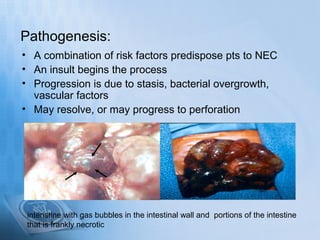
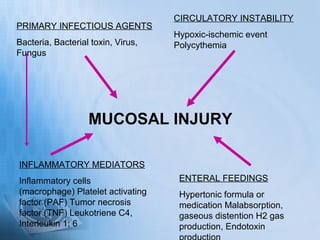
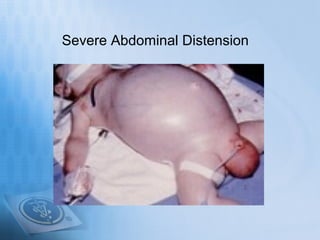
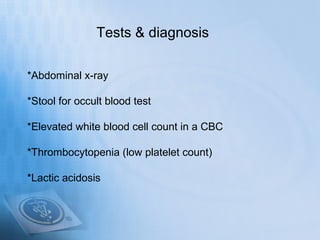
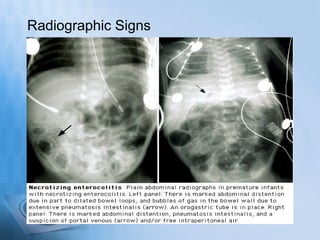
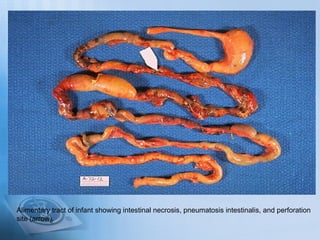
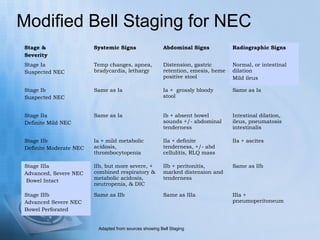
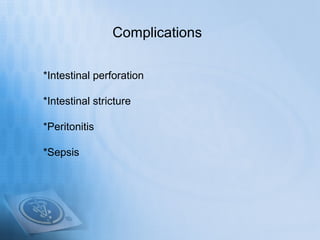
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a serious gastrointestinal condition affecting predominantly premature infants, characterized by inflammation and death of intestinal tissue. Key risk factors include prematurity, low birth weight, and enteral feeding with formula, while symptoms may include abdominal distention, blood in stool, and feeding intolerance. Treatment involves stopping feedings, intravenous fluids, antibiotics, and possibly surgery if complications arise, with a prognosis that depends on the severity of the condition.