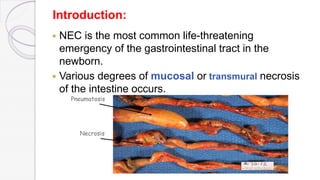
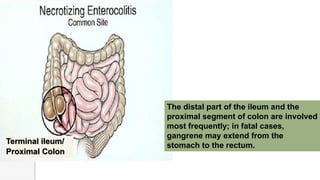
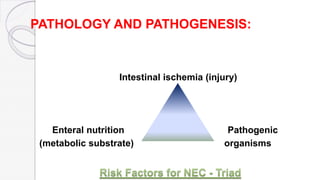
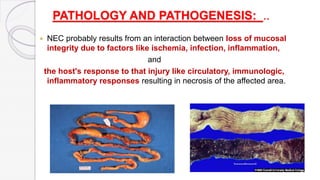
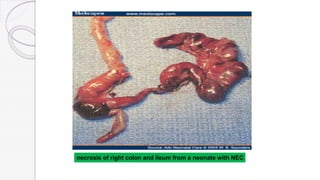
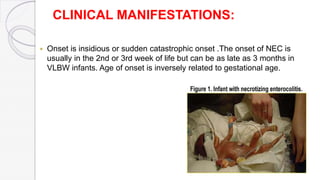
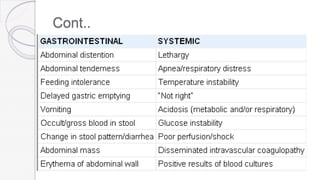
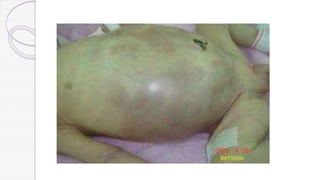
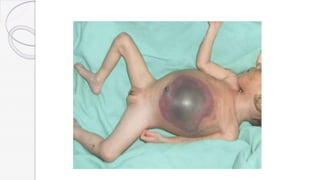
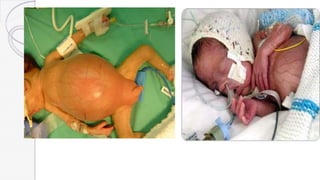
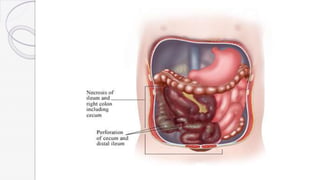
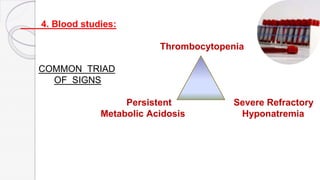
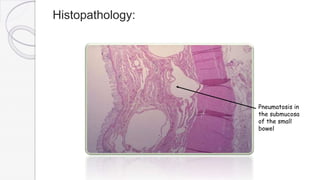
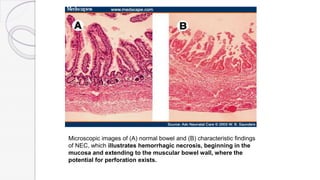
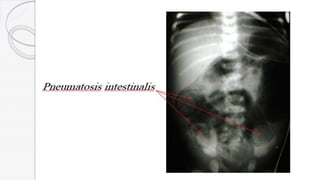
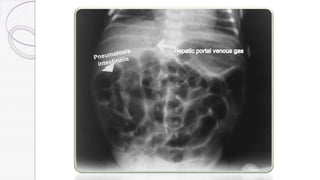
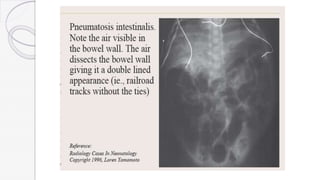
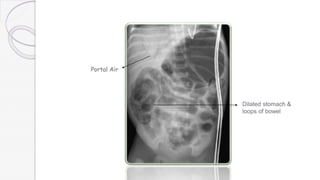
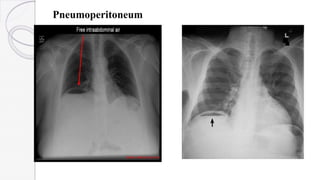
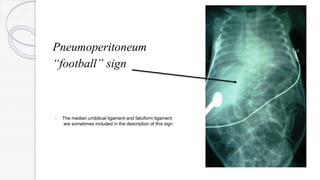
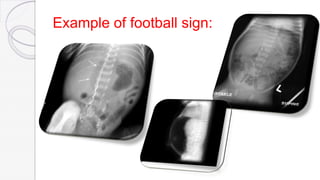
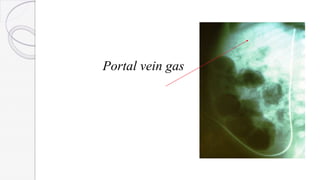
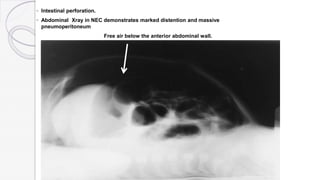
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a life-threatening condition that affects the intestines of premature infants. It results from necrosis of the intestinal tissue and can range from mild to severe. Risk factors include prematurity, formula feeding, and bacterial or viral infections. Symptoms may include abdominal distension, bloody stools, and temperature instability. Diagnosis involves x-rays showing pneumatosis intestinalis or portal venous gas. Treatment focuses on gut rest, broad-spectrum antibiotics, surgery for perforation or failure to improve, and careful feeding advancement after recovery. Outcomes depend on severity but may include strictures, adhesions, or short bowel syndrome.