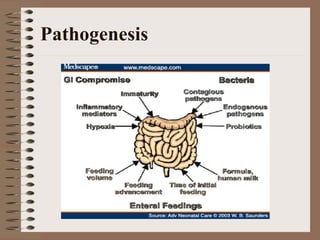
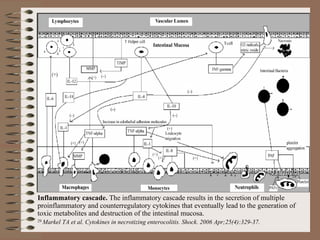
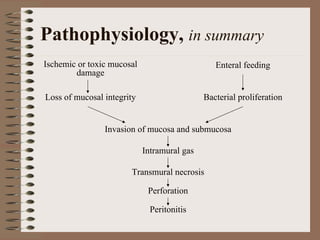
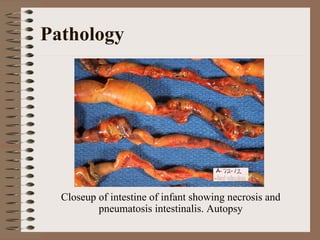
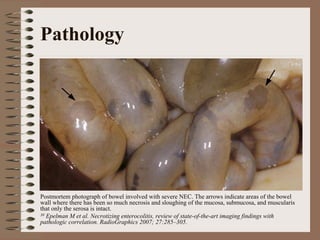
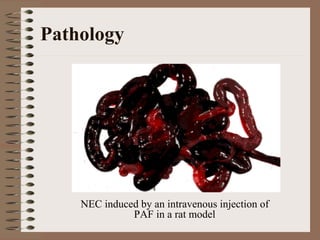
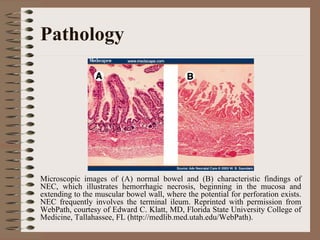
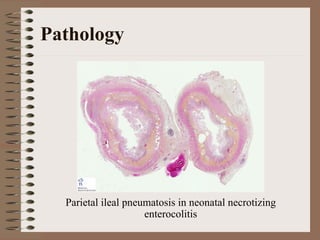
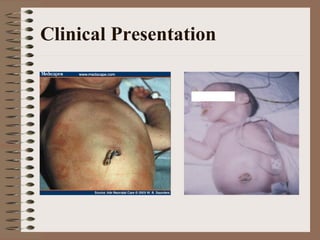
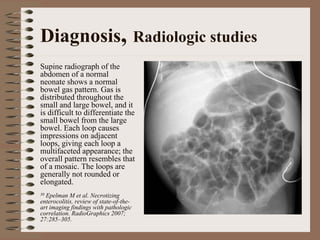
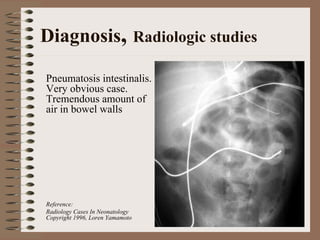
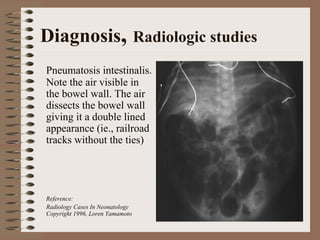
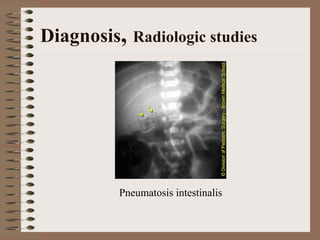
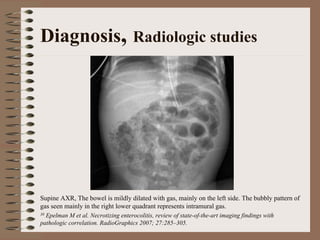
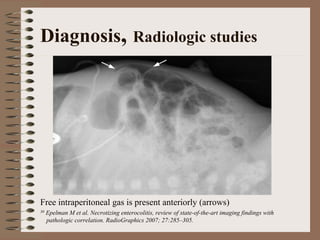
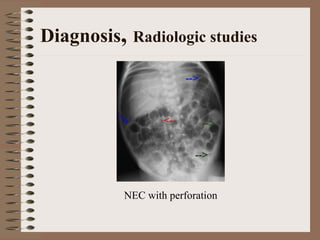
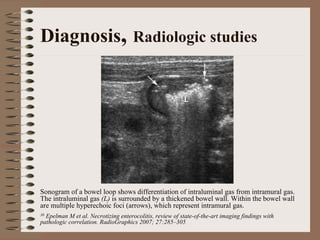
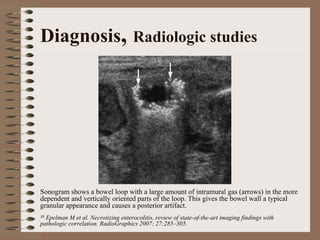
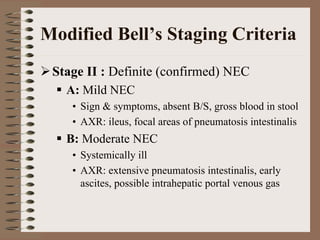
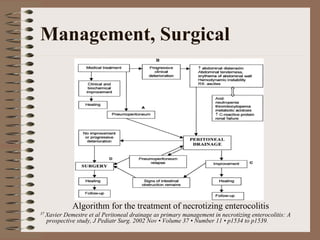
Necrotizing enterocolitis is an acquired intestinal disease of unknown etiology that commonly affects premature infants. The main risk factors are prematurity, genetic factors, maternal health conditions like cocaine use, medications like indomethacin and dexamethasone, and certain enteral feeding practices. The pathogenesis involves an initial hypoxic-ischemic insult to the intestine combined with microbial factors and an excessive inflammatory response that can lead to necrosis of the intestinal tissue. Timely diagnosis and management are important for improving outcomes.