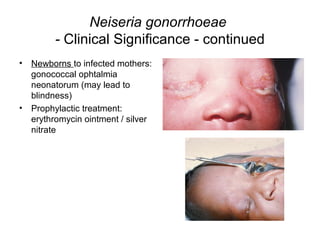
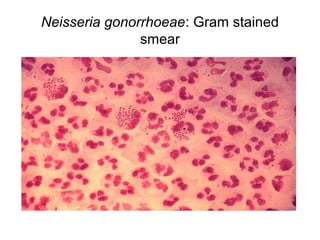
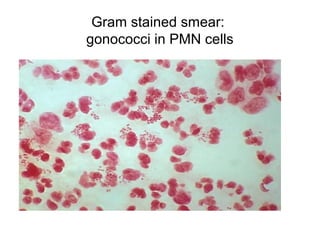
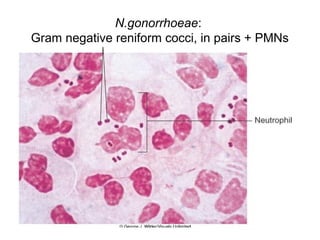
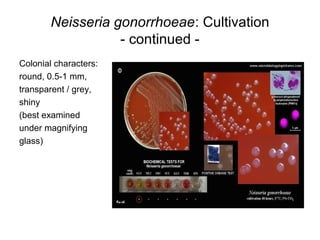
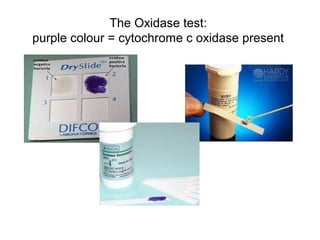
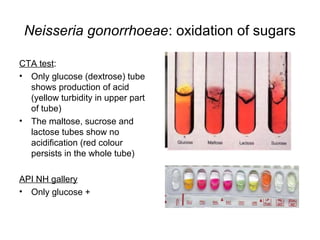
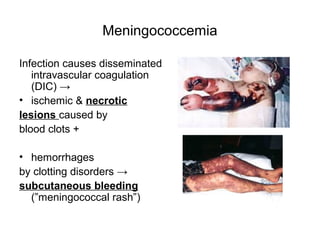
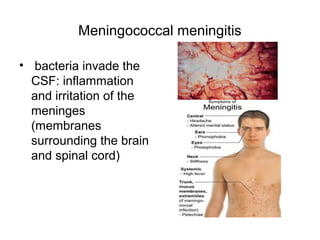
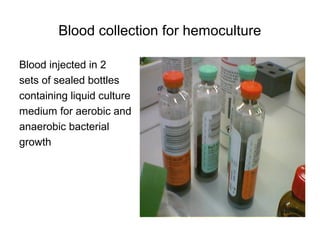
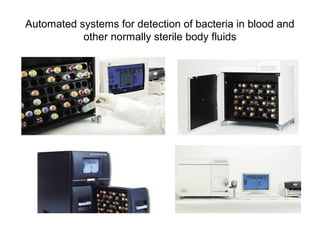
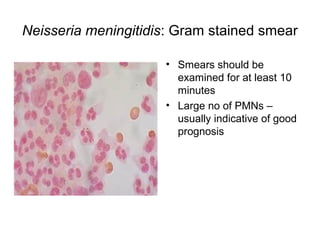
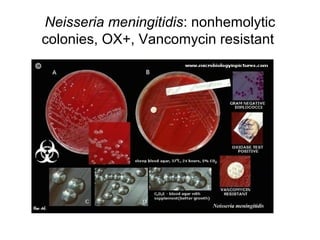
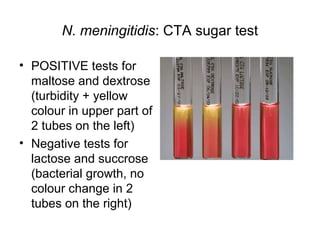
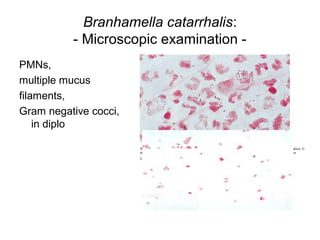
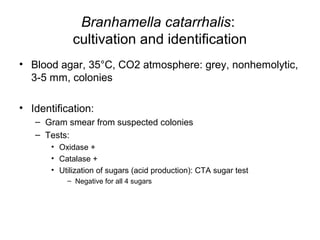
The document provides an overview of the laboratory diagnosis of infections caused by the Neisseria genus, highlighting the pathogenic nature of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Neisseria meningitidis. It details clinical significance, specimen collection methods, and microbiological examination techniques for diagnosing infections like gonorrhea and meningococcal disease. The document also discusses antibiotic susceptibility and the importance of rapid diagnostic methods in clinical settings.