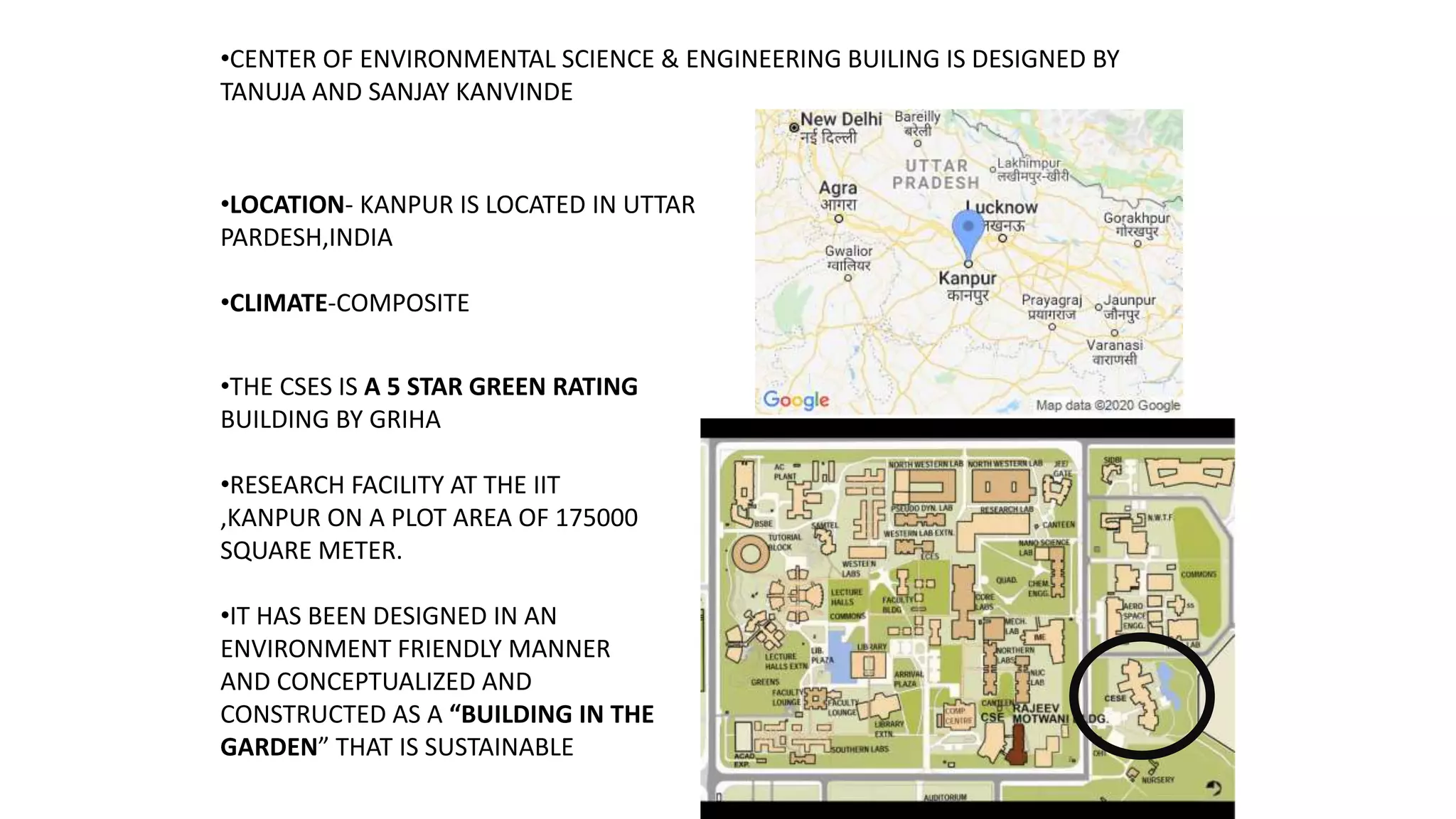
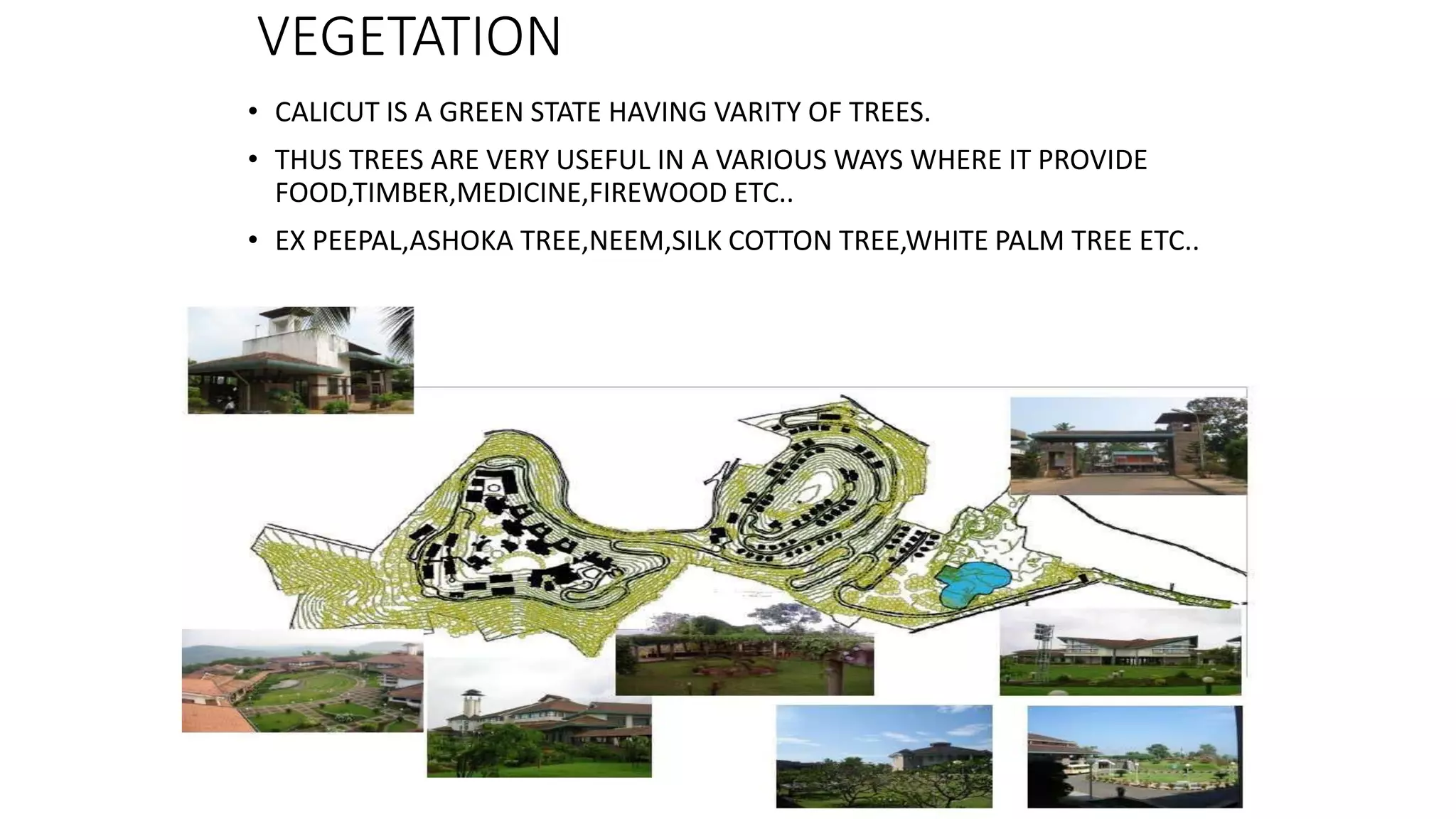
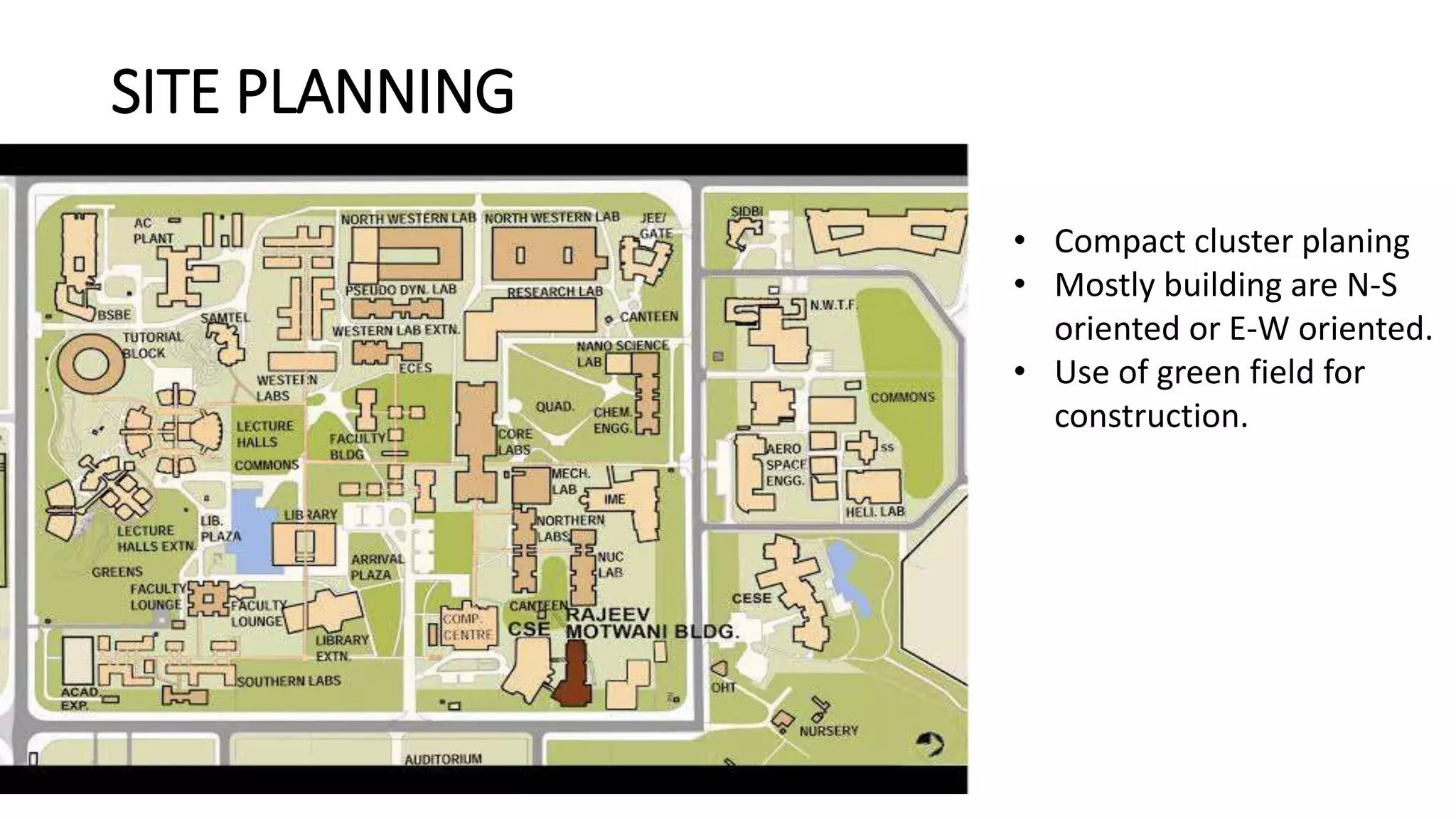
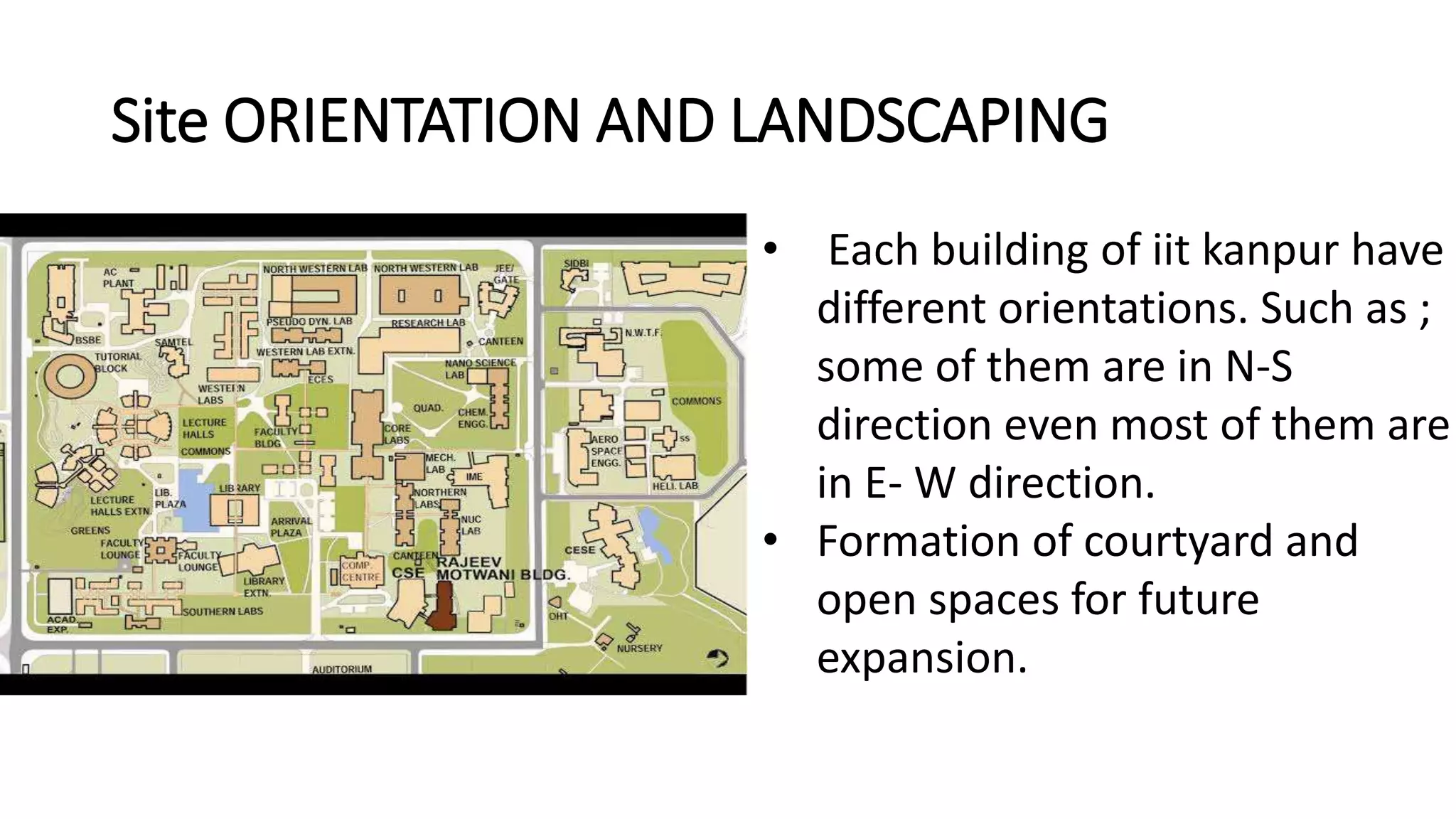
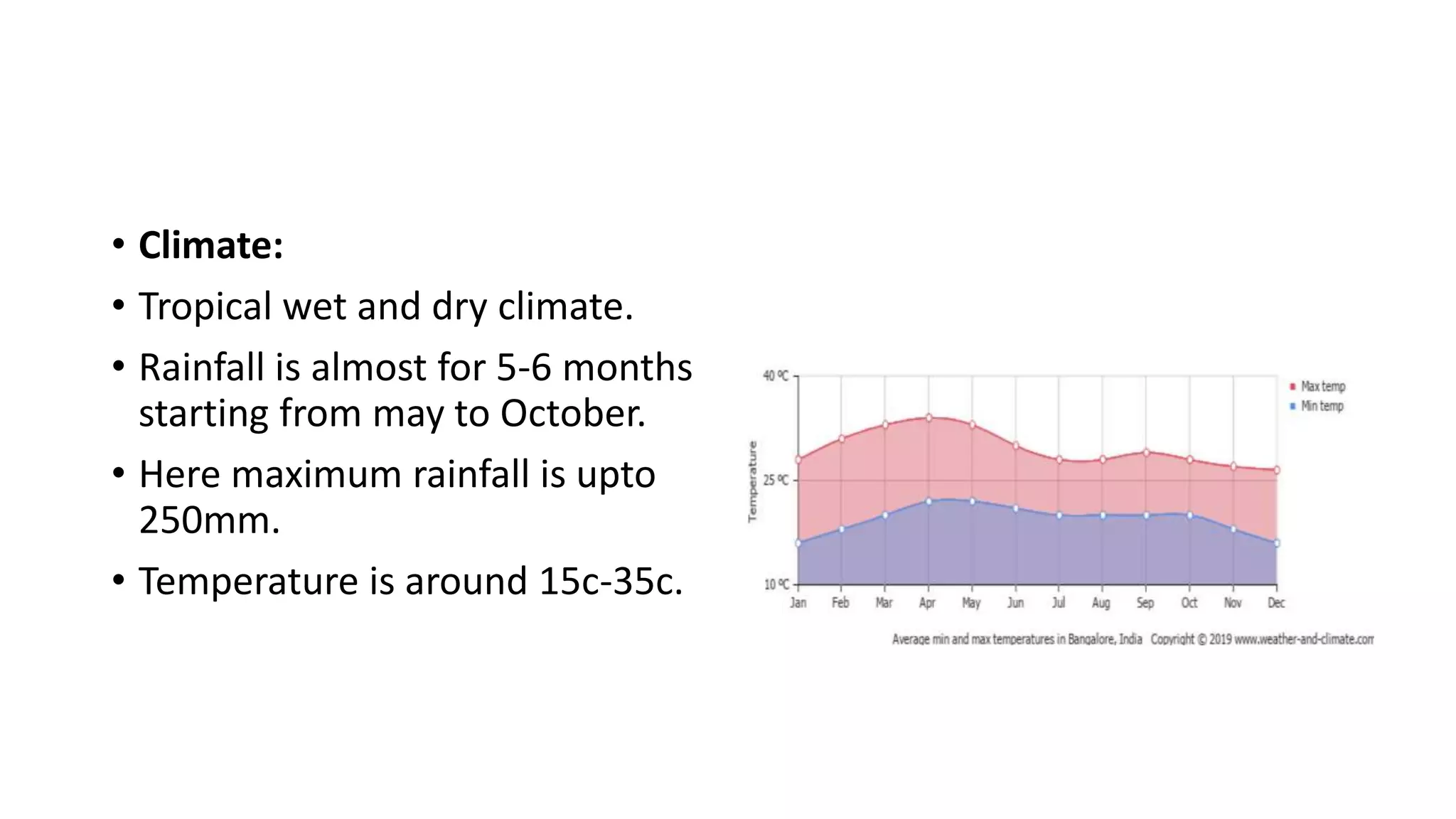
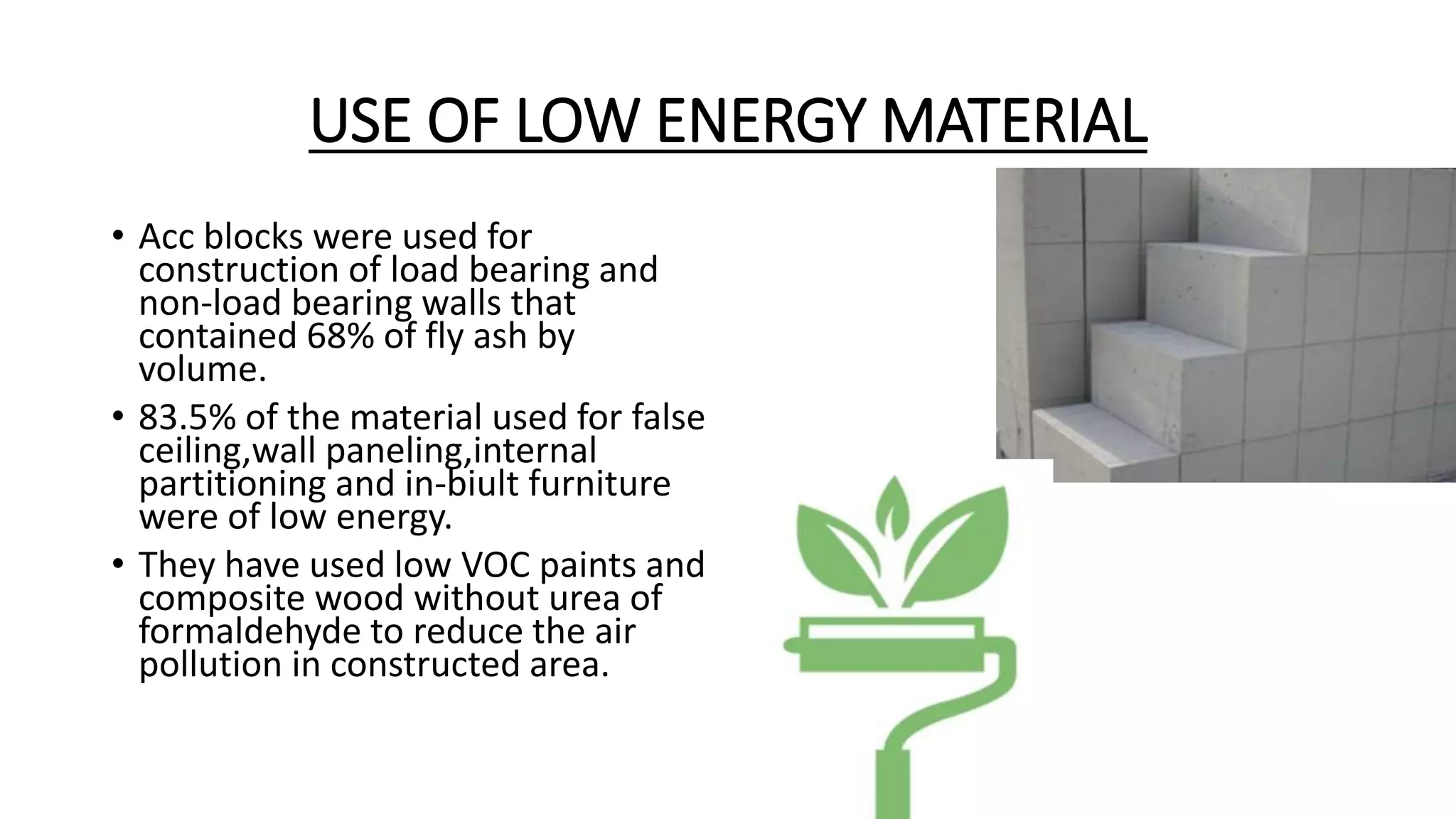
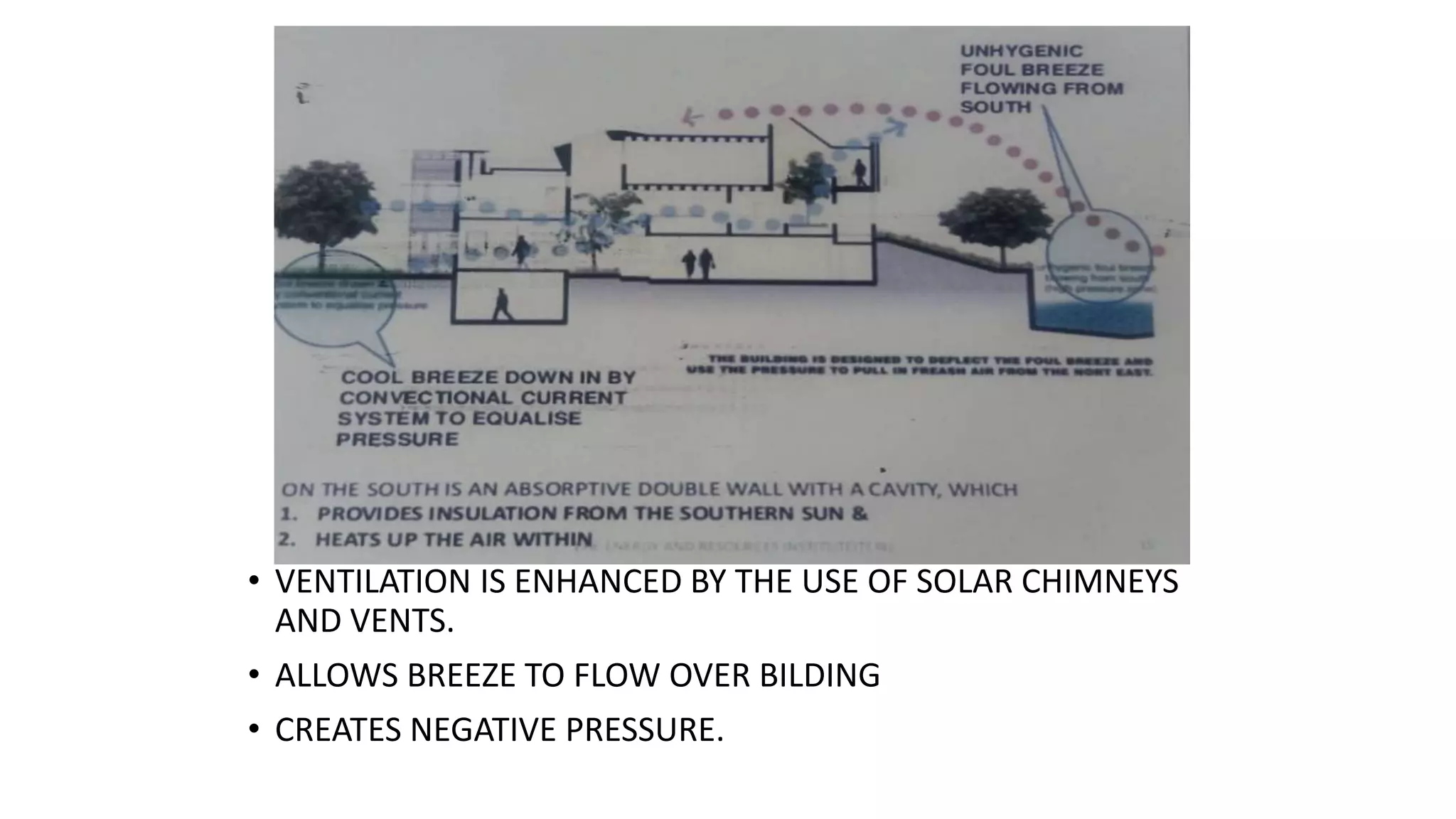
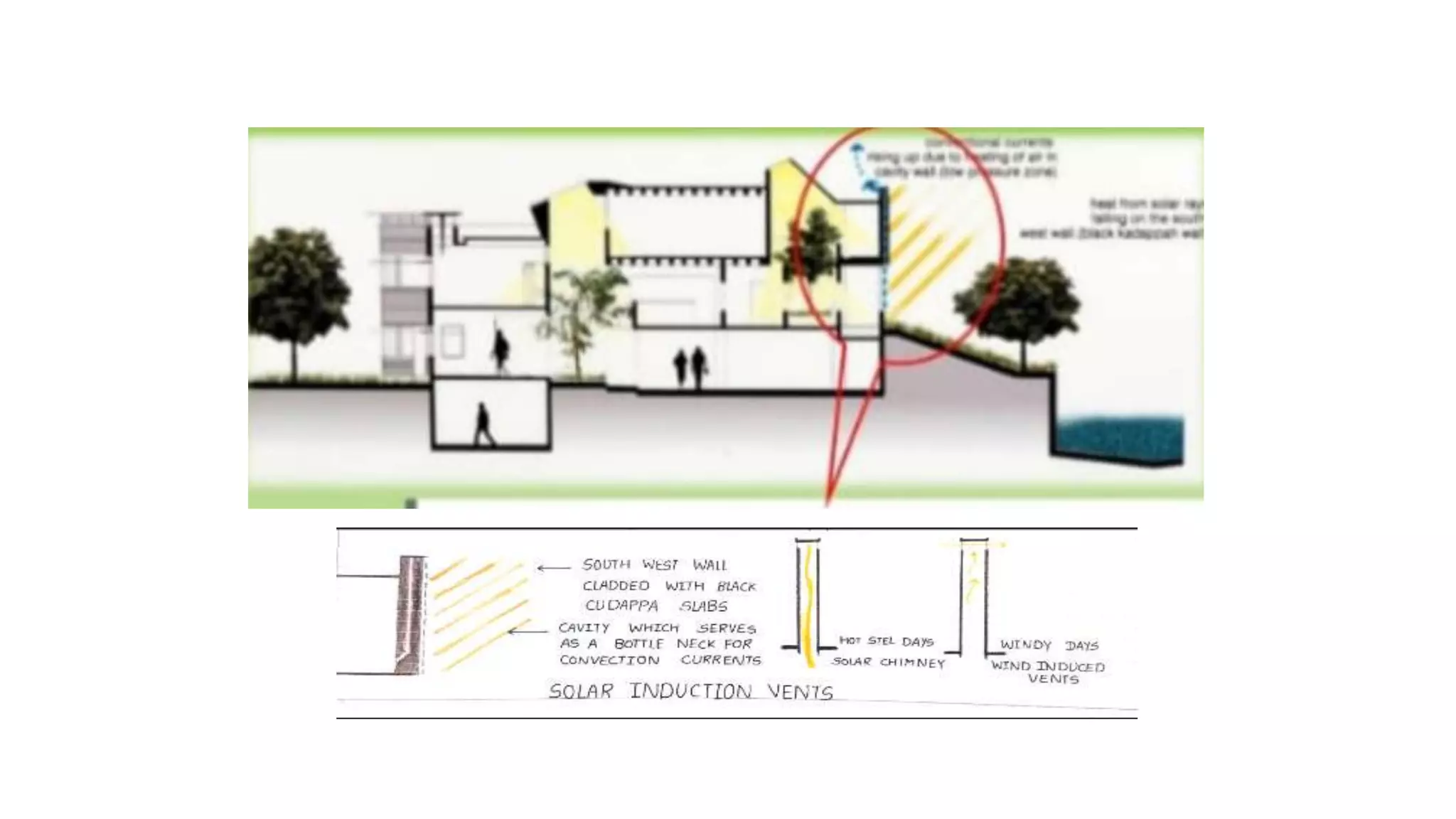
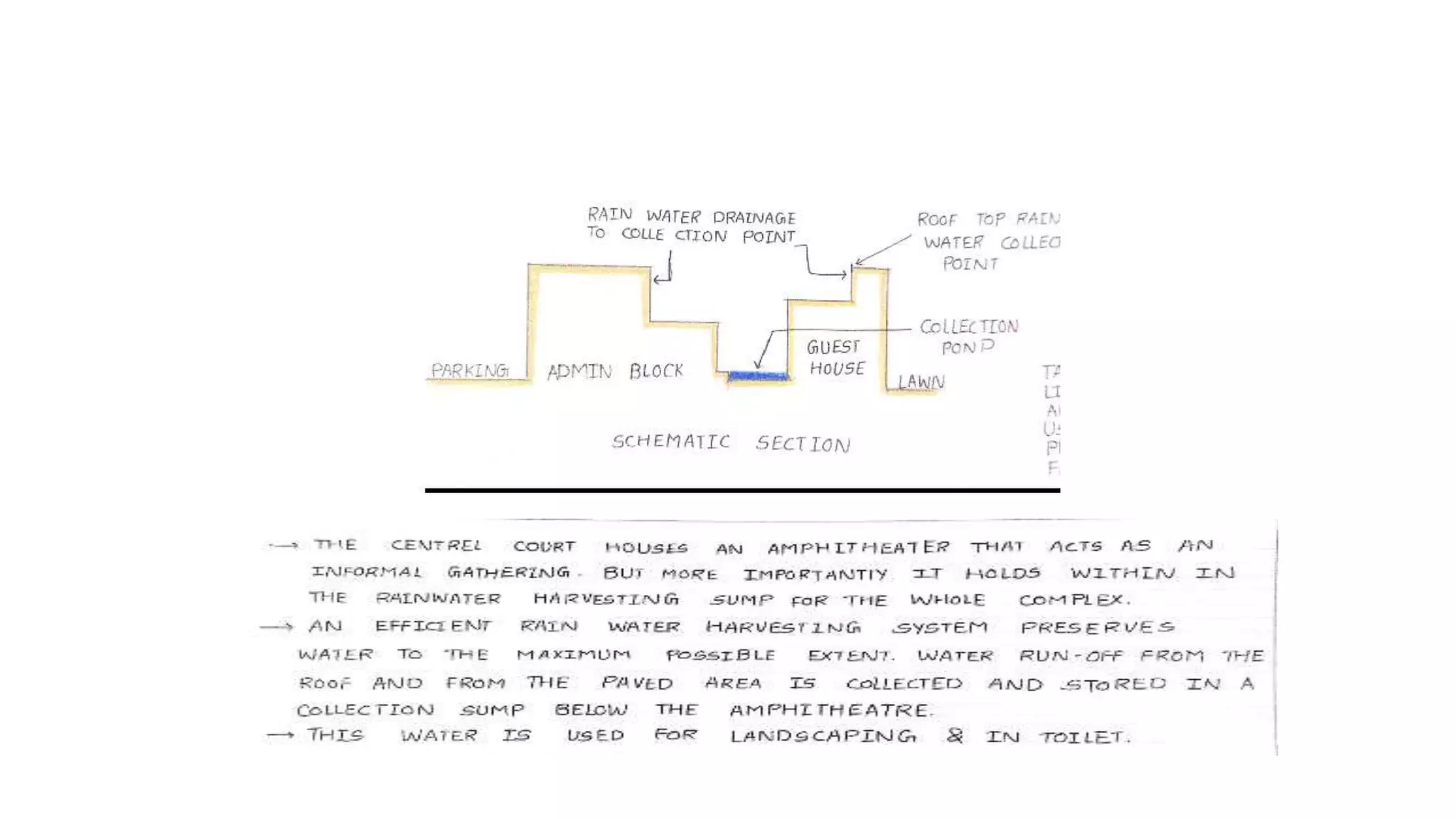
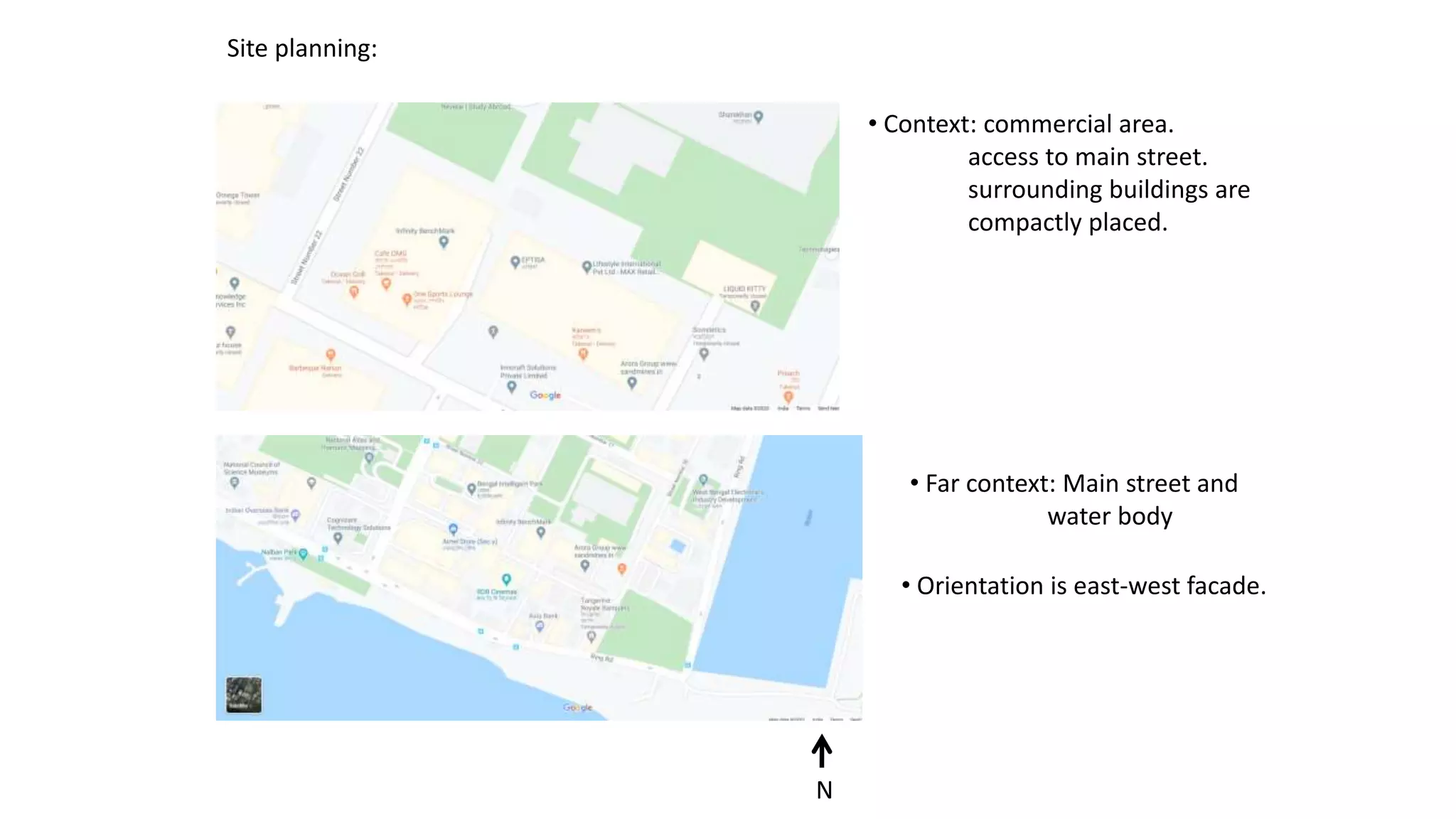
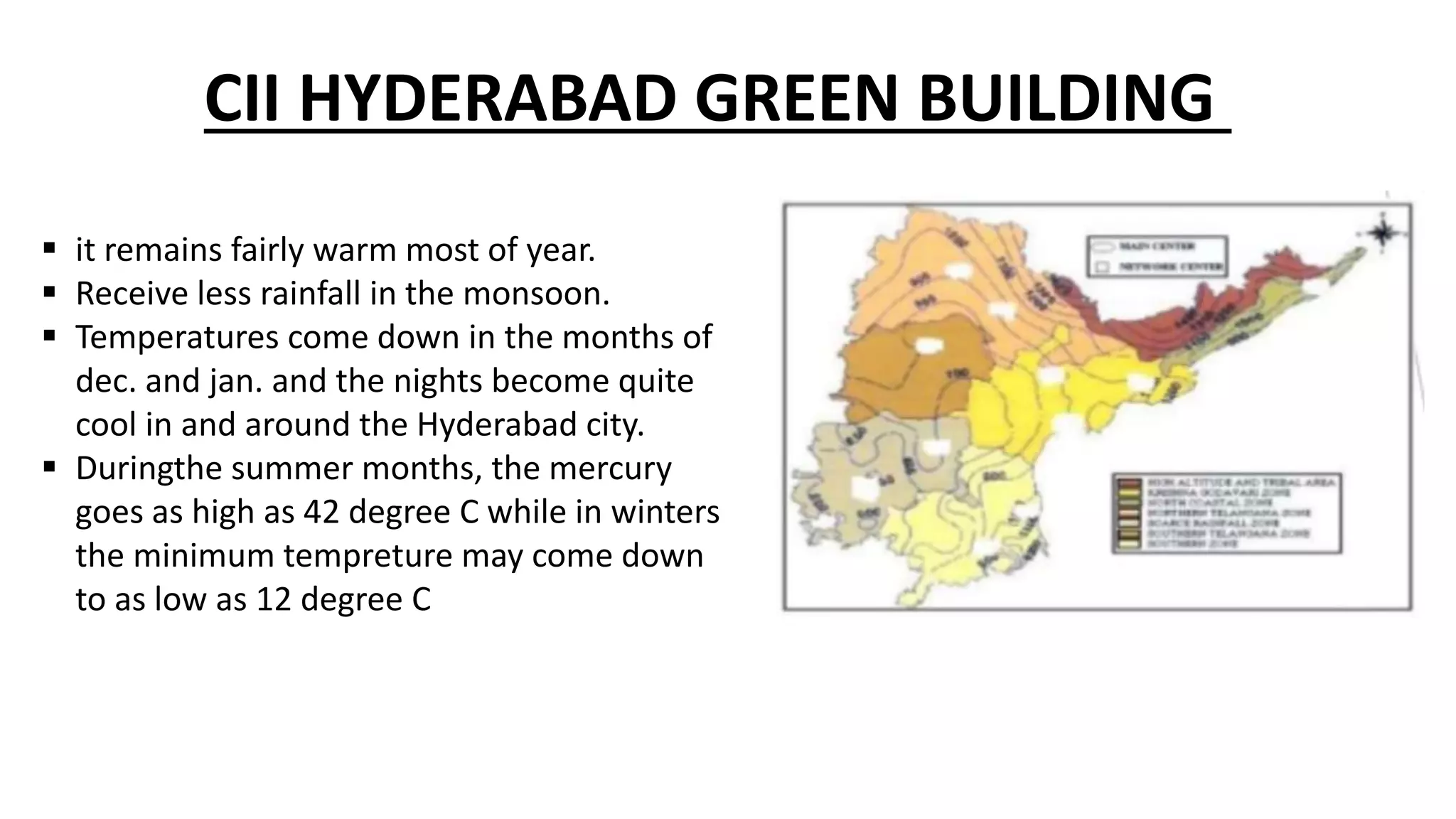
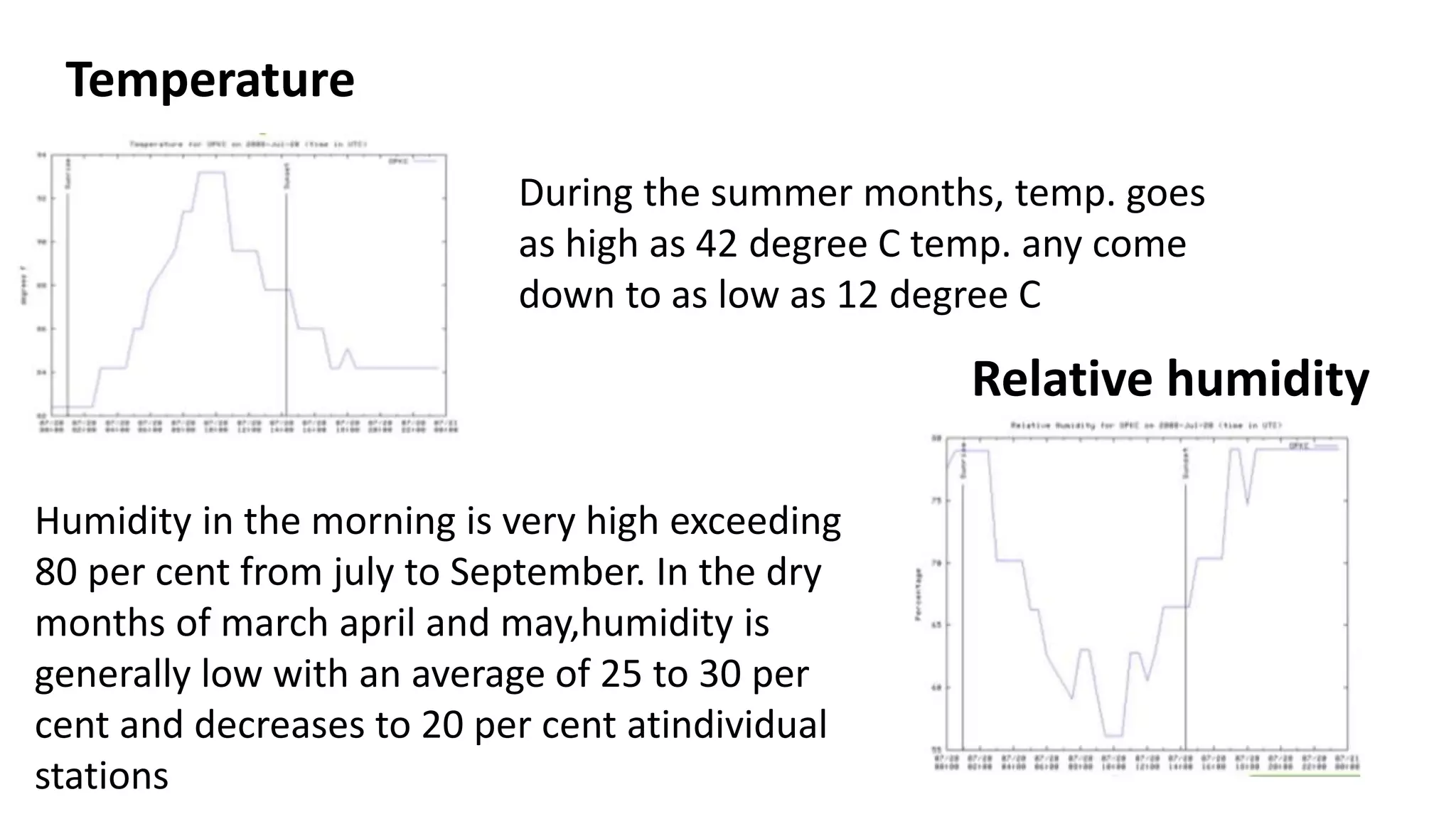
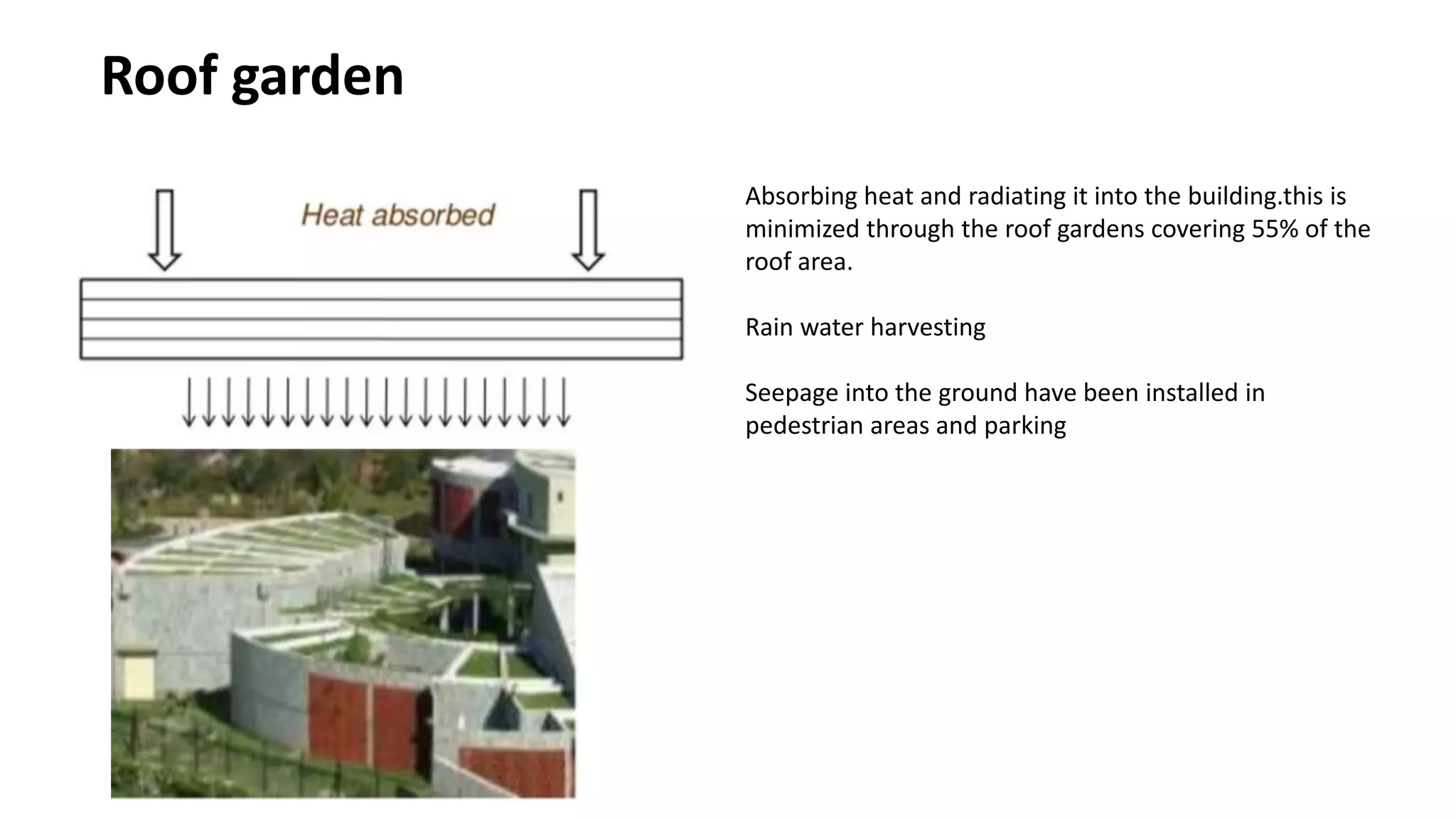
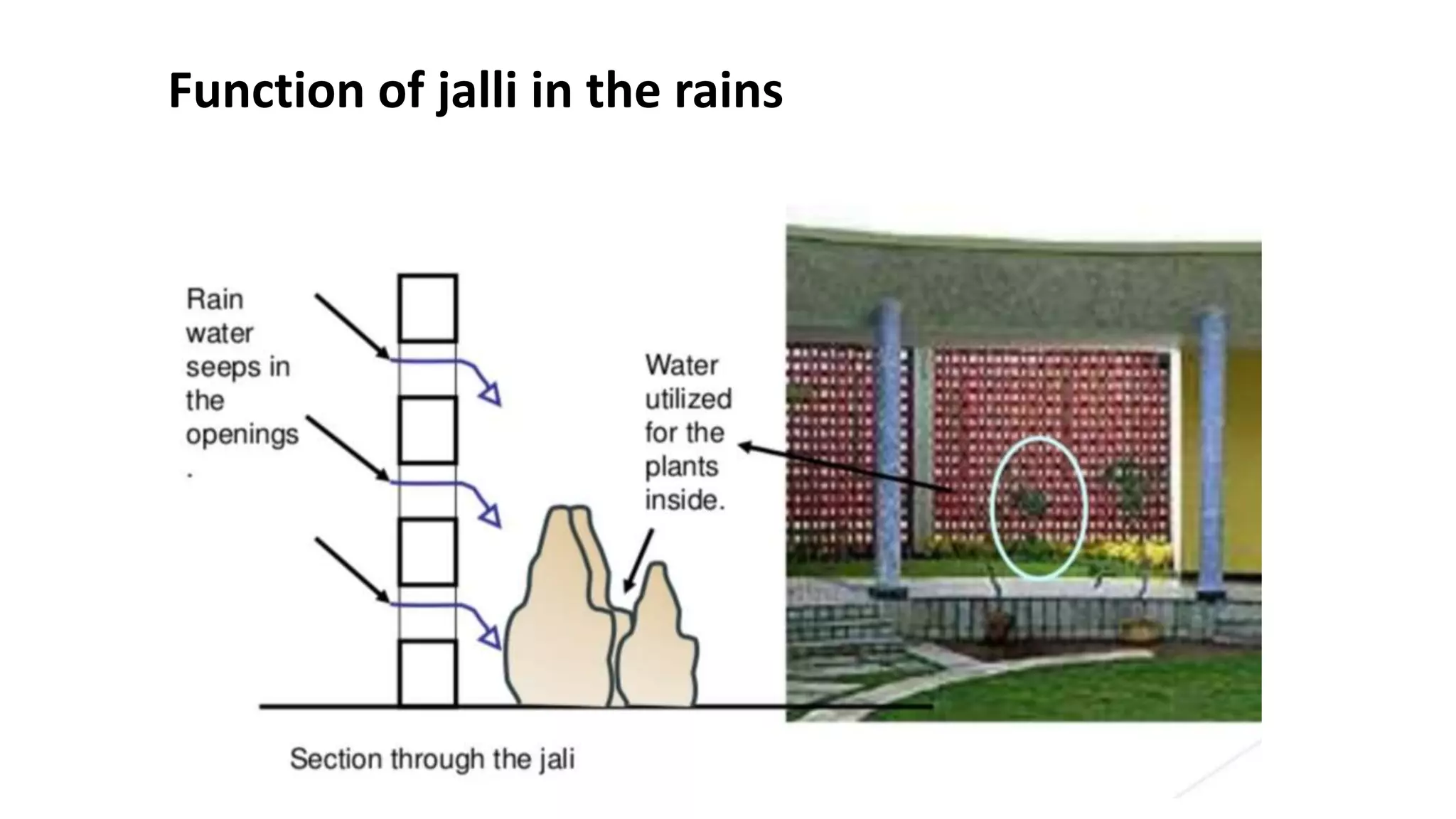
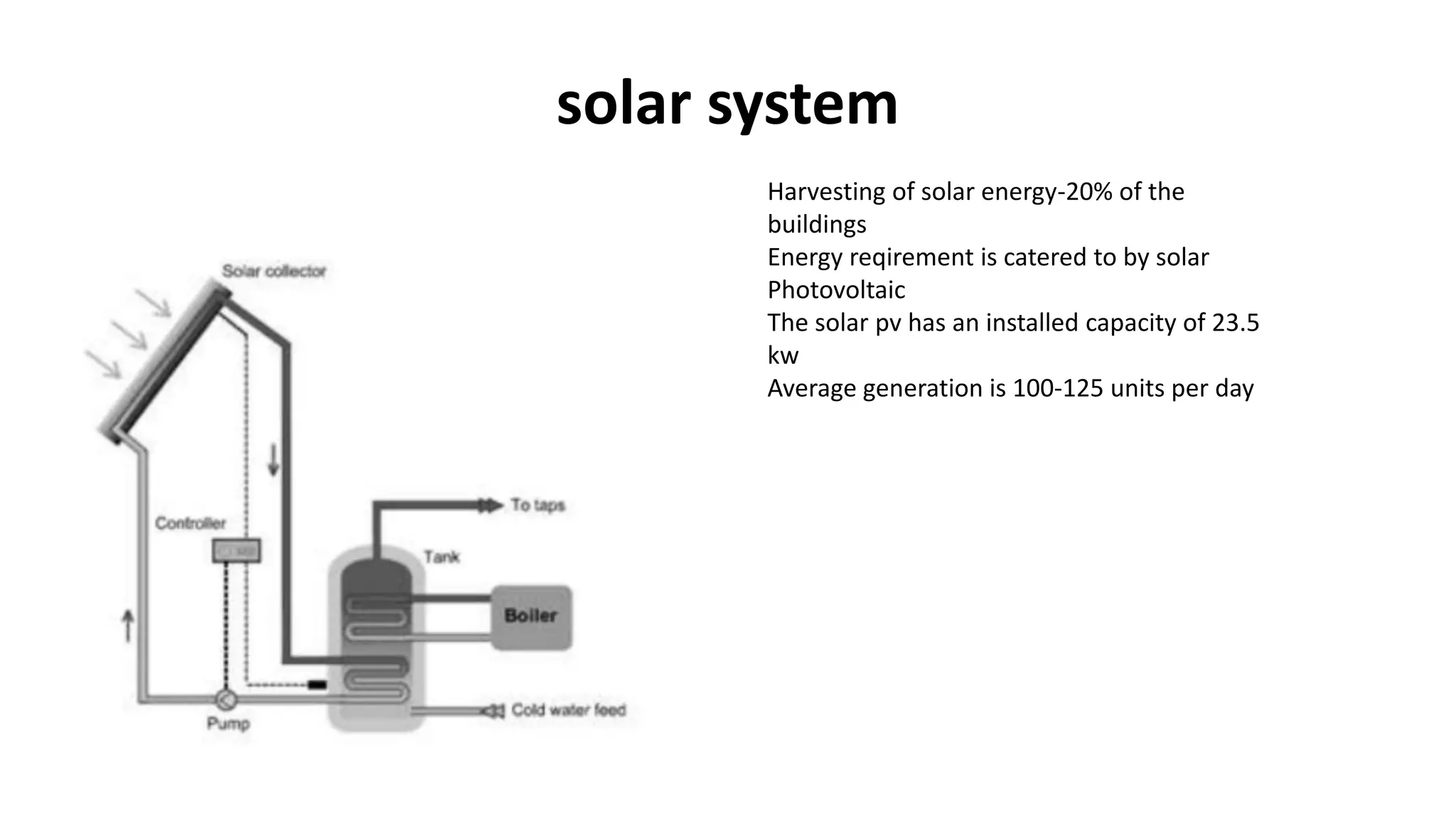
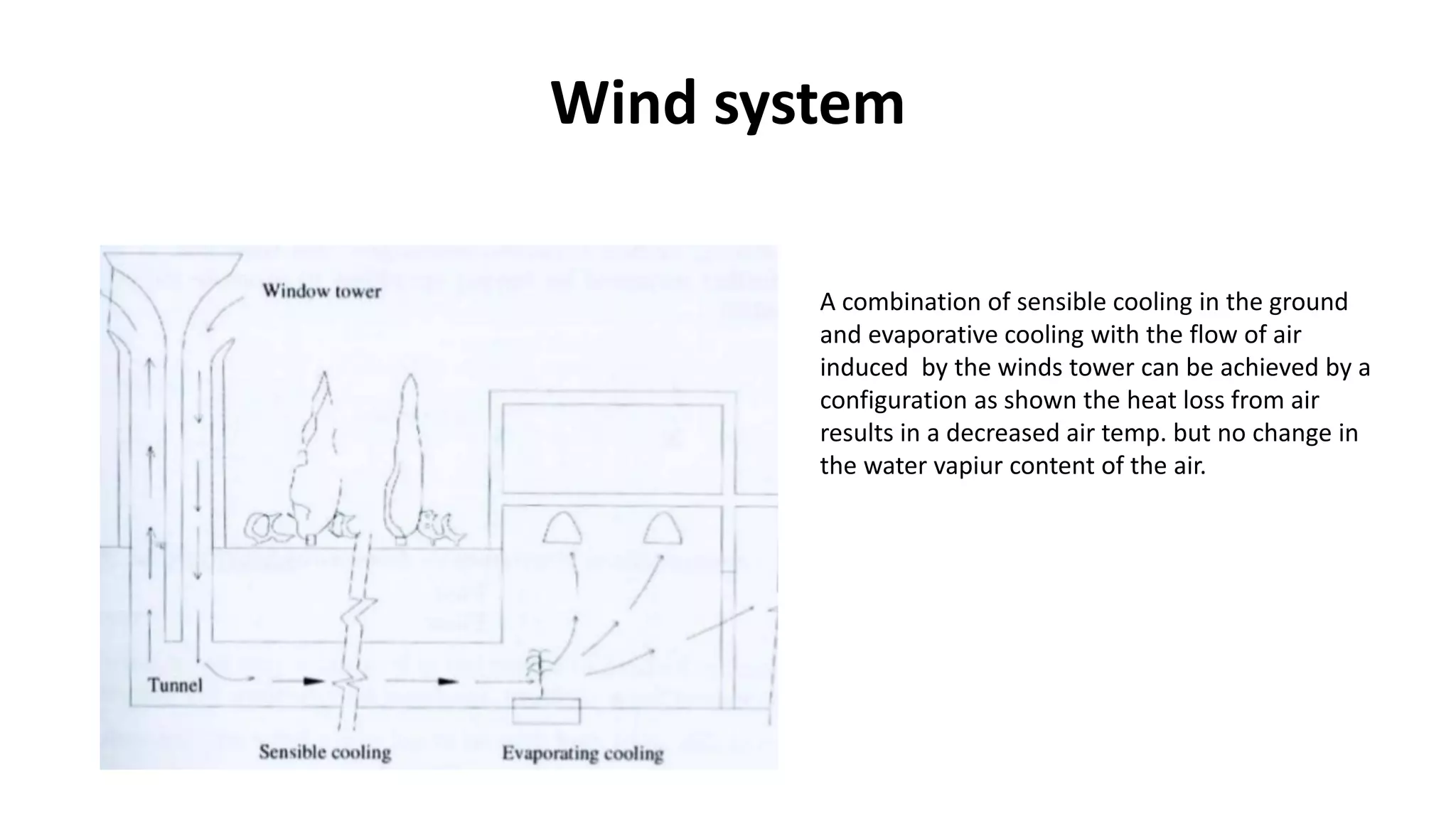
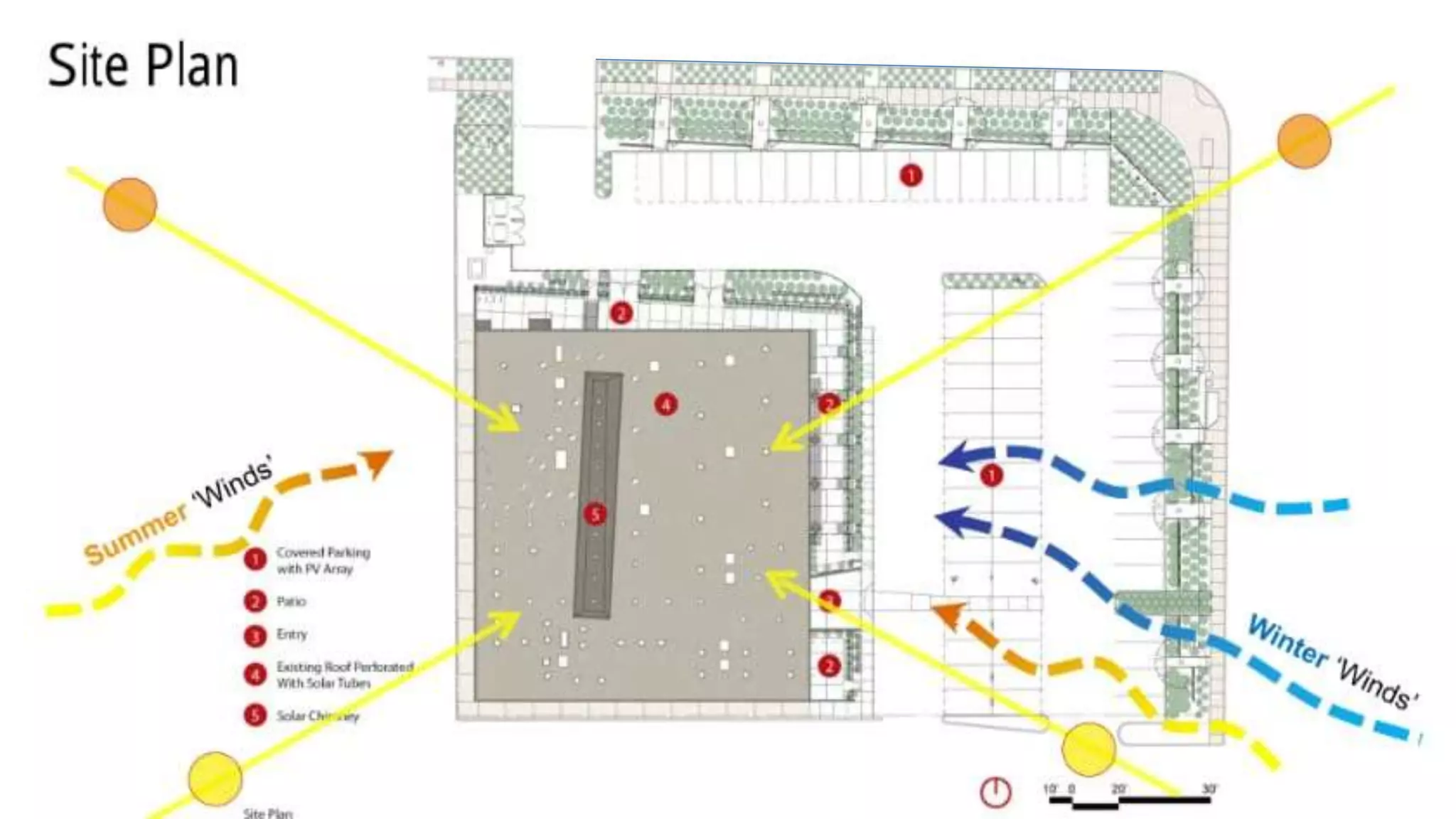
The document outlines various case studies of buildings rated by GRIHA and LEED, including notable examples like the Center for Environmental Science & Engineering at IIT Kanpur and the Indian Institute of Management in Kozhikode. It highlights each building's design, sustainability features, passive and active energy strategies, water management, and environmental integration to achieve high green building ratings. Emphasis is placed on innovative architectural approaches that optimize for local climates and ecosystems while minimizing resource use.