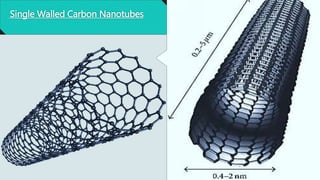
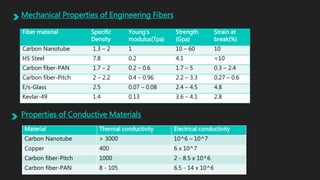
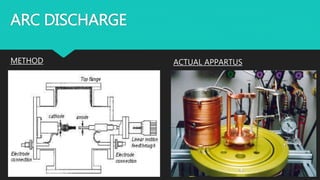
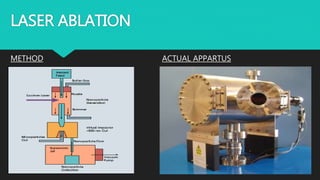
Carbon nanotubes are cylindrical nanostructures made entirely of carbon atoms. They have a length-to-diameter ratio of up to 132,000,000:1. There are two main types: single-walled nanotubes consisting of a single graphene cylinder, and multi-walled nanotubes containing multiple graphene cylinders. Carbon nanotubes were first discovered in the 1970s and were fully characterized in the early 1990s. They exhibit extraordinary strength and electrical conductivity and have a wide variety of potential applications, including in materials science, electronics, optics, and biomedical engineering.