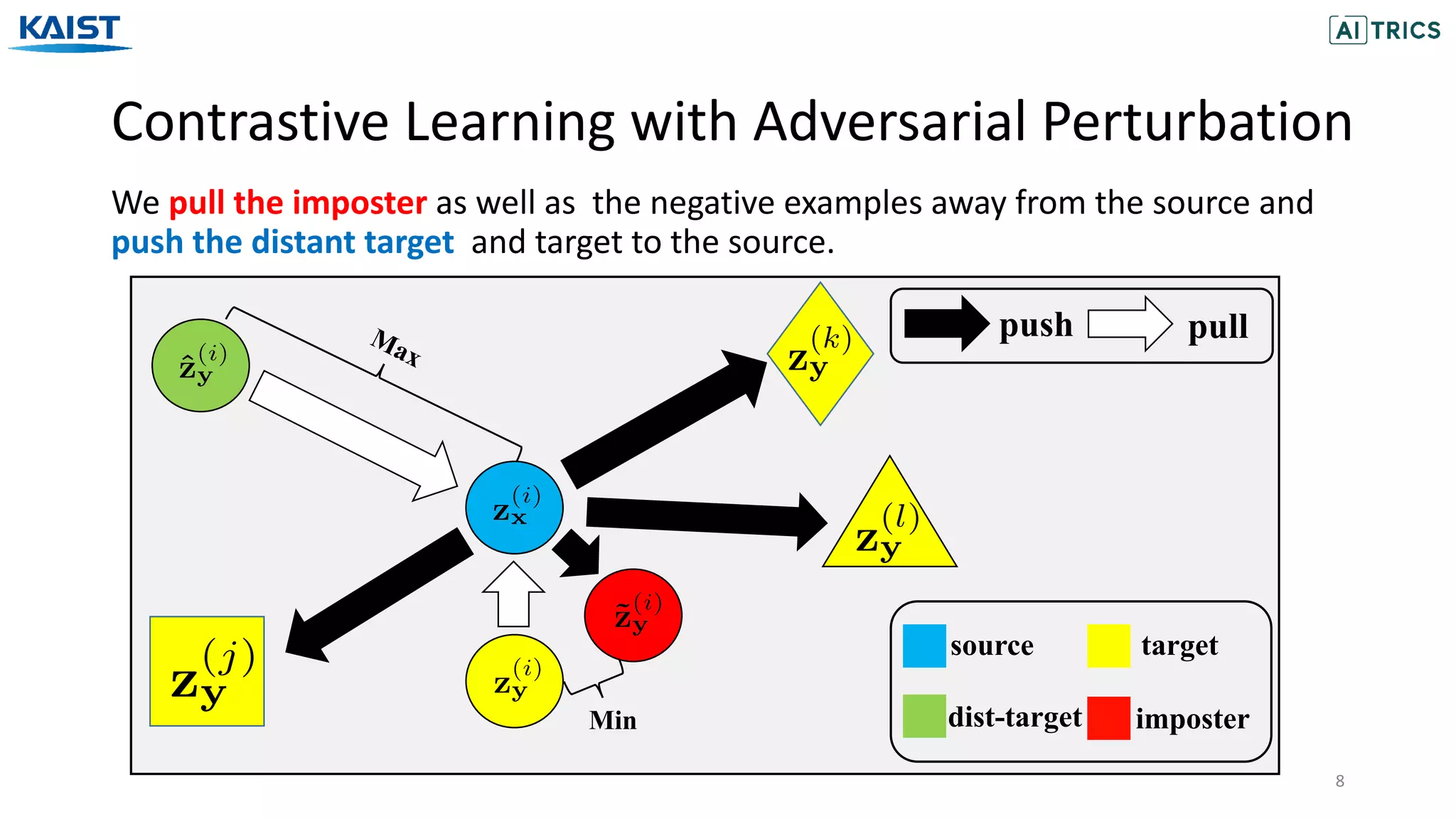
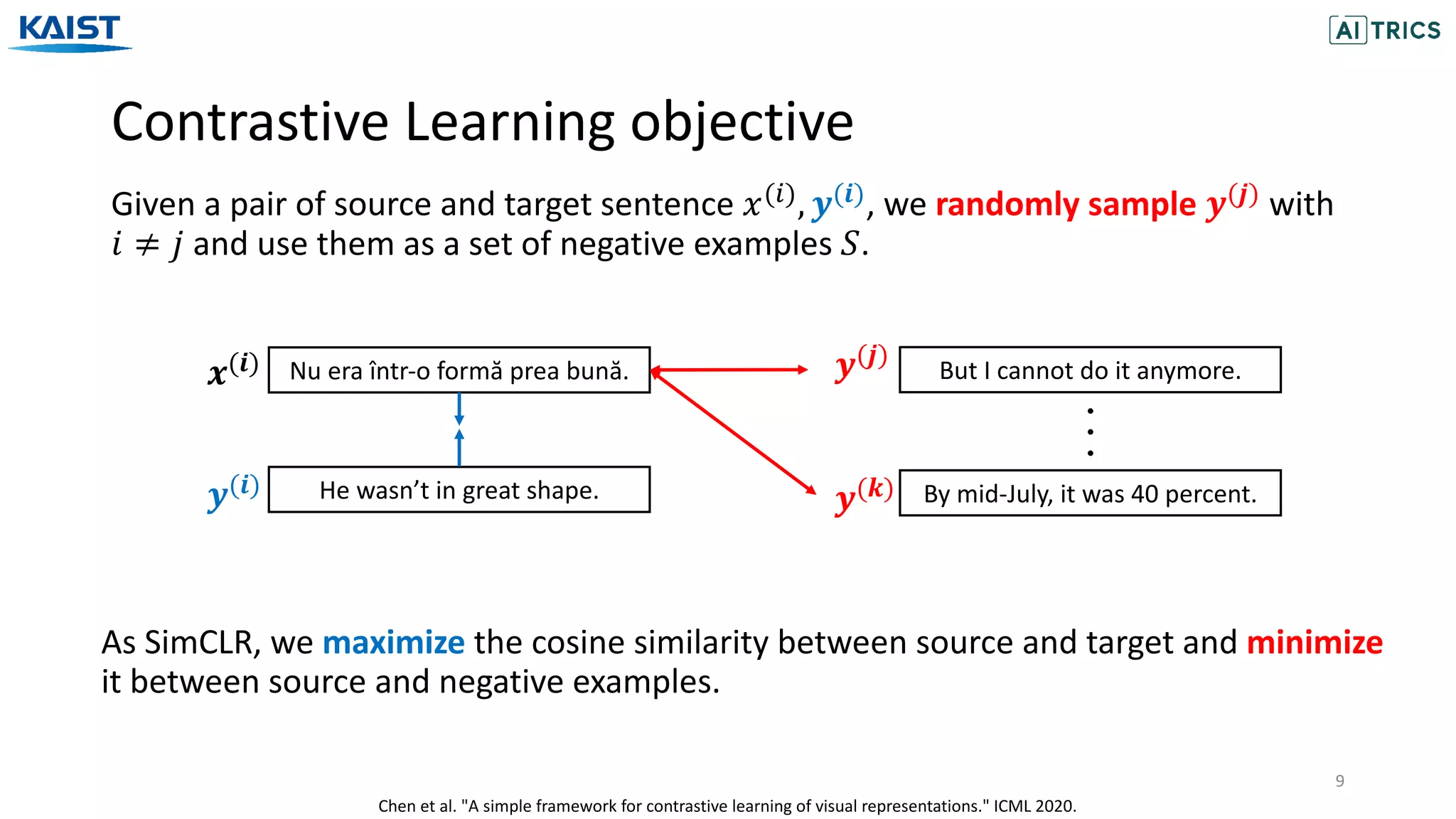
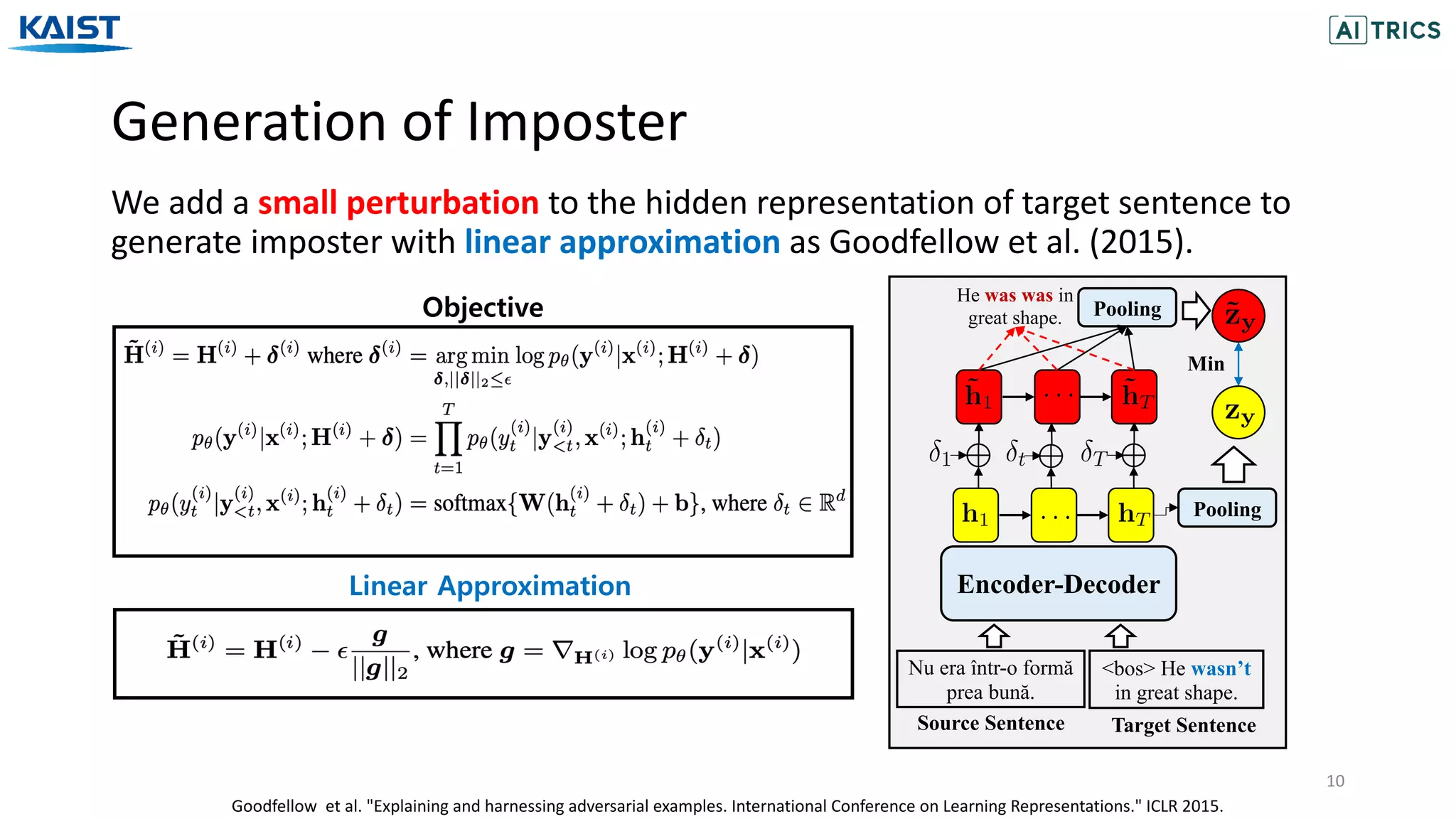
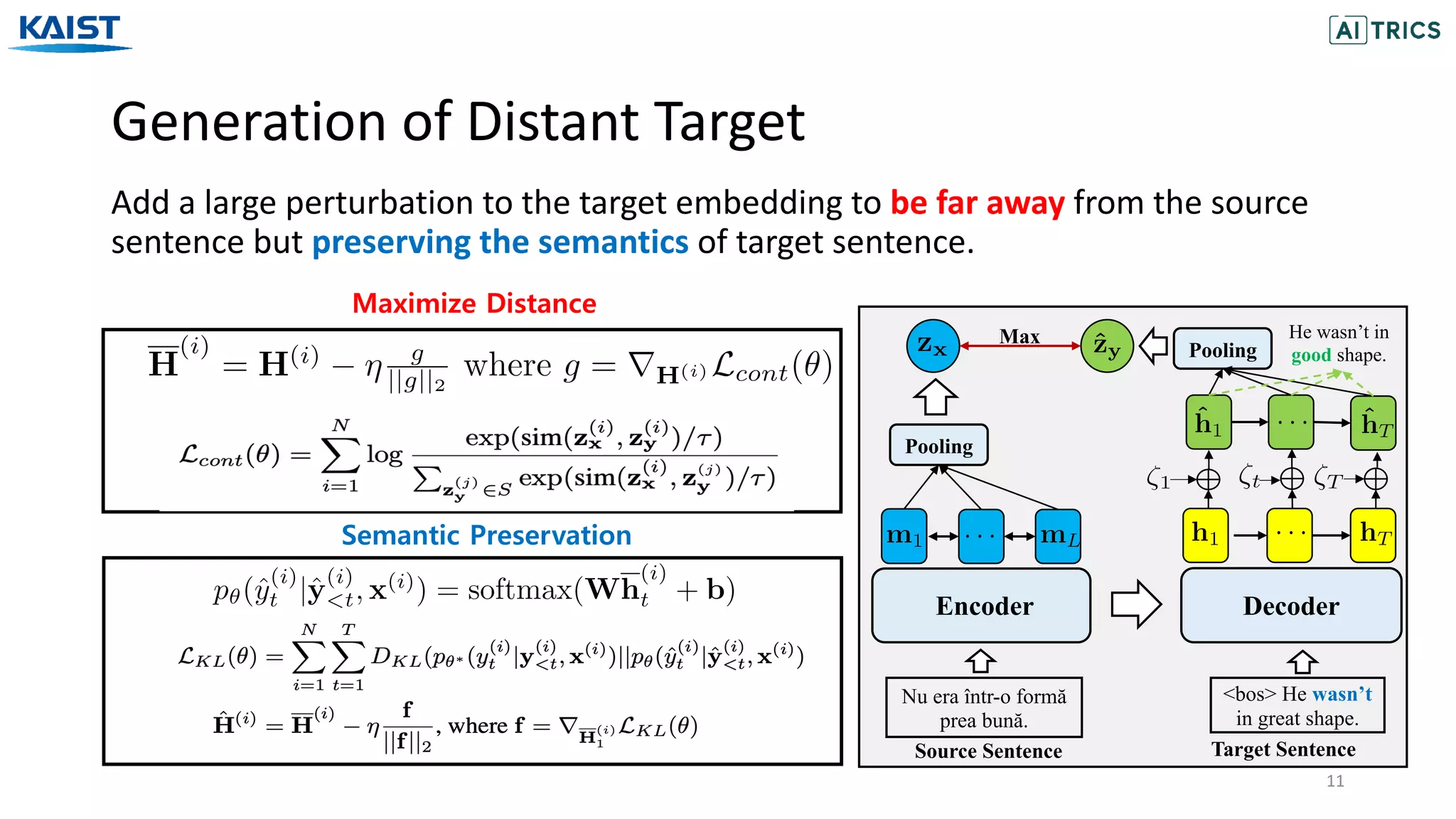
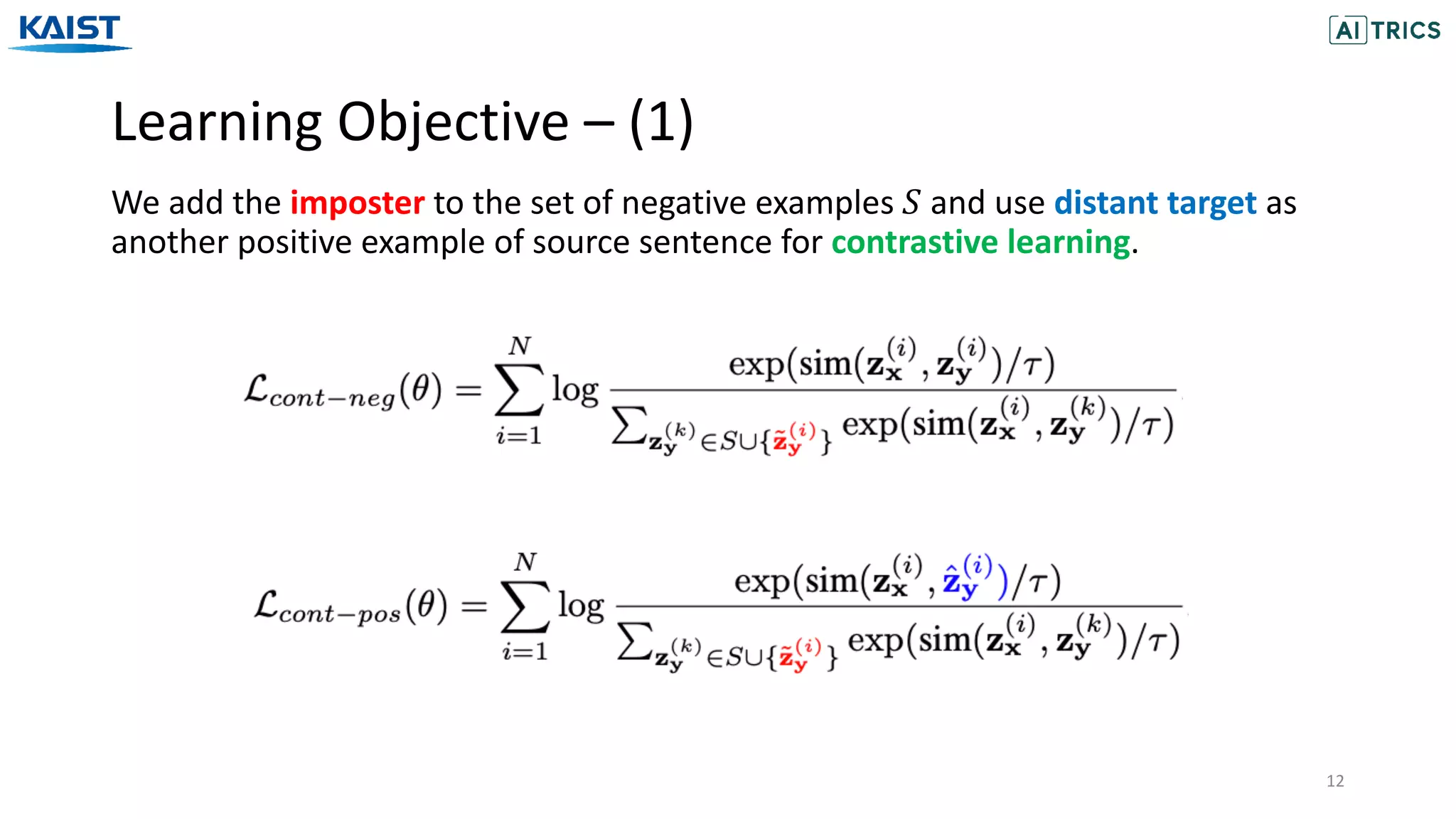
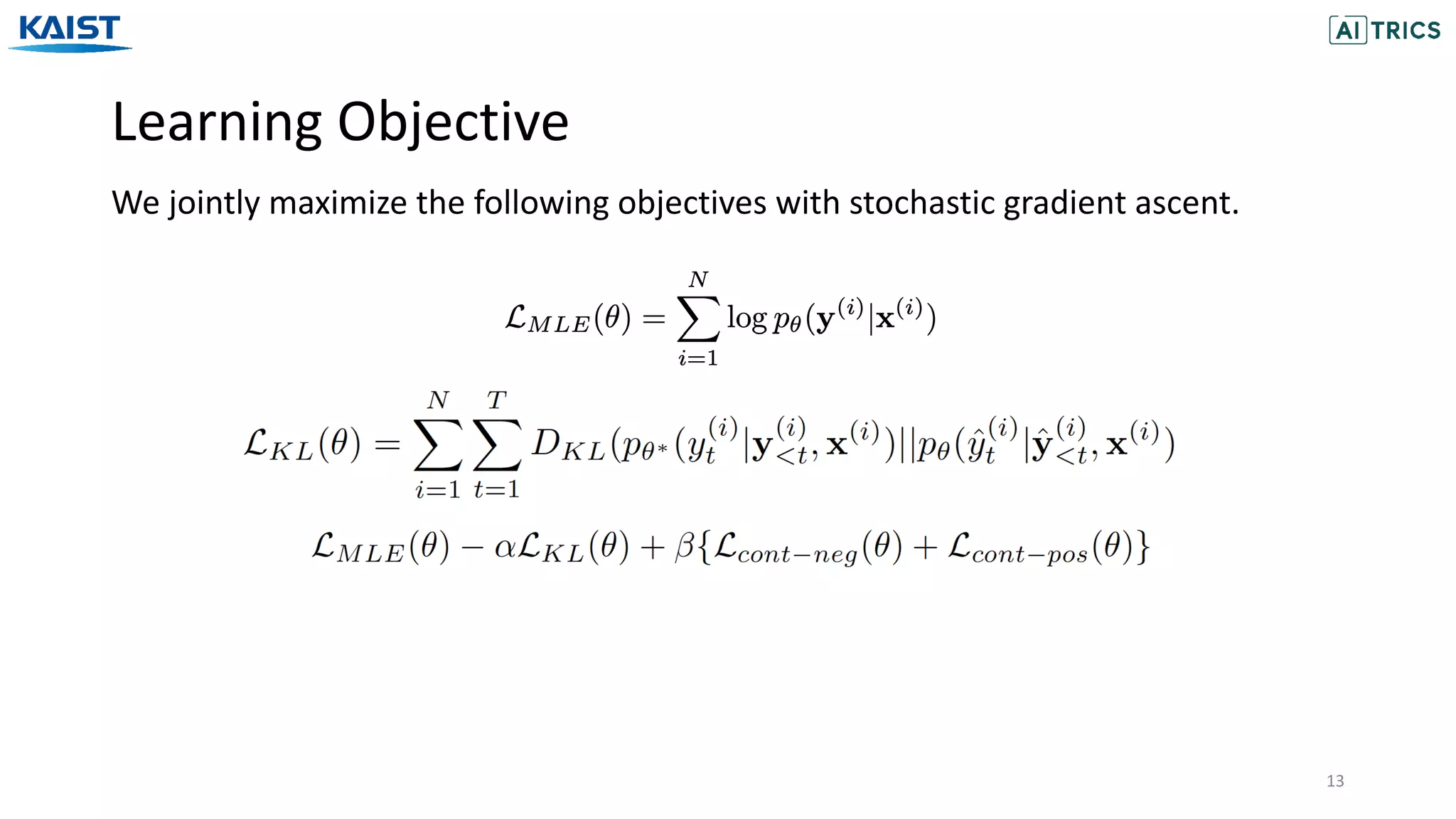
The document presents a novel contrastive learning framework for conditional text generation that addresses the exposure bias problem in sequence-to-sequence models. By leveraging adversarial perturbations to create challenging negative and positive examples, the method demonstrates improved performance on various tasks including machine translation, question generation, and summarization compared to existing baselines. Experimental results indicate the proposed approach outperforms traditional T5 models across key metrics, although future work will focus on enhancing sample efficiency and the quality of generated examples.

![Experimental Setup – (2)
15
3) Baselines
• T5-MLE:
The T5 model trained with maximum likelihood estimation.
• T5-𝛼-MLE:
The T5 model trained with MLE but decode target sequence with temperature
scaling 𝛼 in softmax.
• T5-MLE-contrastive:
Naïve contrastive learning with MLE.
[Caccia 2020]Caccia et al., Language gans falling short, ICLR 2019](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iclr2021contrastivelearningwithadversarialperturbationsforconditionaltextgeneration-210514140037/75/Contrastive-Learning-with-Adversarial-Perturbations-for-Conditional-Text-Generation-15-2048.jpg)
![Experimental Setup – (2)
16
3) Baselines
• T5-SSMBA [Ng 2020]:
Generating additional examples by denoising and reconstructing target
sentences with masked language model
• T5-WordDropout Contrastive [Yang 2019]:
Generate negative examples by removing the most frequent word from the
target sentence.
• T5-R3f [Aghajanyan 2021]:
Add a Gaussian noise and enforce consistency loss.
[Ng 2020] Ng et al, Ssmba: Self-supervised manifold based data augmentation for improving out-of-domain robustness, EMNLP 2020
[Yang2021] Reducing word omission errors in neural machine translation: A contrastive learning approach, ACL 2019
[Aghajanyan 2019] Better fine-tuning by reducing representational collapse, ICLR2021](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/iclr2021contrastivelearningwithadversarialperturbationsforconditionaltextgeneration-210514140037/75/Contrastive-Learning-with-Adversarial-Perturbations-for-Conditional-Text-Generation-16-2048.jpg)