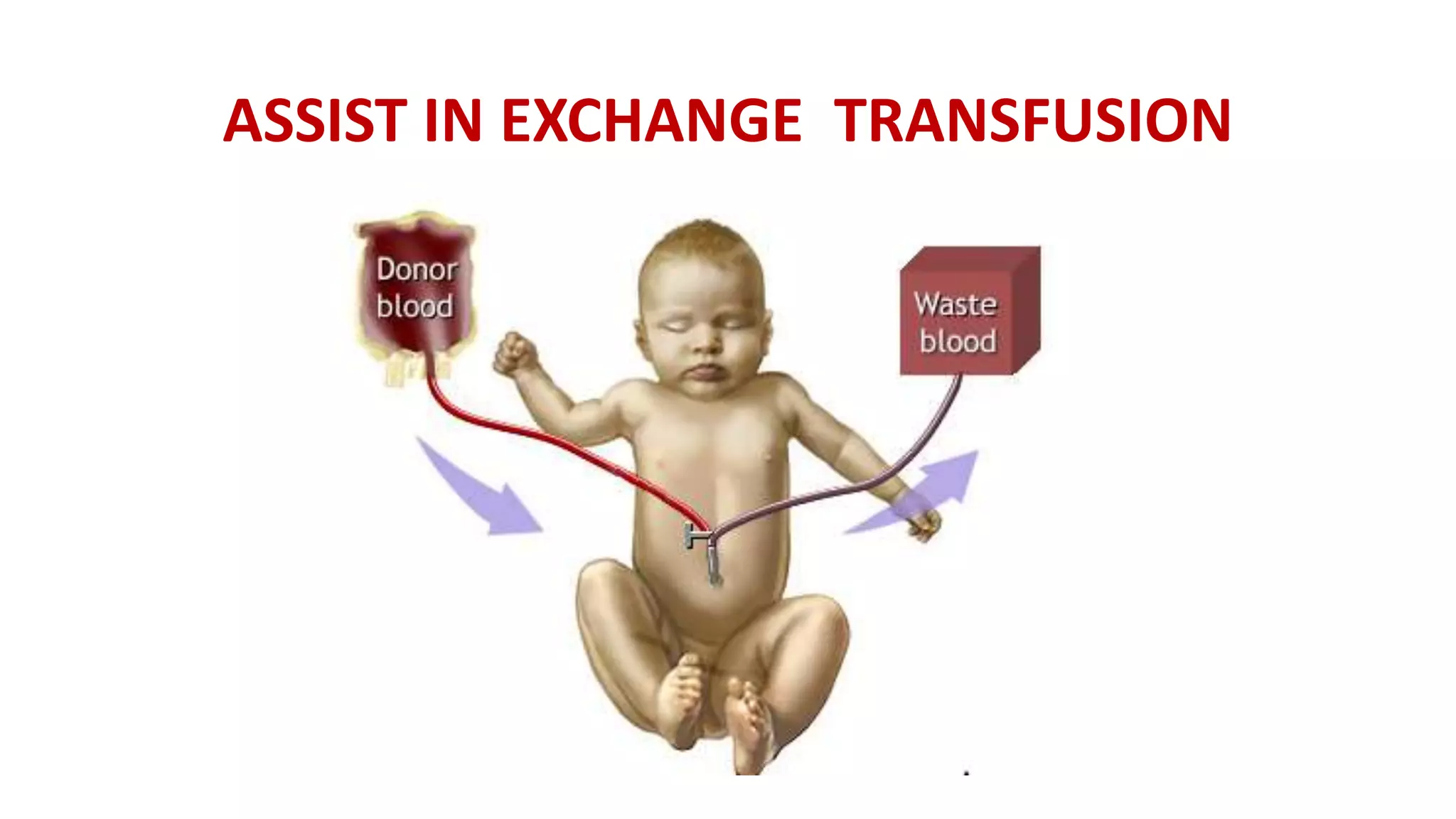
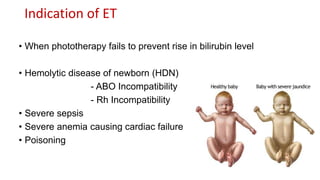
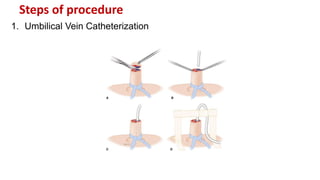
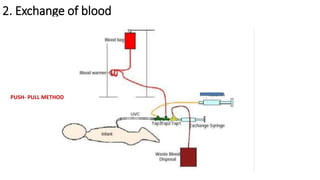
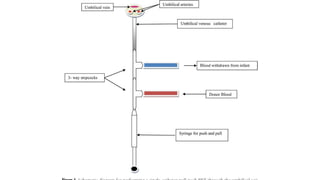
The document outlines the procedure for exchange transfusion (ET) in neonates, detailing its historical background, definitions, indications, necessary preparations, equipment, and procedural steps. It emphasizes the management of hemolytic disease of the newborn and associated complications while highlighting safety measures during the procedure, including monitoring and post-exchange care. Additionally, it includes information on potential complications and responsibilities of the healthcare team throughout the process.