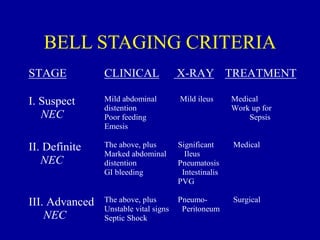
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a leading cause of emergency surgery in neonates, most commonly affecting very low birthweight preterm infants. It involves inflammation and necrosis of the bowels. Risk factors include prematurity, enteral feedings, and circulatory instability. Clinically, infants may experience feeding intolerance and abdominal distension. Diagnosis involves abdominal x-rays showing signs like pneumatosis intestinalis or portal venous gas. Treatment involves stopping feeds, antibiotics, and possible surgery for severe or perforated cases. Long-term complications can include strictures and short bowel syndrome.