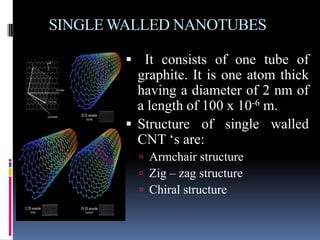
This document discusses nanotechnology and carbon nanotubes (CNTs). It defines nanotechnology as working at the nanoscale of 1-100 nm. CNTs are allotropes of carbon that are cylindrical in shape with a diameter of 2 nm or less. There are two main types of CNTs - single-walled CNTs which are one atom thick, and multi-walled CNTs which contain multiple graphite layers. CNTs are manufactured using methods like pyrolysis, laser evaporation, and chemical vapor deposition. They have excellent mechanical and electrical properties and are being researched for applications in electronics, energy storage, filtration and other areas.