1) Birth asphyxia, also known as perinatal asphyxia, refers to impaired gas exchange during birth that leads to hypoxemia, hypercarbia, and fetal acidosis as evidenced by an umbilical cord arterial blood pH <7.0.
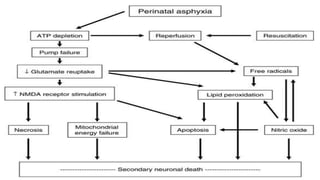
2) It can cause hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) and multi-organ damage in newborns. Long term sequelae of birth asphyxia include cerebral palsy, cognitive delays, seizures, and visual/auditory processing difficulties.
3) Diagnosis is based on criteria such as an umbilical cord blood pH <7.0, Apgar score of 0-3 for more than 5 minutes,



![Definition:
It refers to a condition during pregnancy and labor in which
impaired gas exchange leads to;
Hypoxemia, and
Hypercarbia.
Fetal acidosis,
It is evidenced by fetal acidosis as measured in umbilical arterial
blood pH <7.0
[Cloherty and Stark’s Manual of Neonatal Care ;pg .820]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/birthasphyxia-220522183549-29b3fd18/85/Birth-Asphyxia-pptx-4-320.jpg)