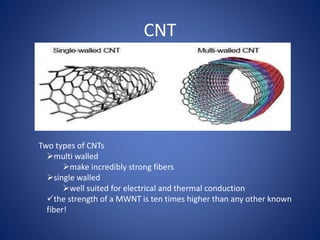
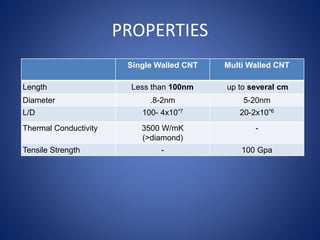
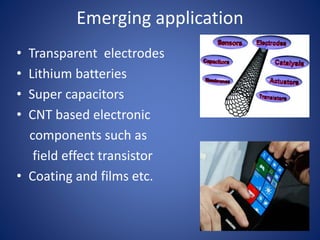
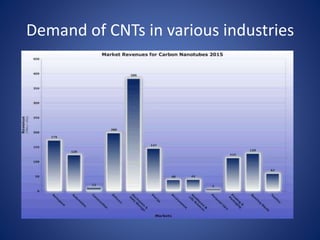
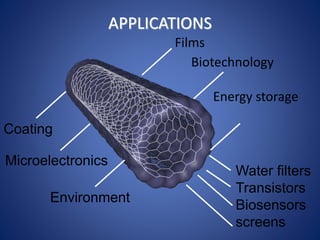
Carbon nanotubes are allotropes of carbon with a cylindrical structure that can be either single-walled or multi-walled. They have extraordinary properties including being stronger than steel but lighter than aluminum, with excellent thermal and chemical stability and conductive properties. Carbon nanotubes have many potential applications such as in transparent electrodes, lithium batteries, solar cells, and electronics. However, issues around cost and toxicity must still be addressed before their widespread commercial use.