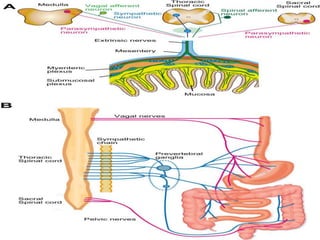
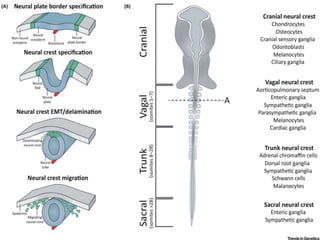
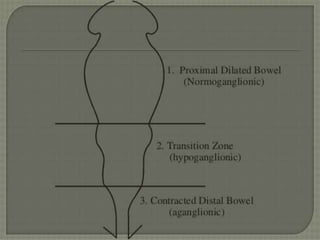
1. Hirschsprung disease is a developmental disorder caused by the absence of ganglion cells in the myenteric and submucosal plexuses of the distal intestine.
2. It presents in neonates as intestinal obstruction due to functional obstruction at the level of aganglionosis.
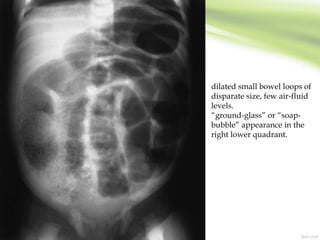
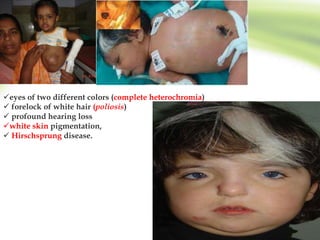
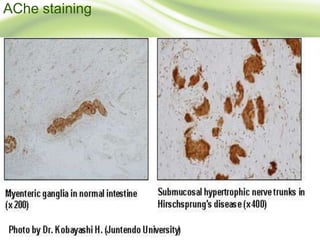
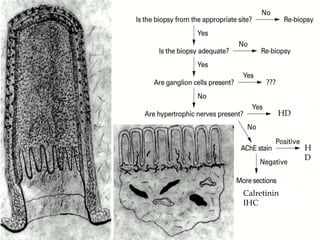
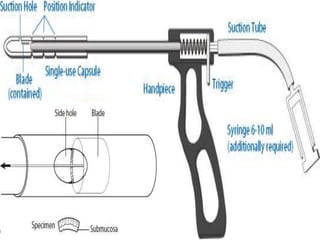
3. Diagnosis involves clinical features like failure to pass meconium, imaging studies to identify transition zone, and rectal biopsy to show absence of ganglion cells.
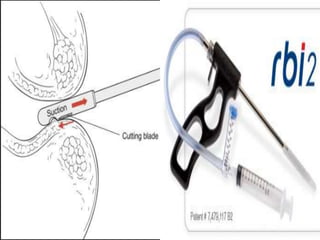
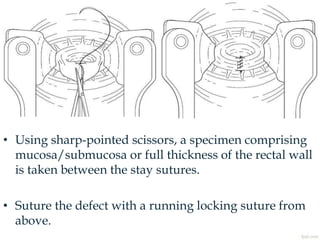
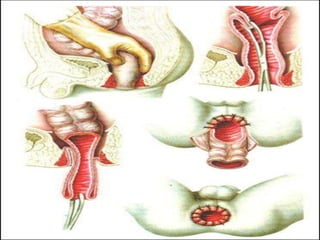
4. Surgical treatment involves pull-through procedures like Swenson, Duhamel or Soave to resect aganglionic segment and join normal bowel above.