This document provides an overview of viruses, including their general characteristics, morphology, structure, classification criteria, and methods for laboratory diagnosis. Key points include:
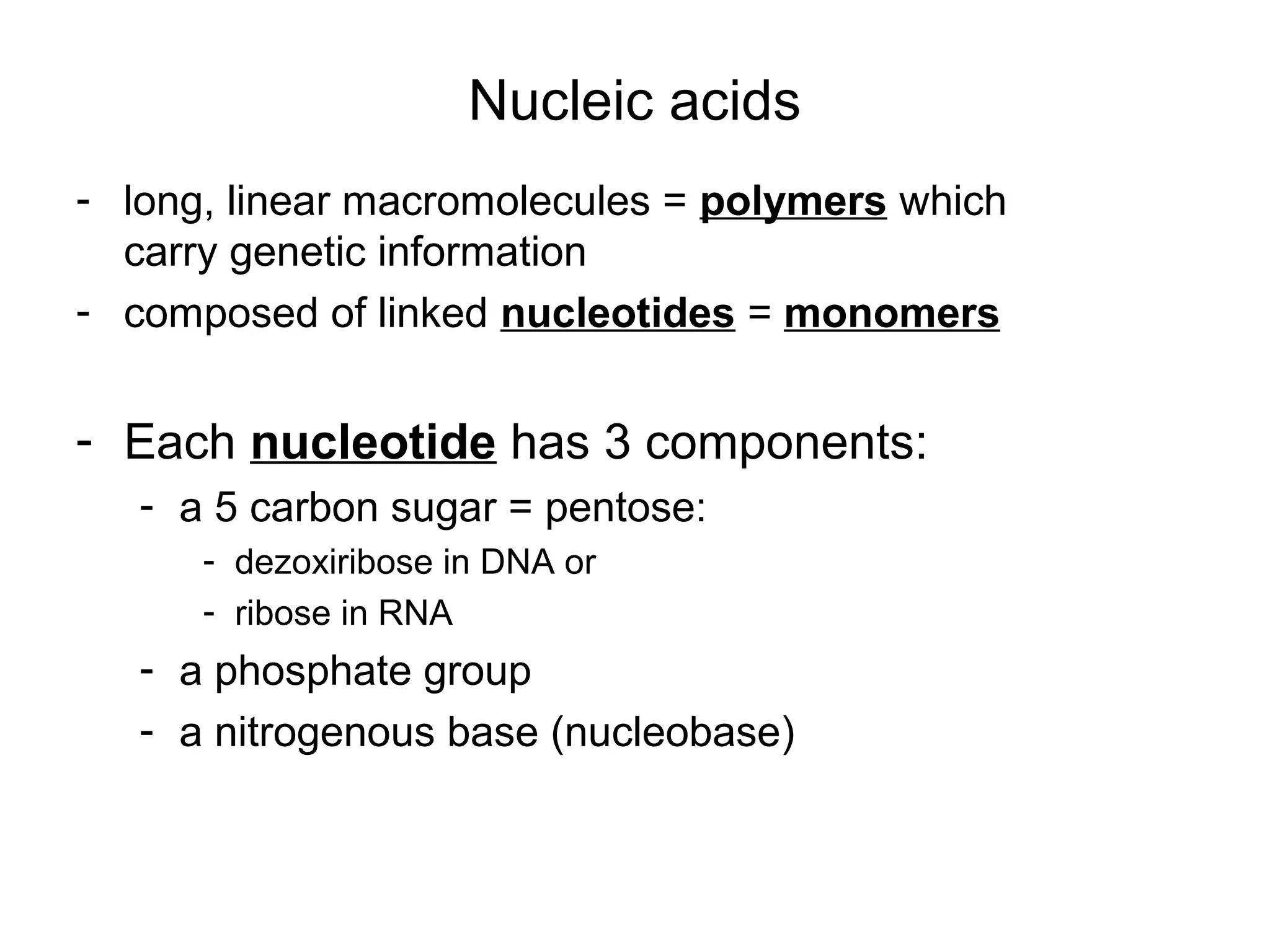
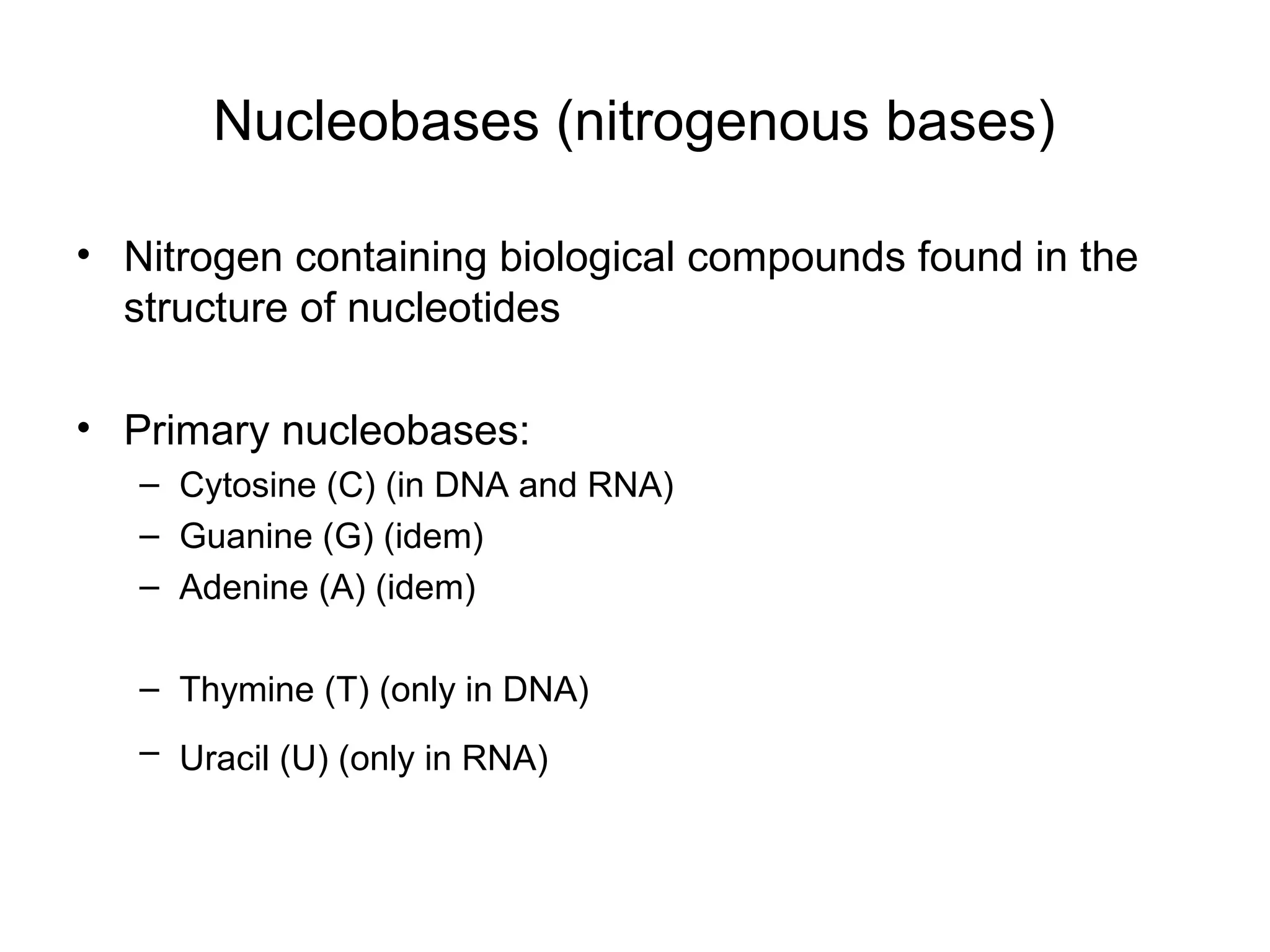
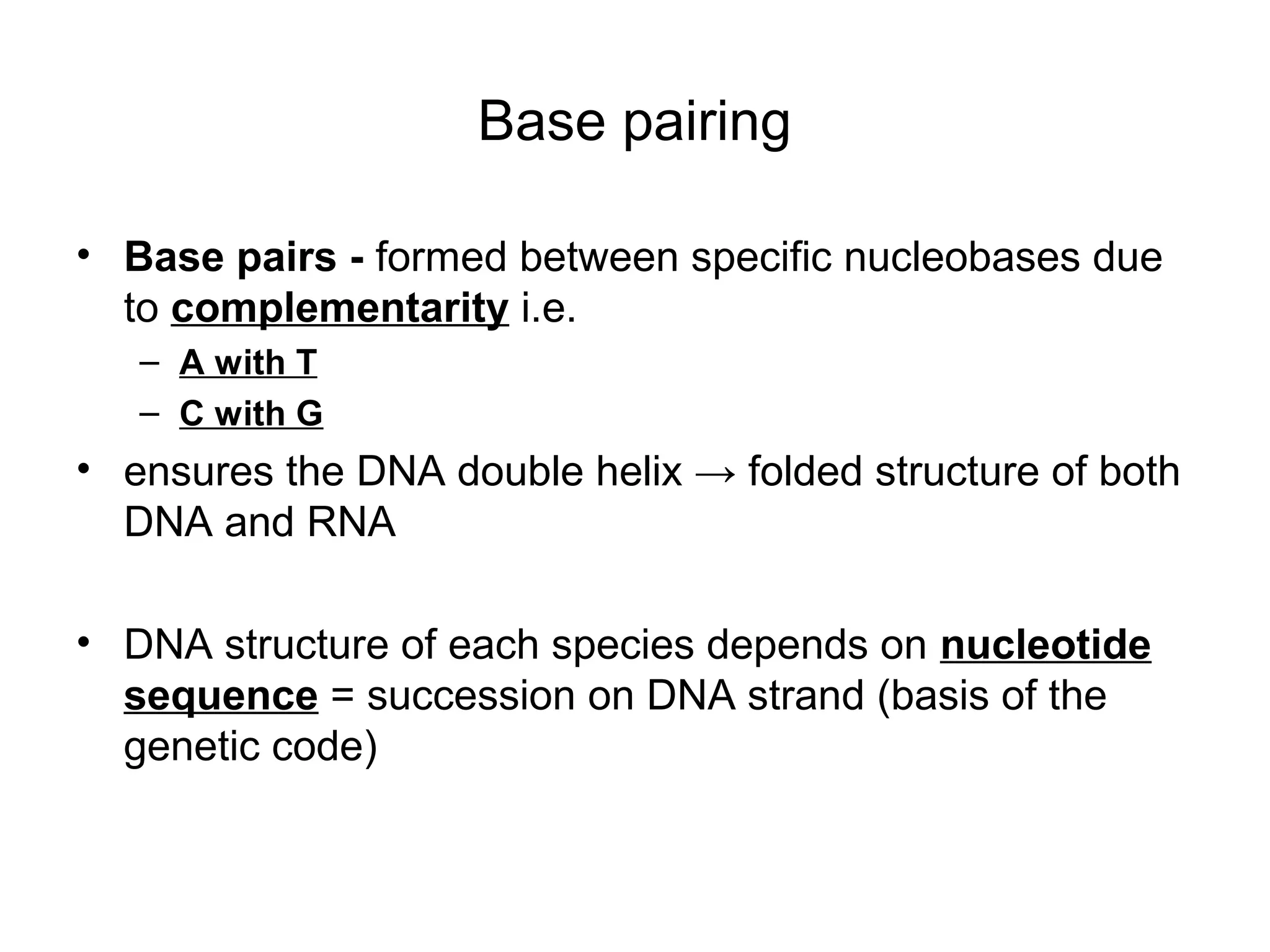
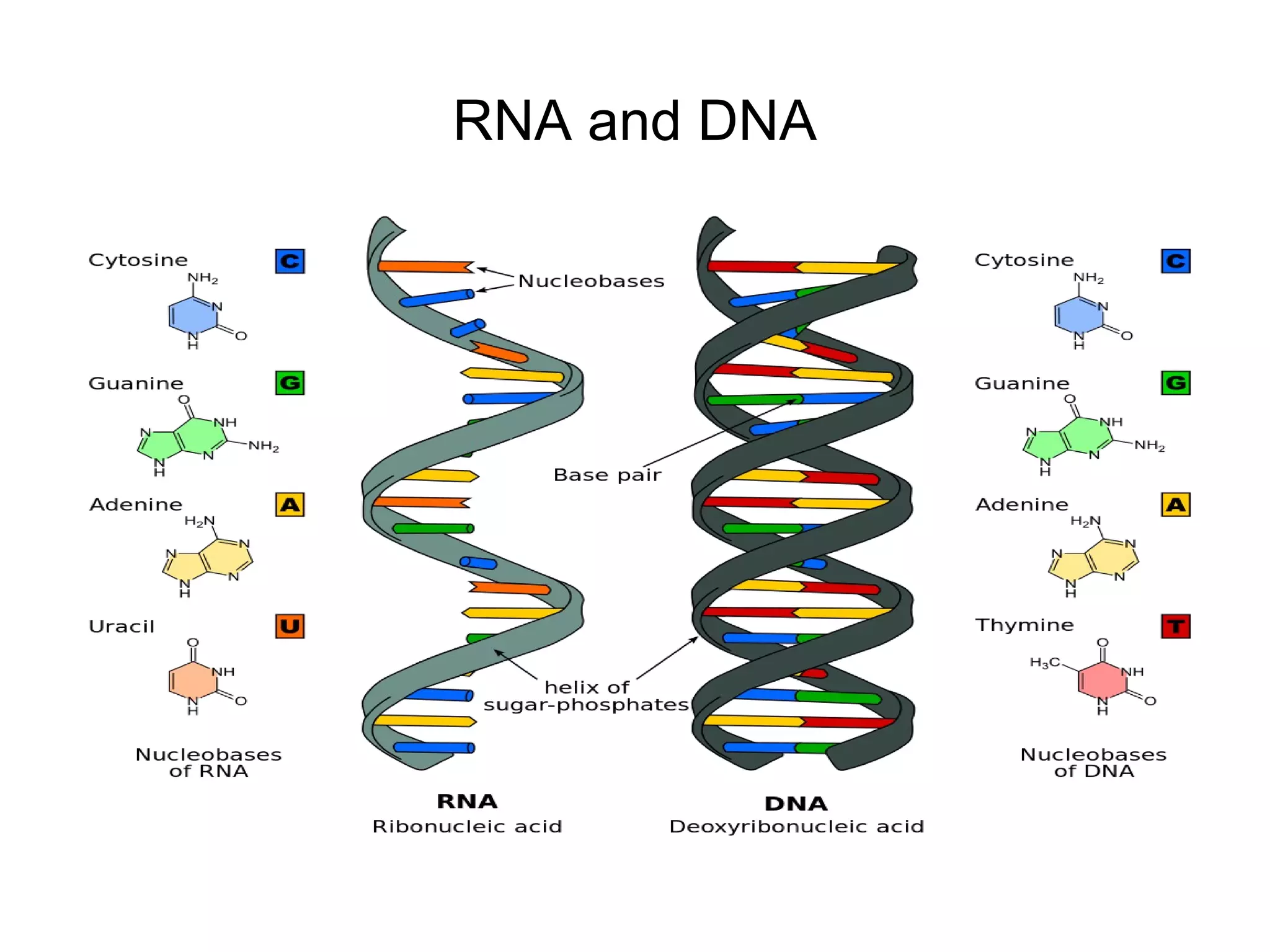
- Viruses are small infectious agents that require a host cell to replicate and are made up of nucleic acids surrounded by a protein capsid.
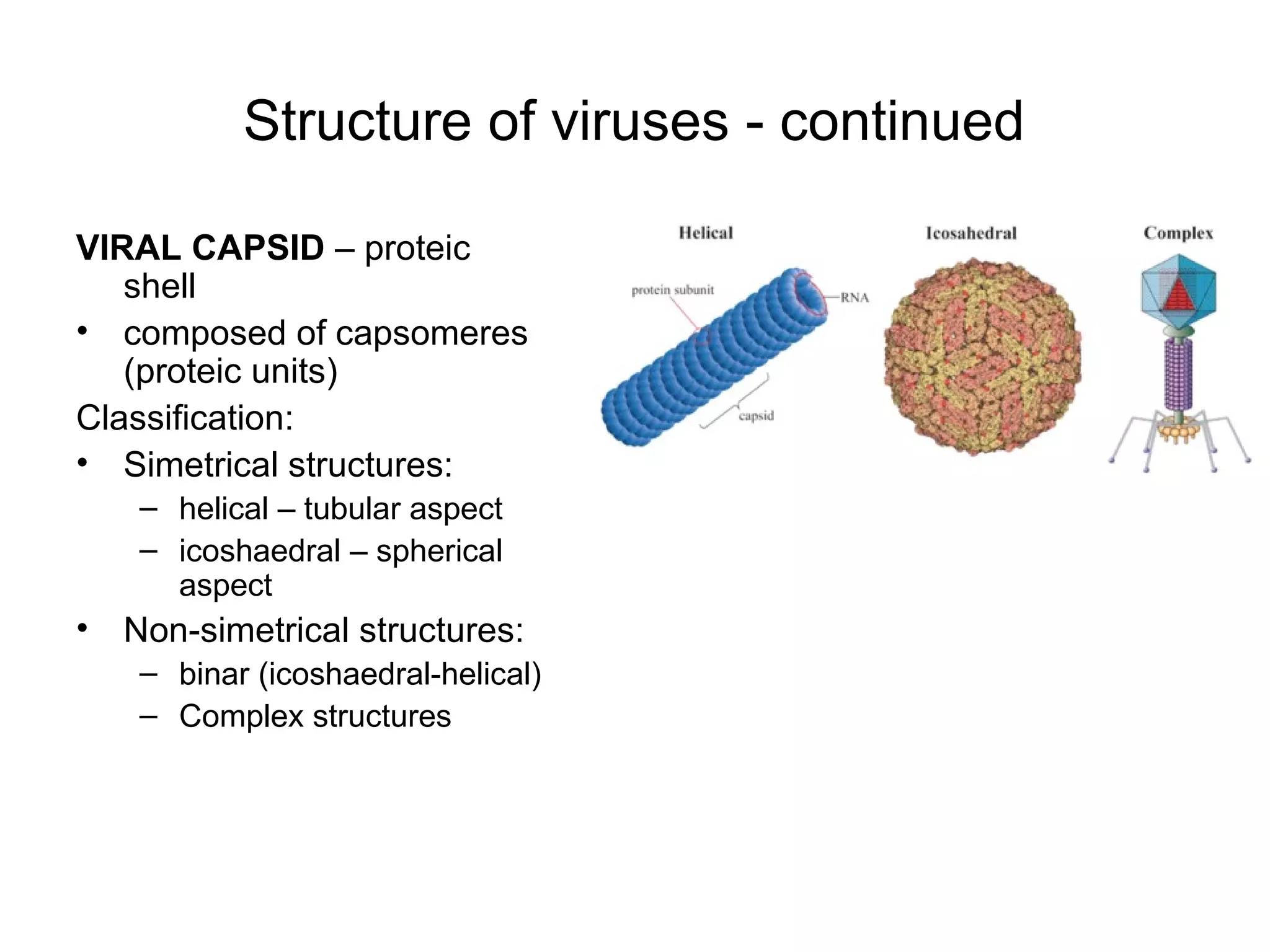
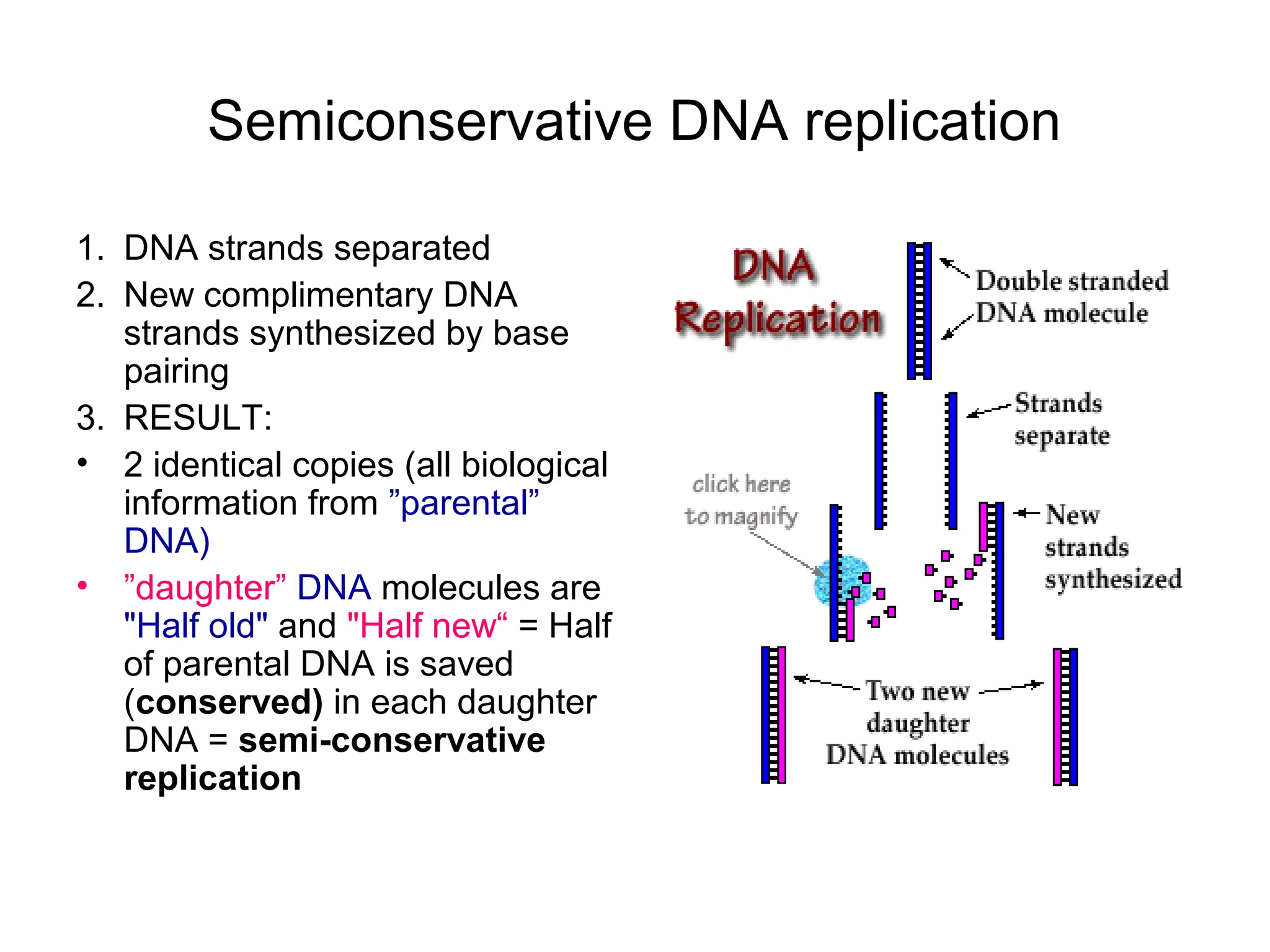
- Morphology varies between spherical, tubular, and complex shapes depending on the virus. Viruses also have either DNA or RNA genomes.
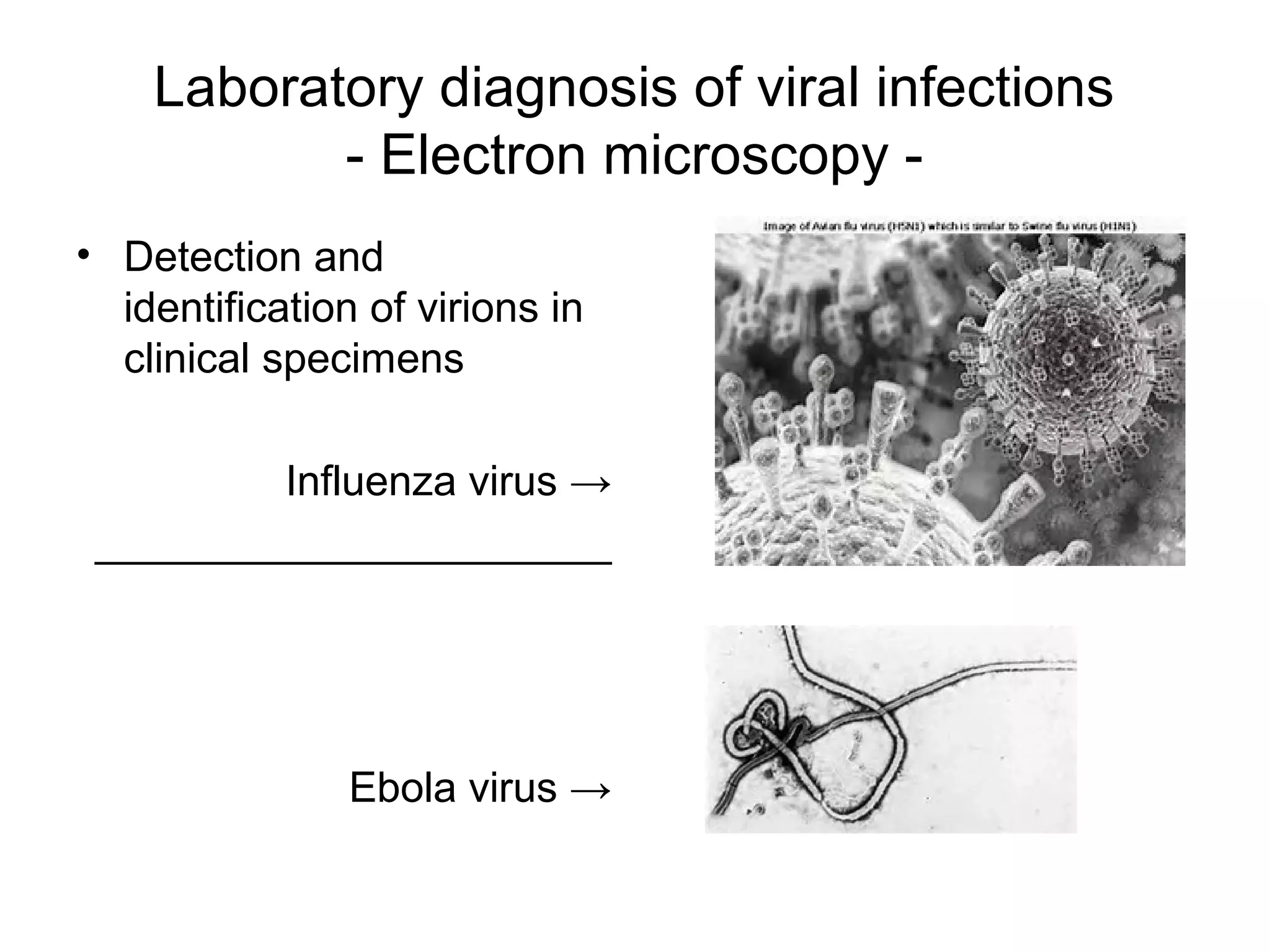
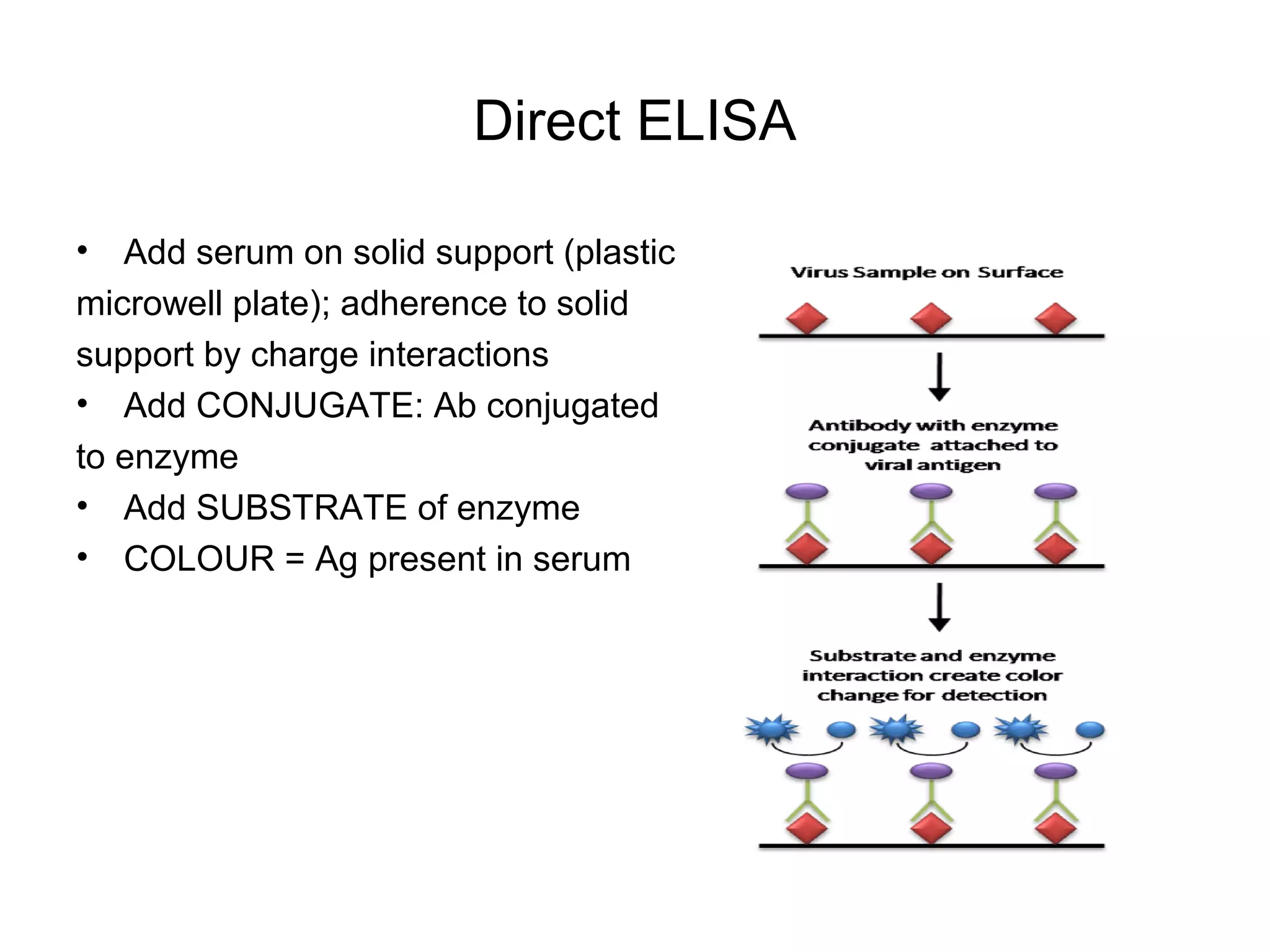
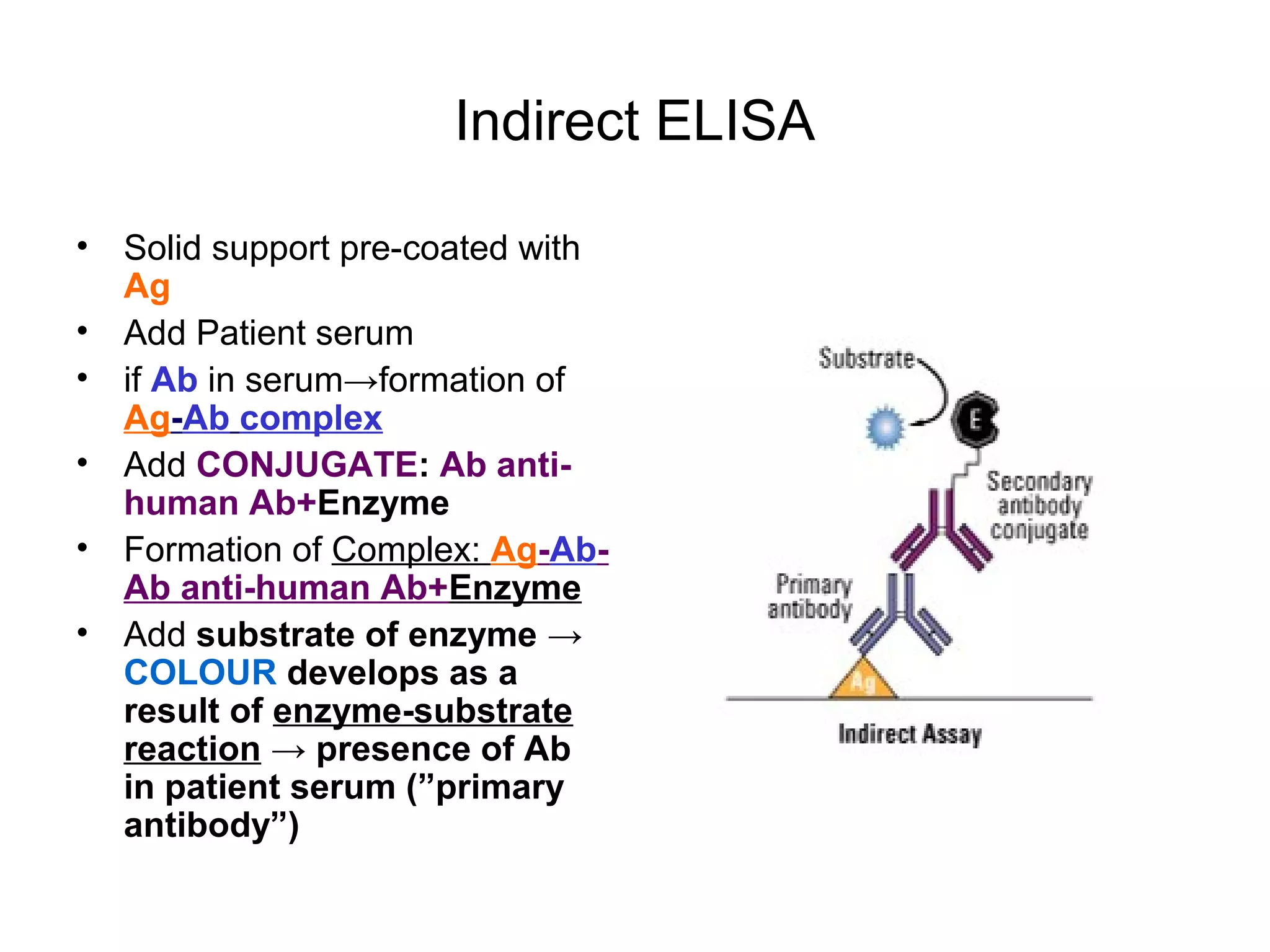
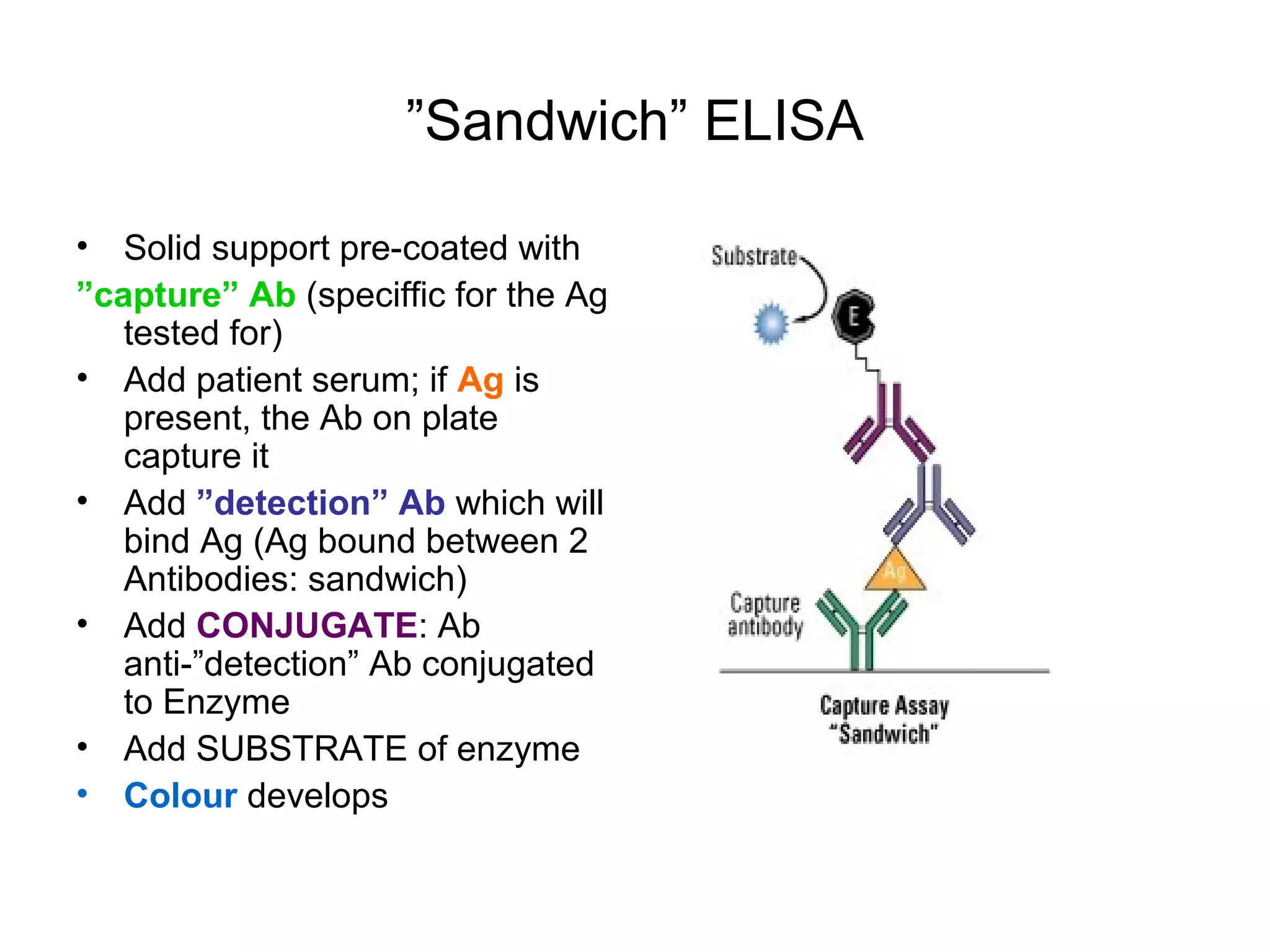
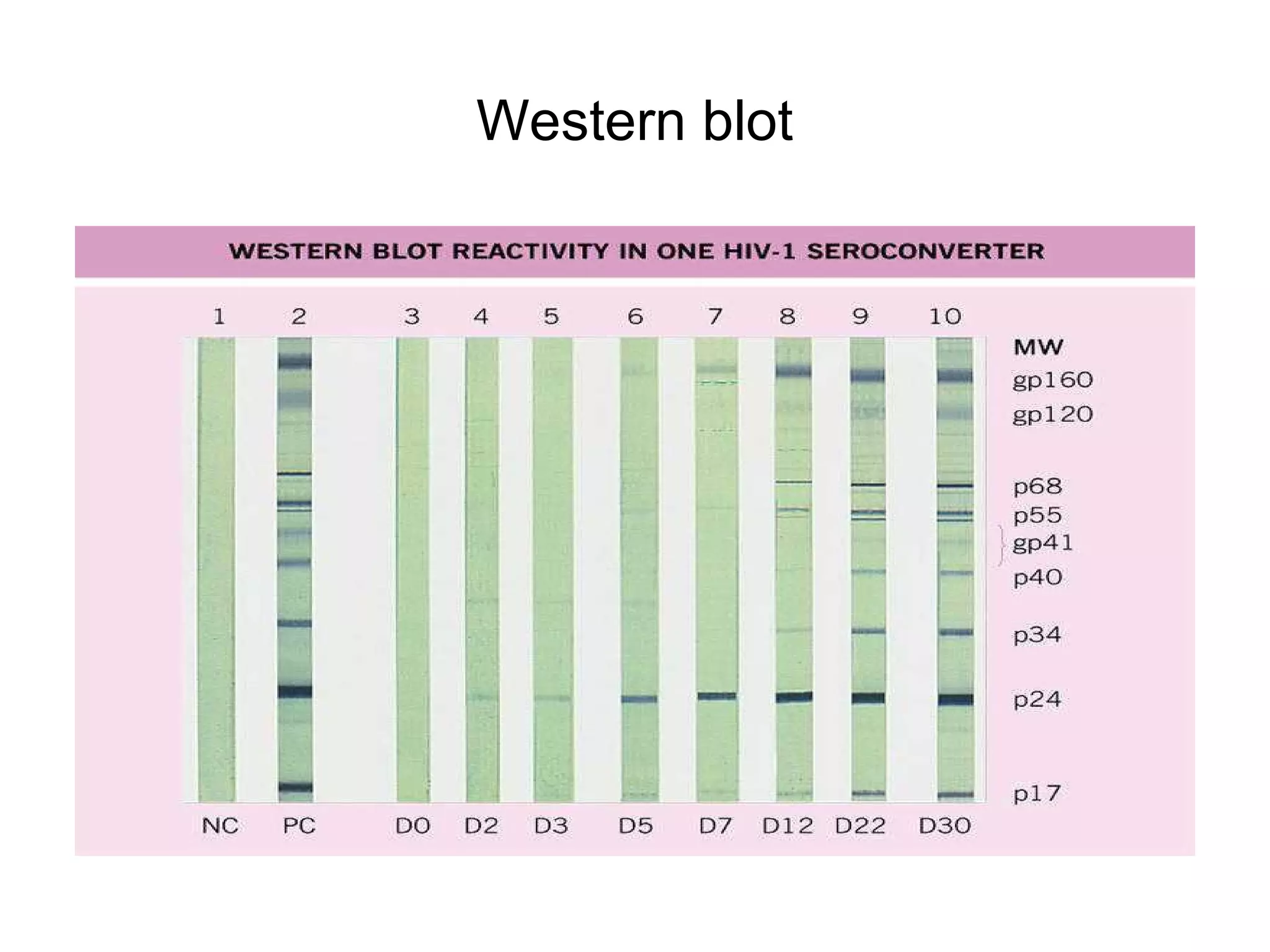
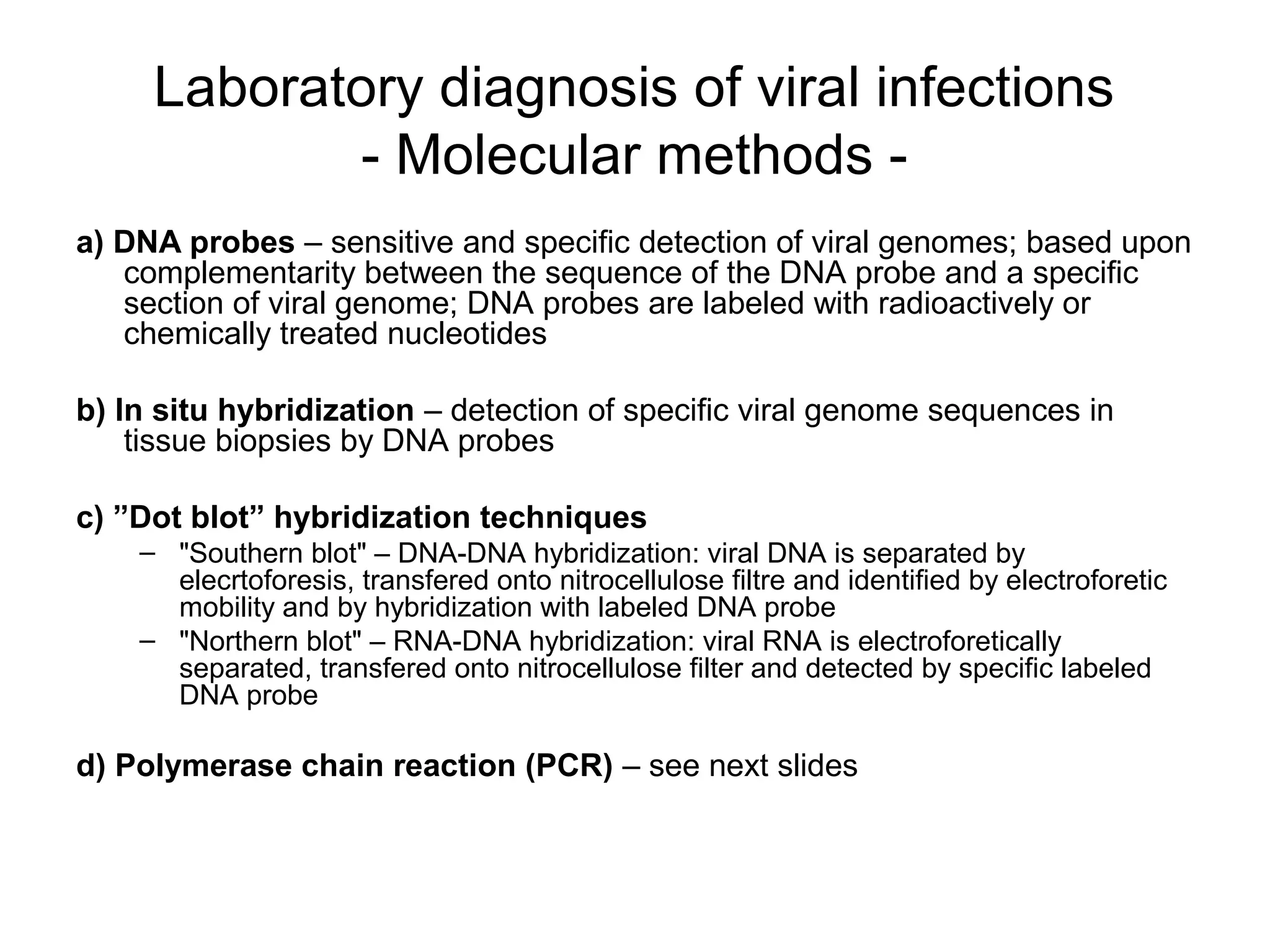
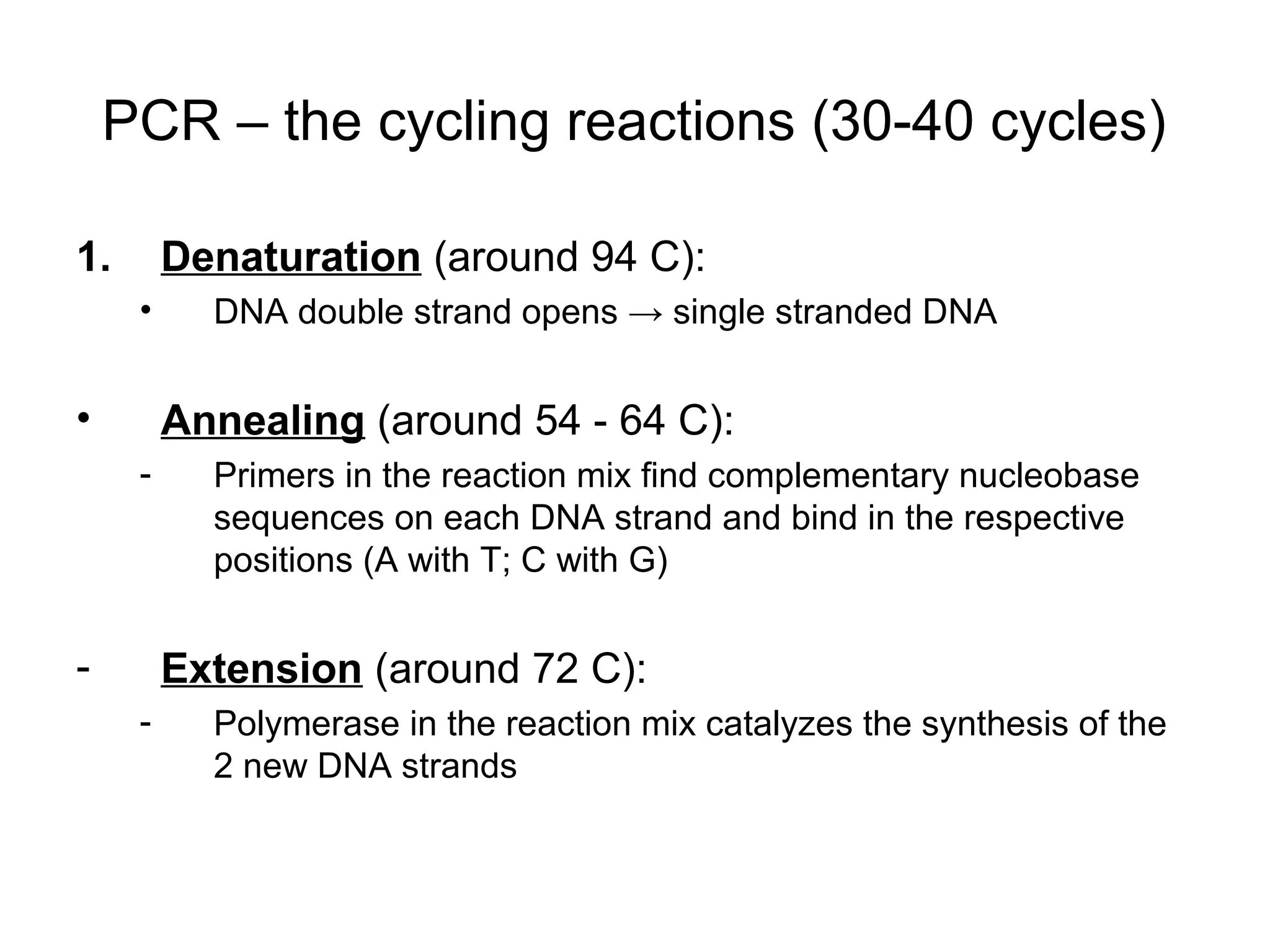
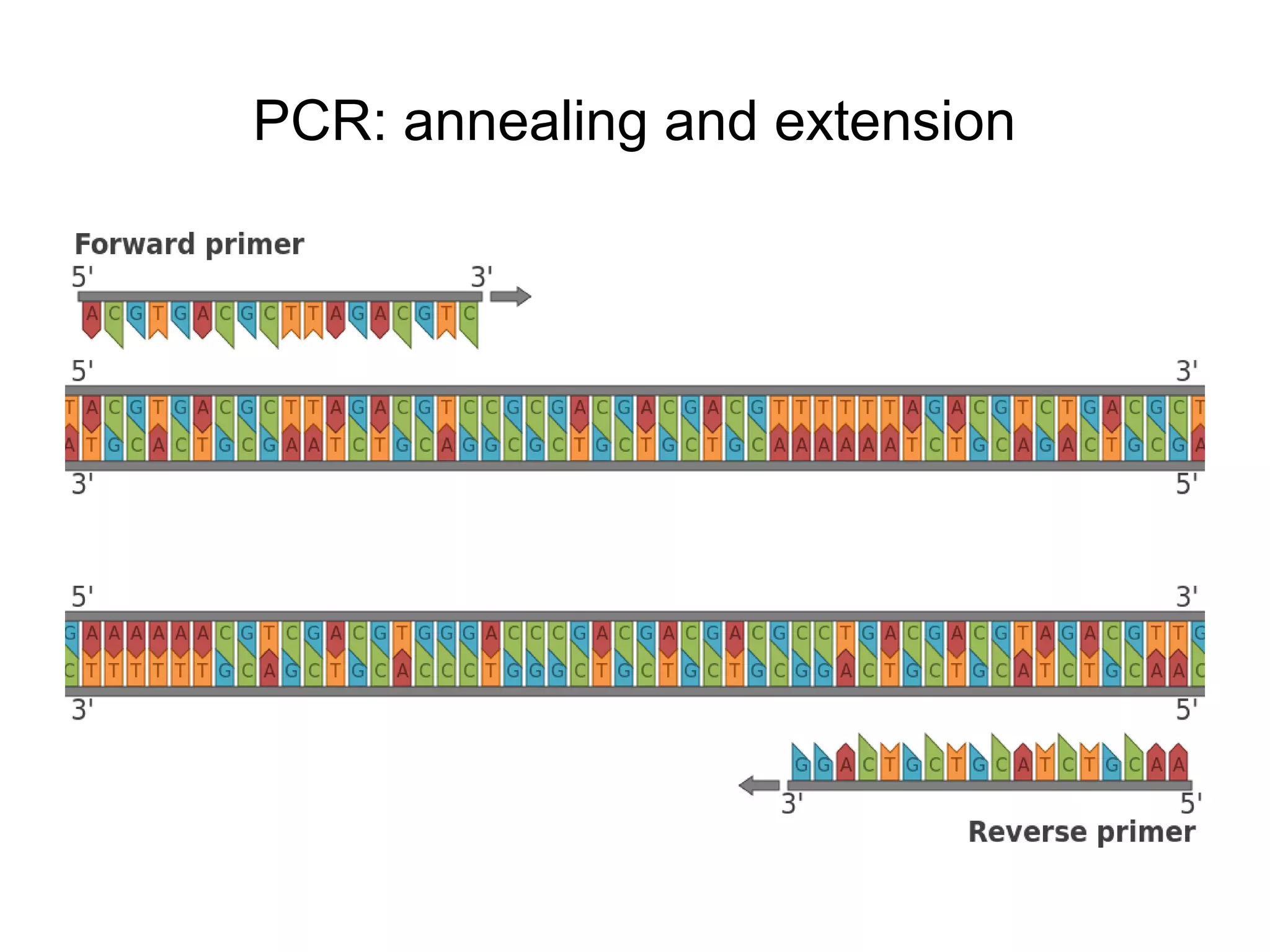
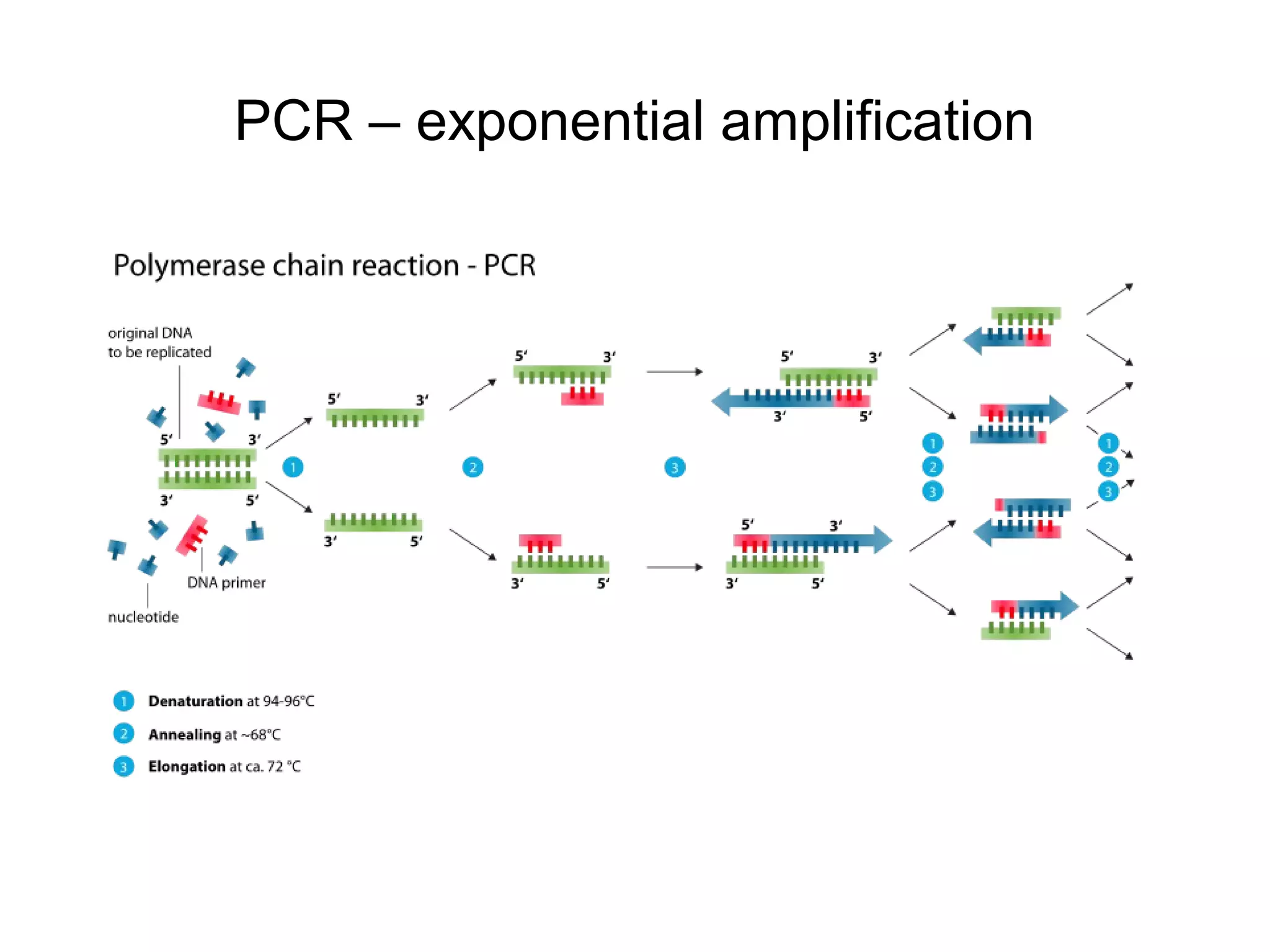
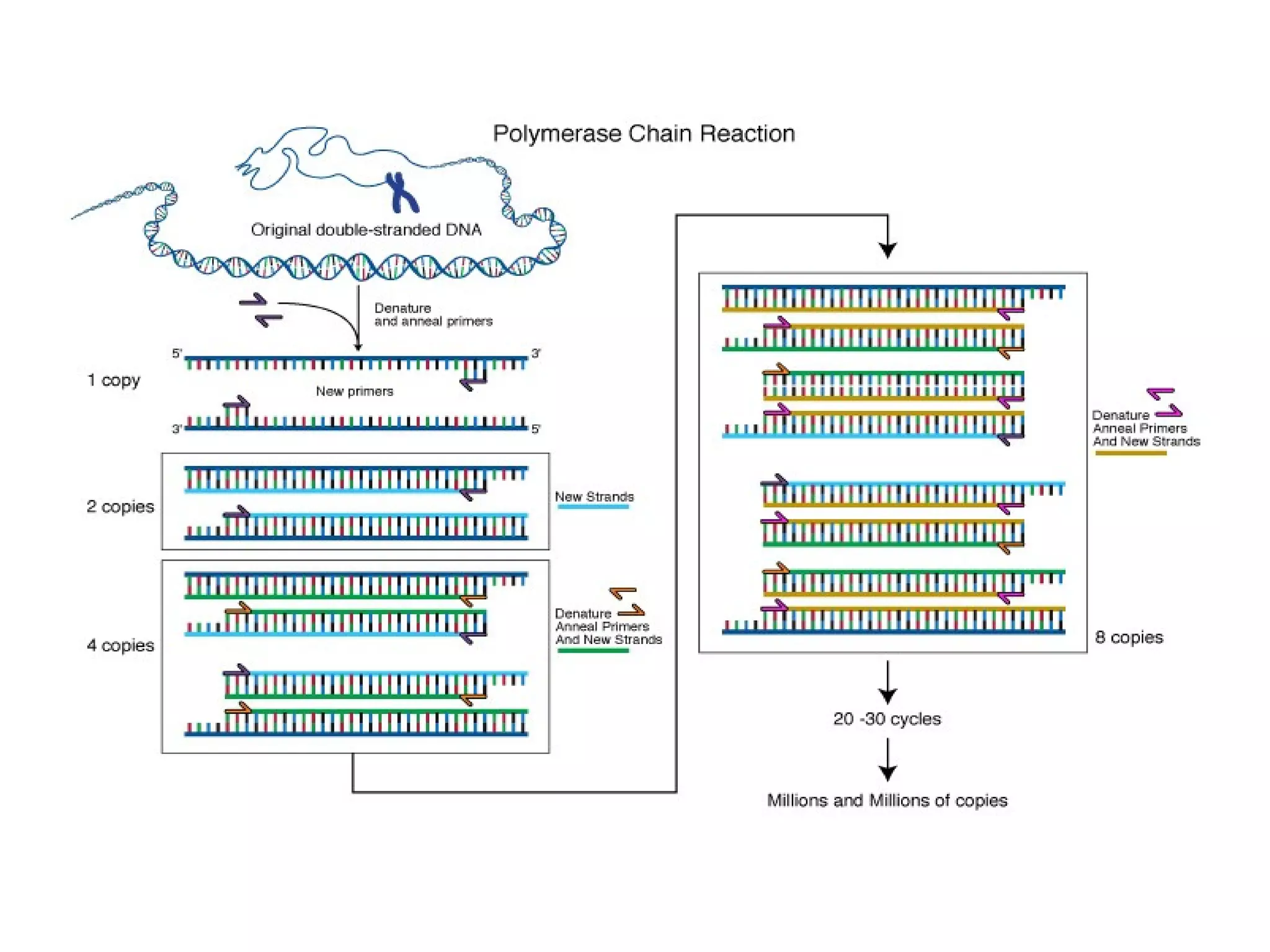
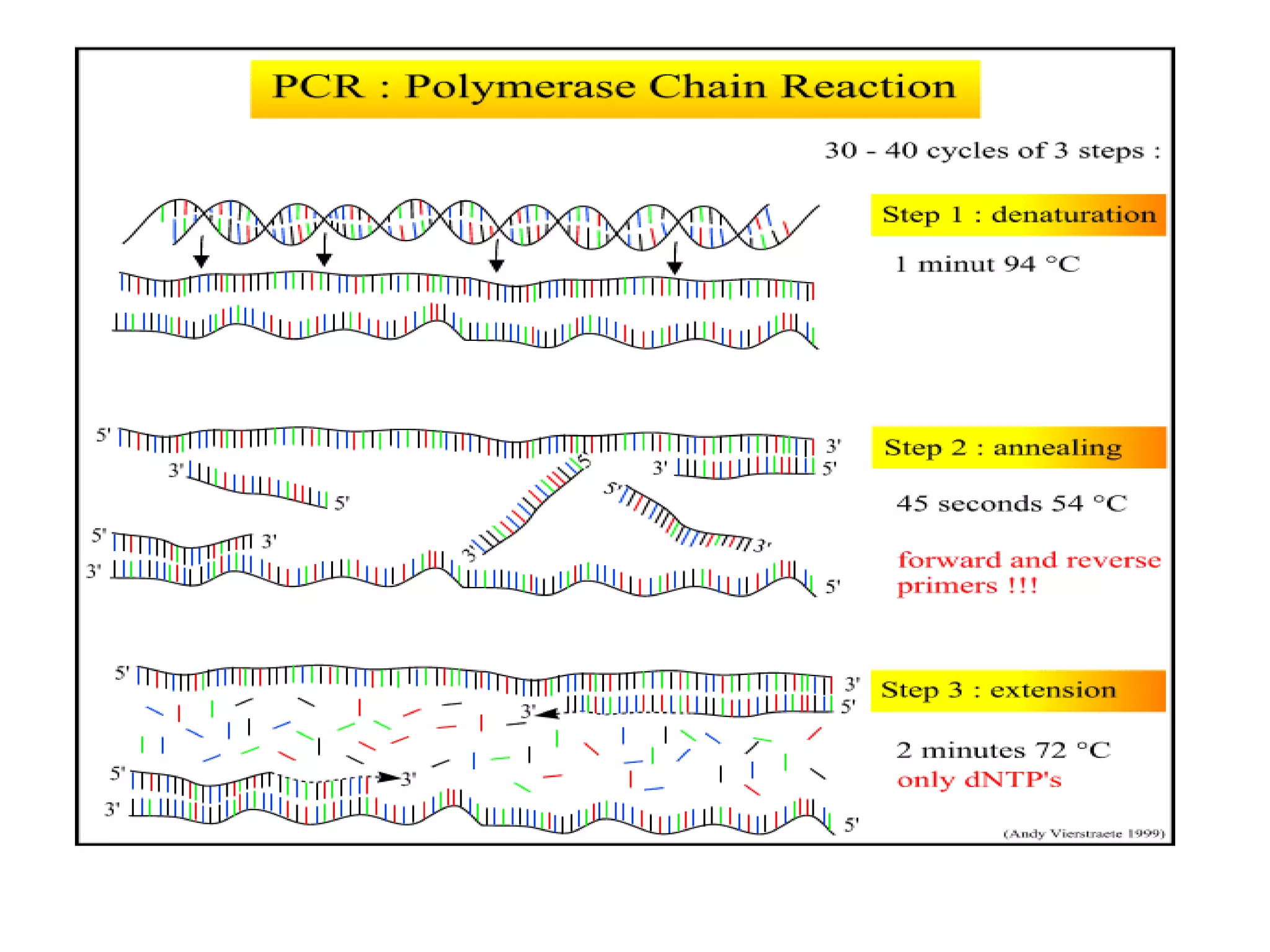
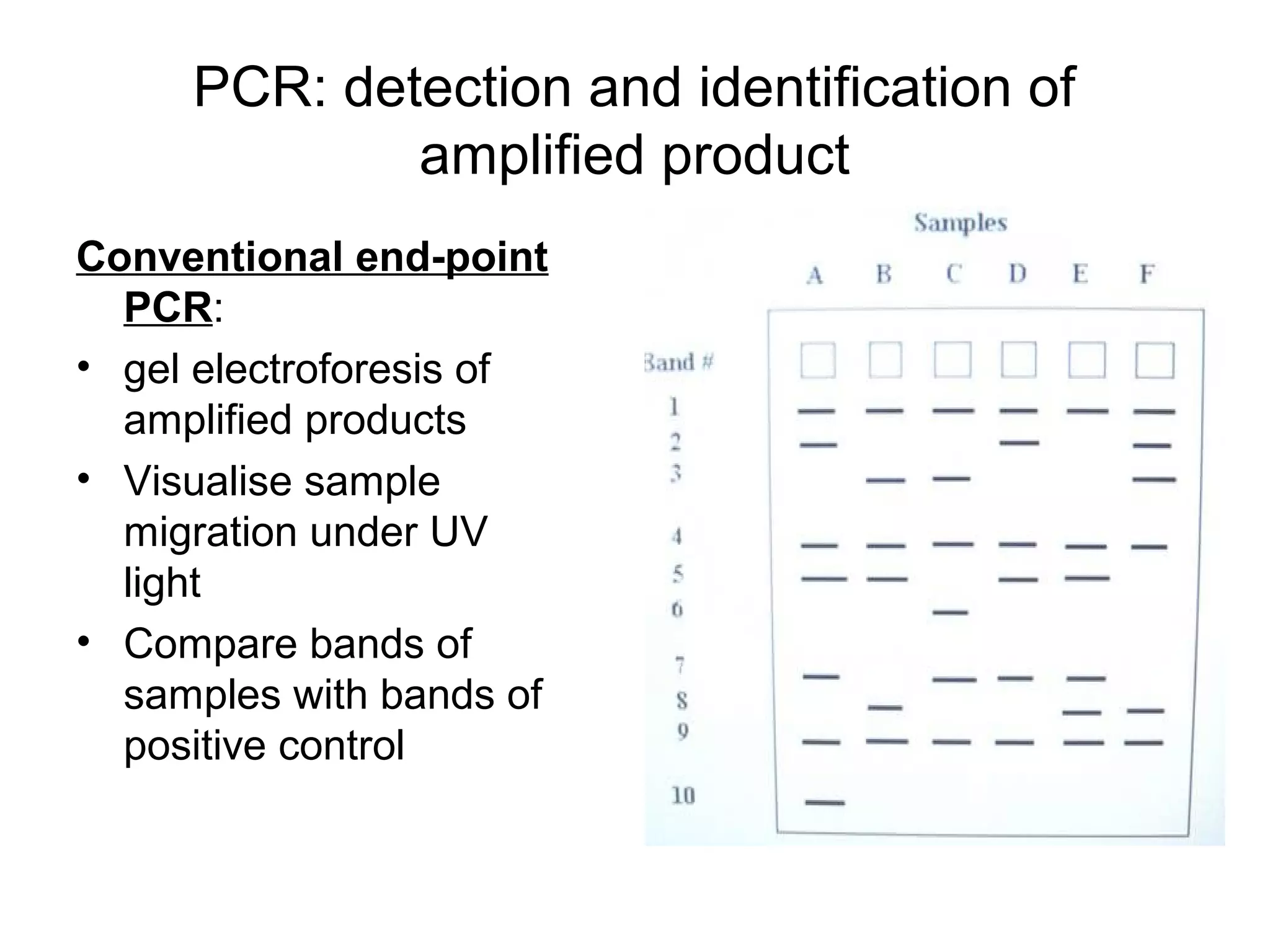
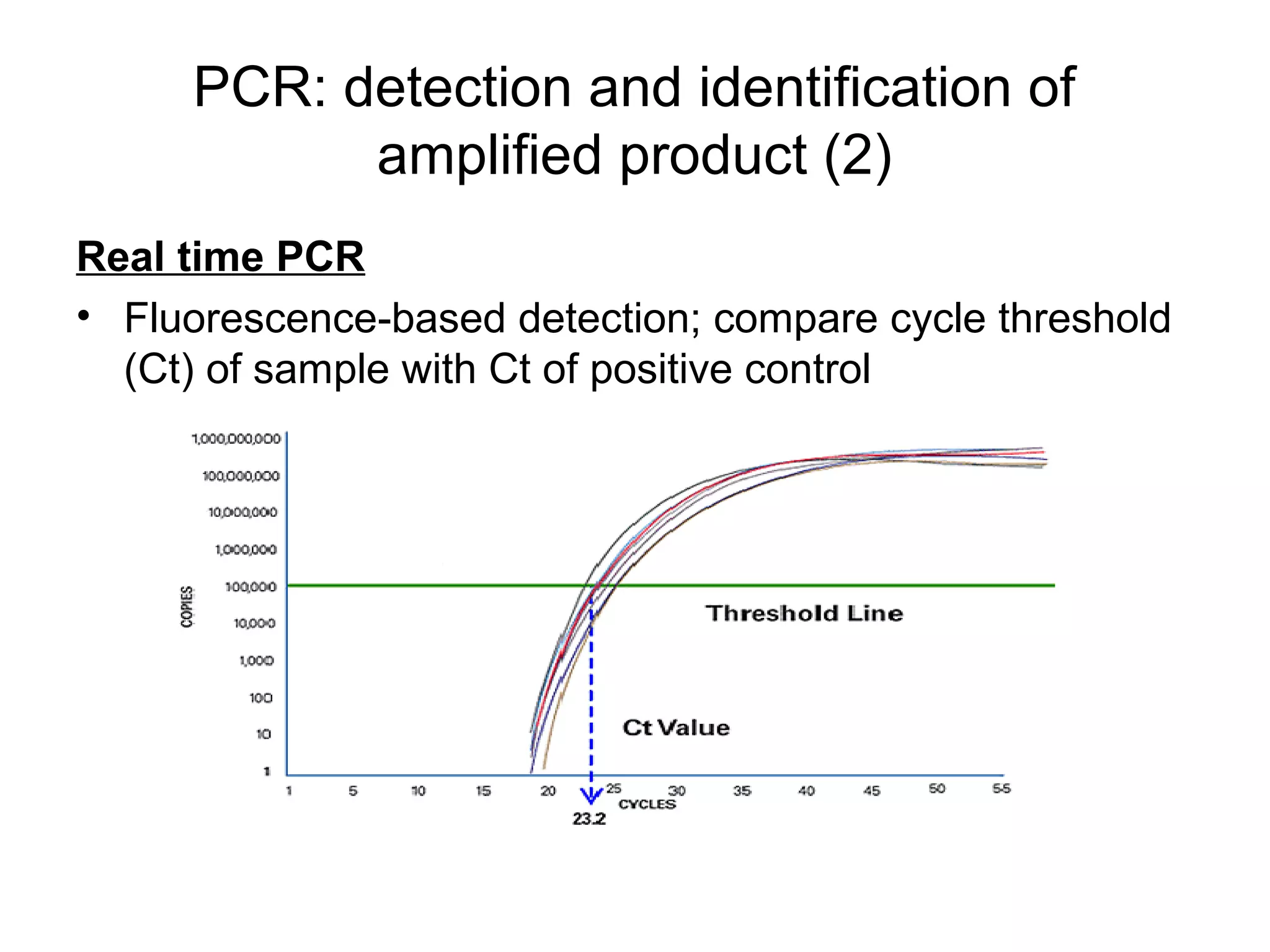
- Laboratory diagnosis methods examine viral particles, detect viral proteins/genetic material, and measure antibody response. Techniques include electron microscopy, cell culture, serology like ELISA, and molecular methods like PCR.