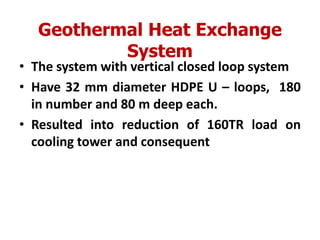
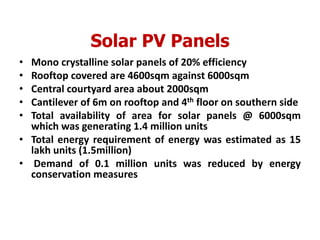
The document summarizes India's first net zero energy building called the Indira Paryavaran Bhawan located in New Delhi. It generates as much renewable energy from solar panels as it consumes annually. Specifically, it has an annual energy demand of 1.4 million kWh but generates 1.4 million kWh from rooftop and courtyard solar panels made of mono-crystalline panels. Through various energy efficiency measures like insulation, efficient HVAC systems, regenerative lifts, and geothermal heating/cooling, the building reduces its energy consumption by 13% compared to a conventional building. It achieves net zero status while also gaining platinum certification under India's green building rating system.