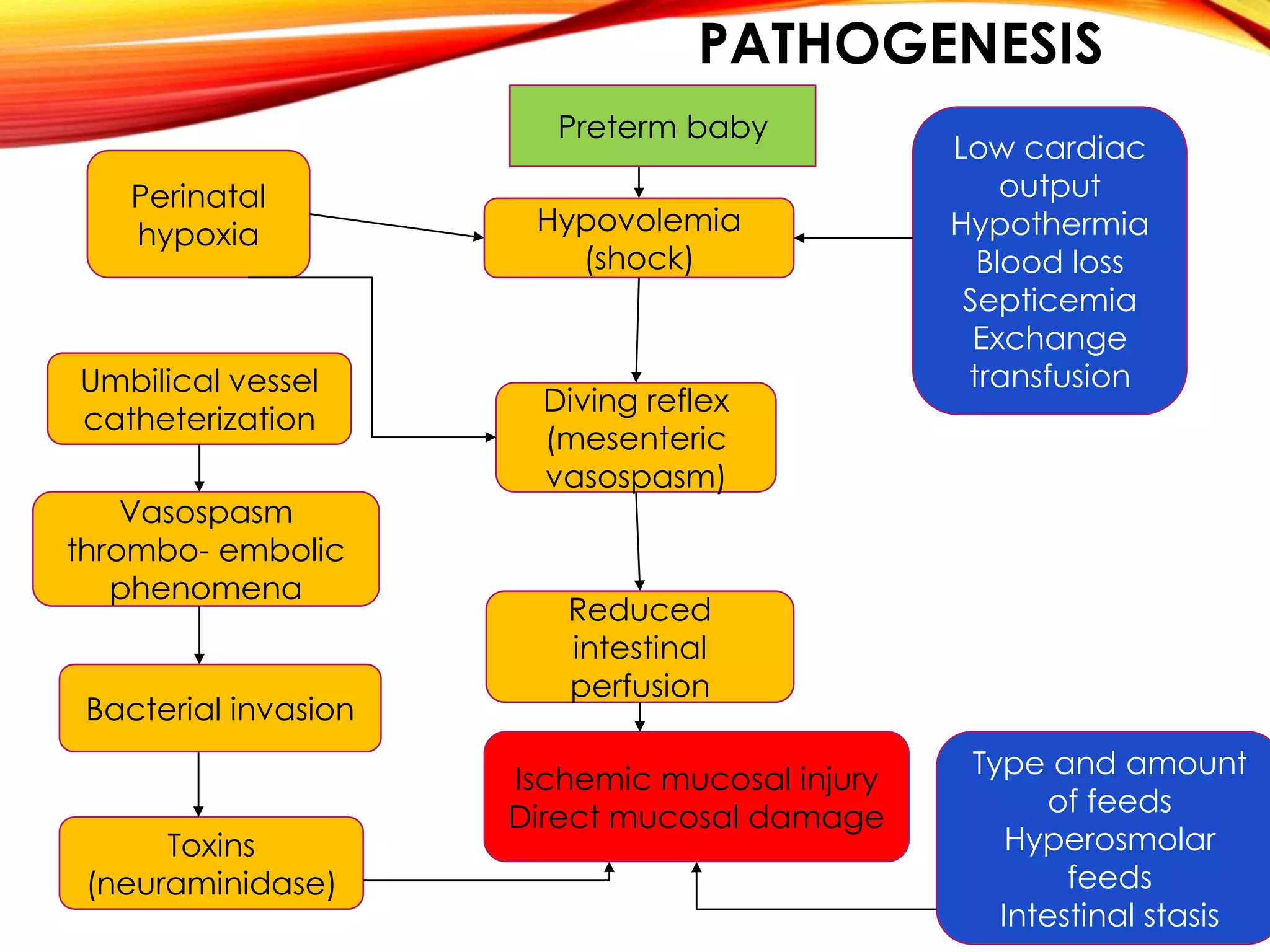
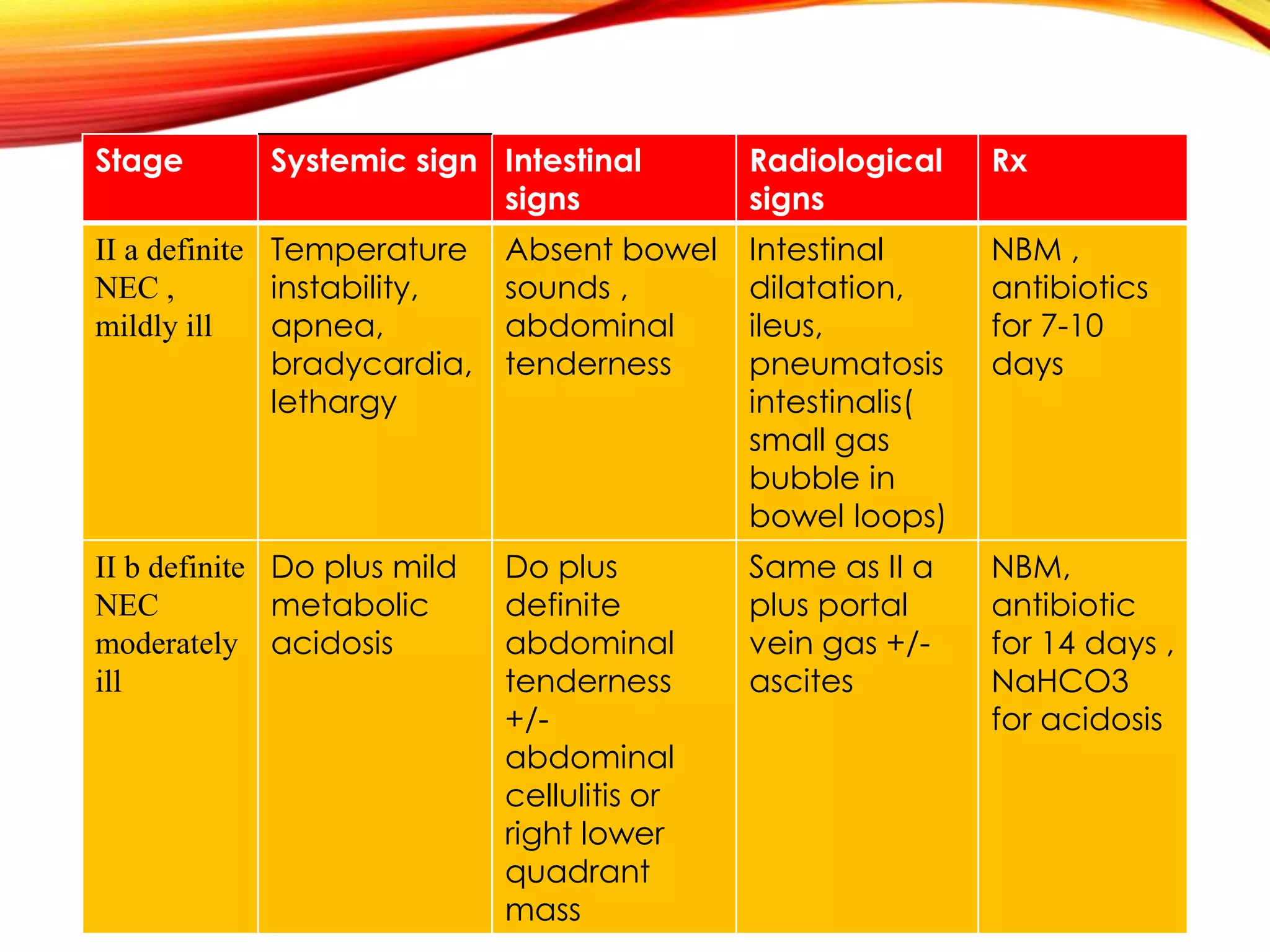
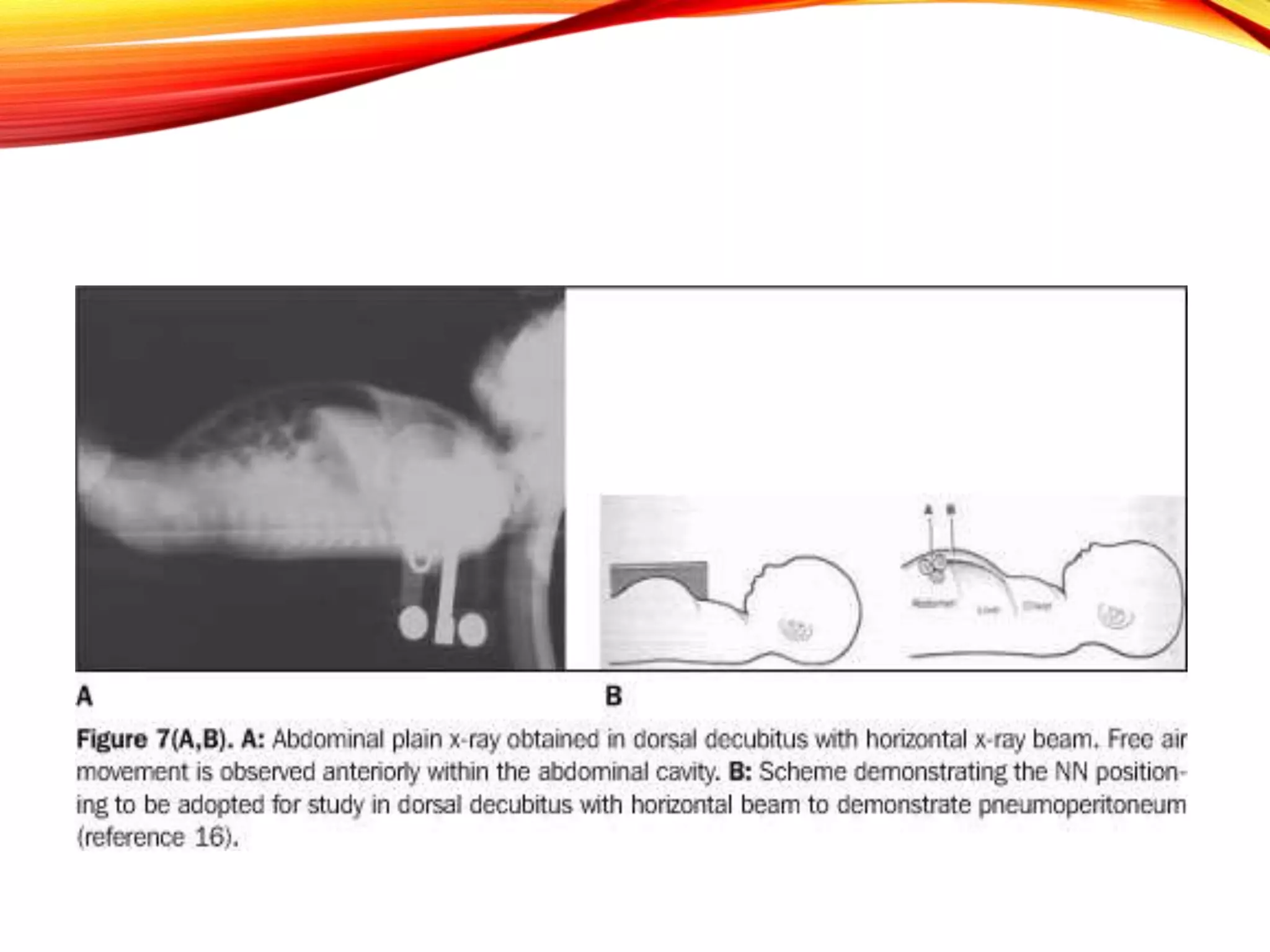
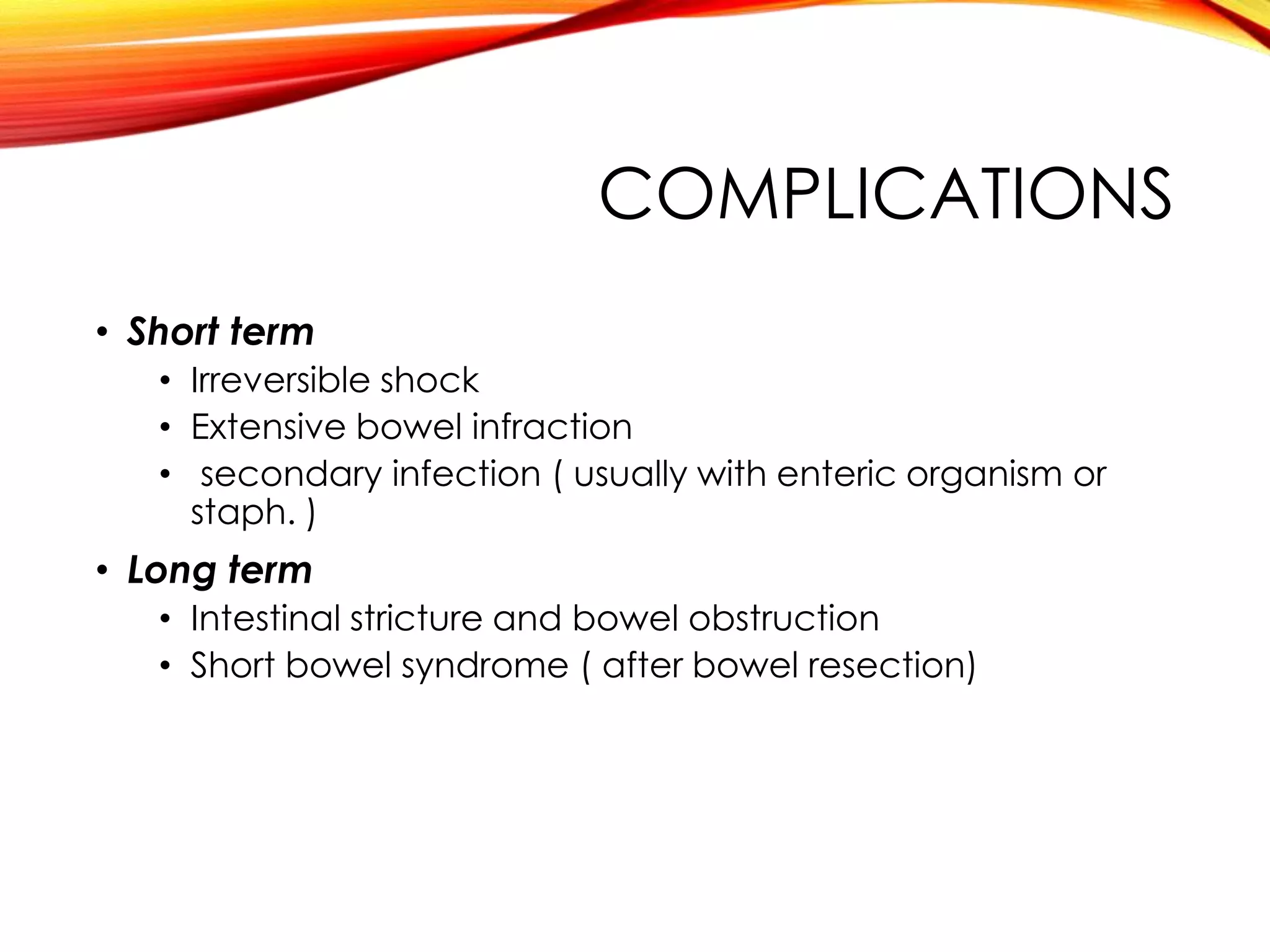
Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a devastating intestinal disease that primarily affects premature infants. It has multifactorial causes related to prematurity including rapid feeding advances, hypoxia, and indomethacin use. Clinically, infants may experience feeding intolerance and signs of sepsis. Diagnosis is supported by abdominal x-ray findings such as pneumatosis intestinalis. Management involves stopping feeds, antibiotics, and surgery for perforated or necrotic bowel. Despite treatment, NEC carries high mortality and morbidity rates, including short bowel syndrome.