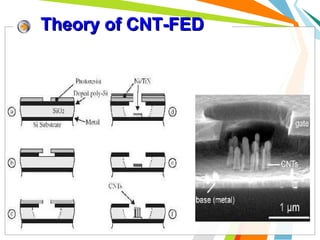
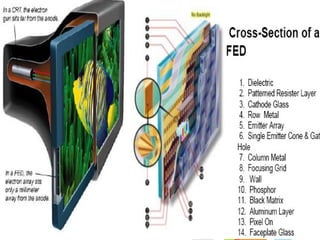
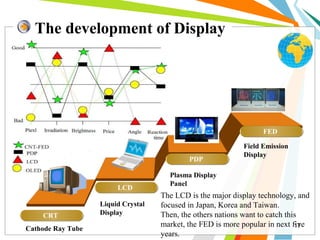
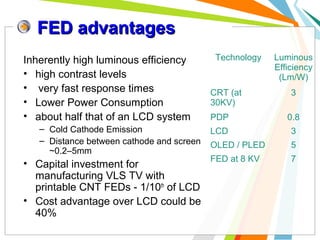
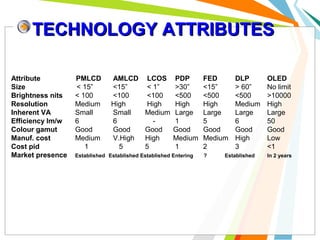
This document discusses the use of carbon nanotubes in field emission displays. It begins with an introduction to carbon nanotubes, explaining their hexagonal structure and strong yet lightweight properties. It then discusses field emission displays and how they work using electron emission from microtips. The document proposes using carbon nanotubes as the electron emitters in field emission displays due to their high aspect ratio and ability to emit electrons at low voltages. The remainder of the document discusses the components and working principles of field emission displays, compares their attributes to other display technologies, and presents images of carbon nanotube field emission displays.