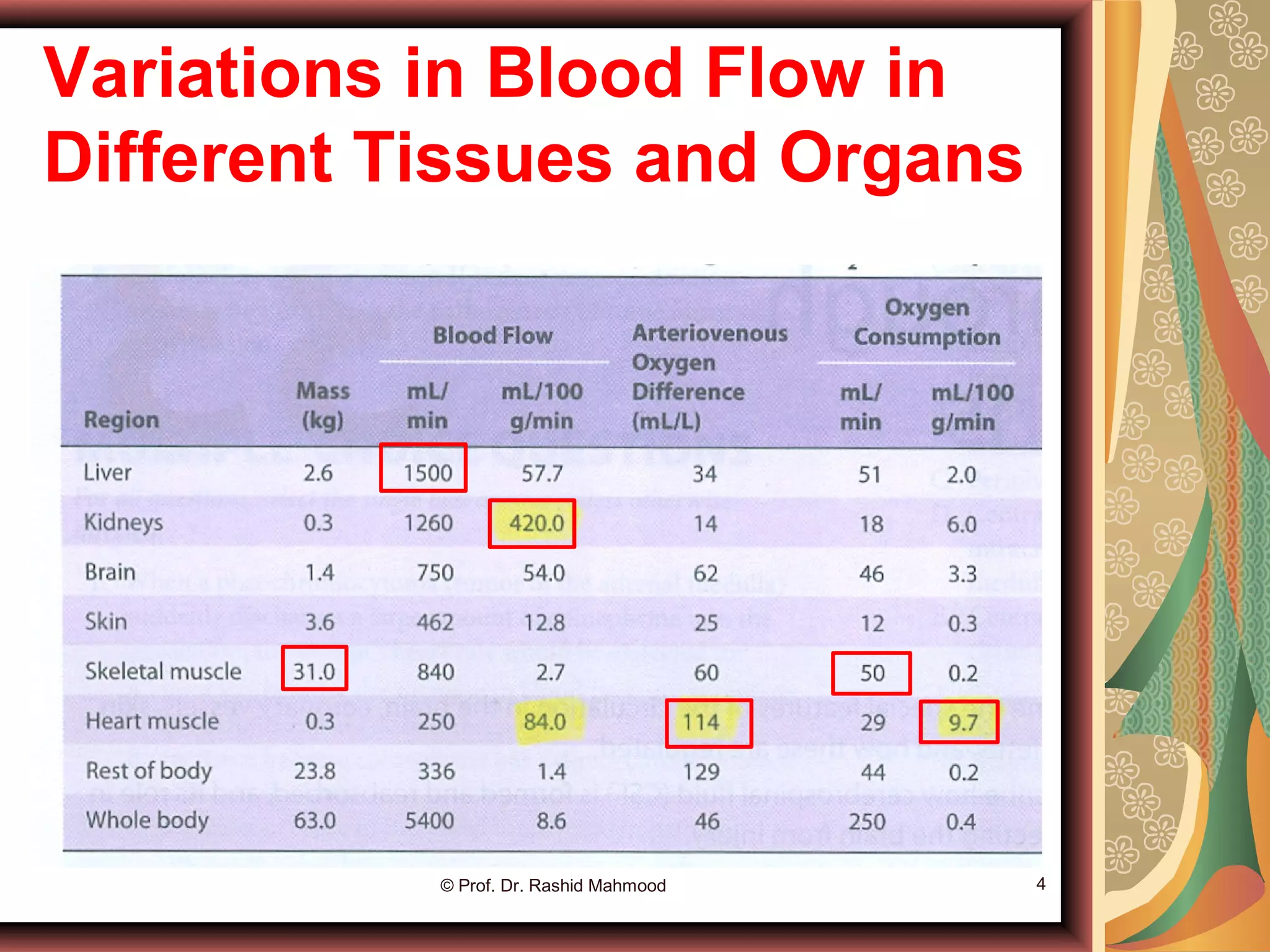
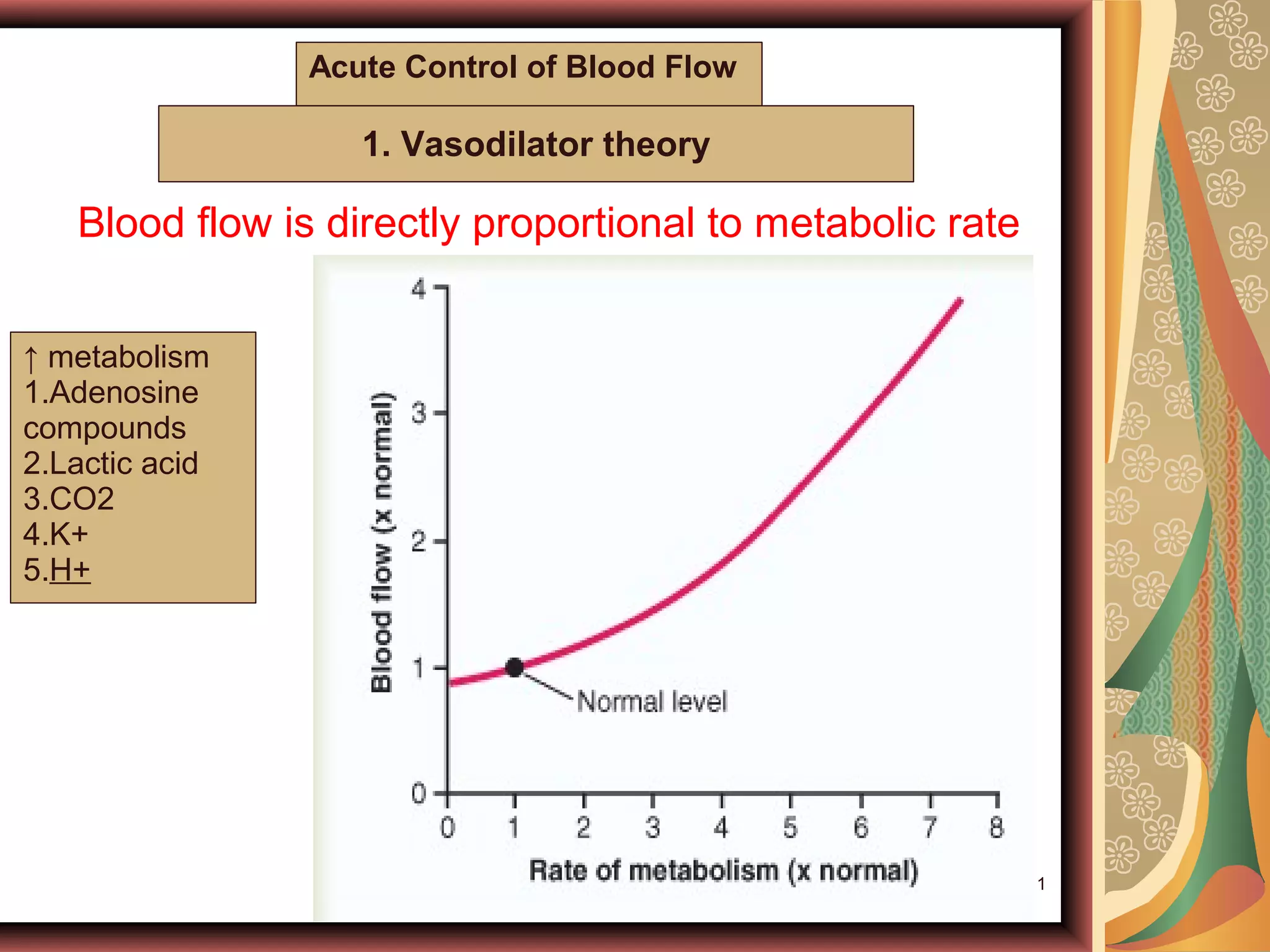
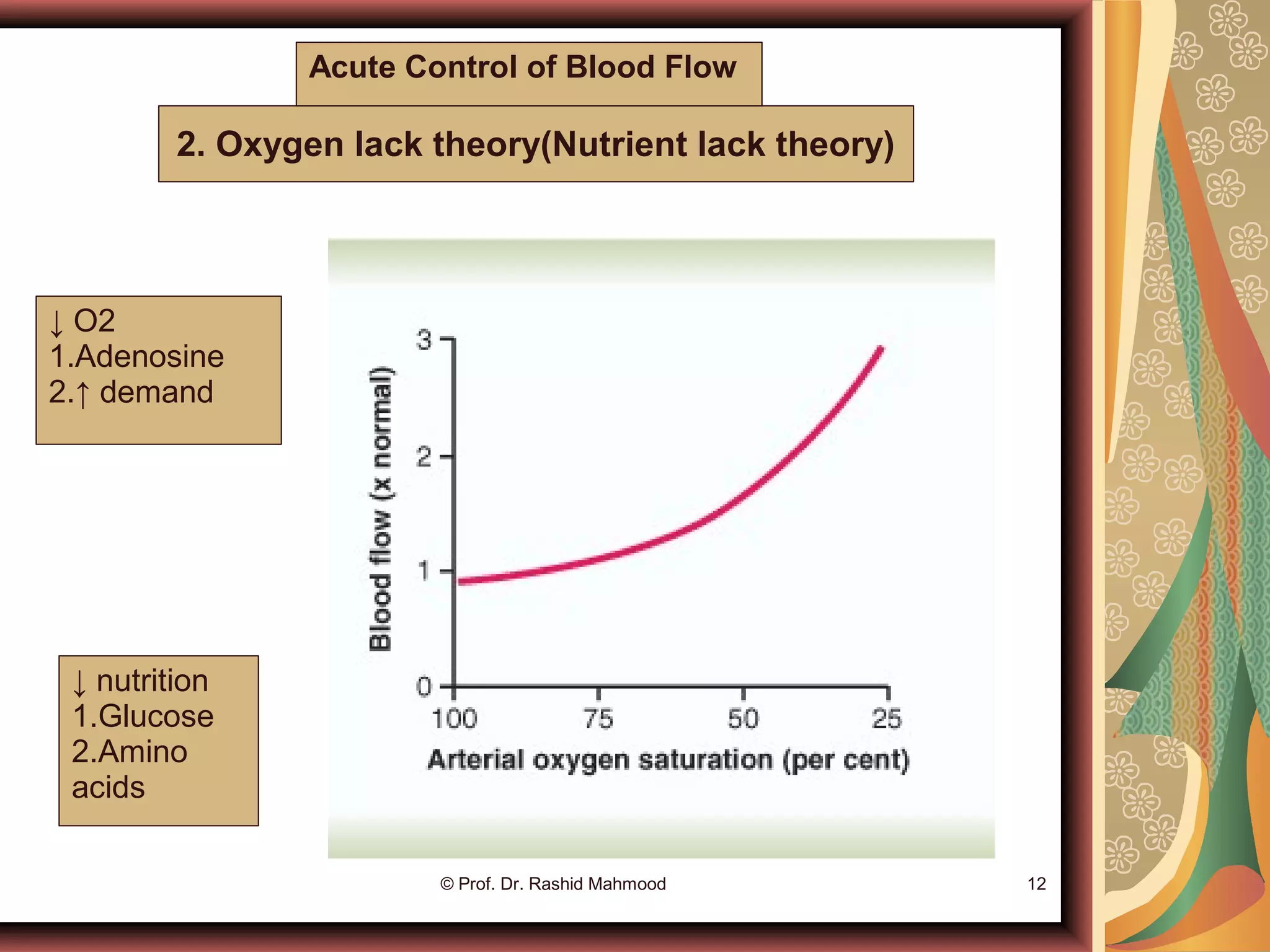
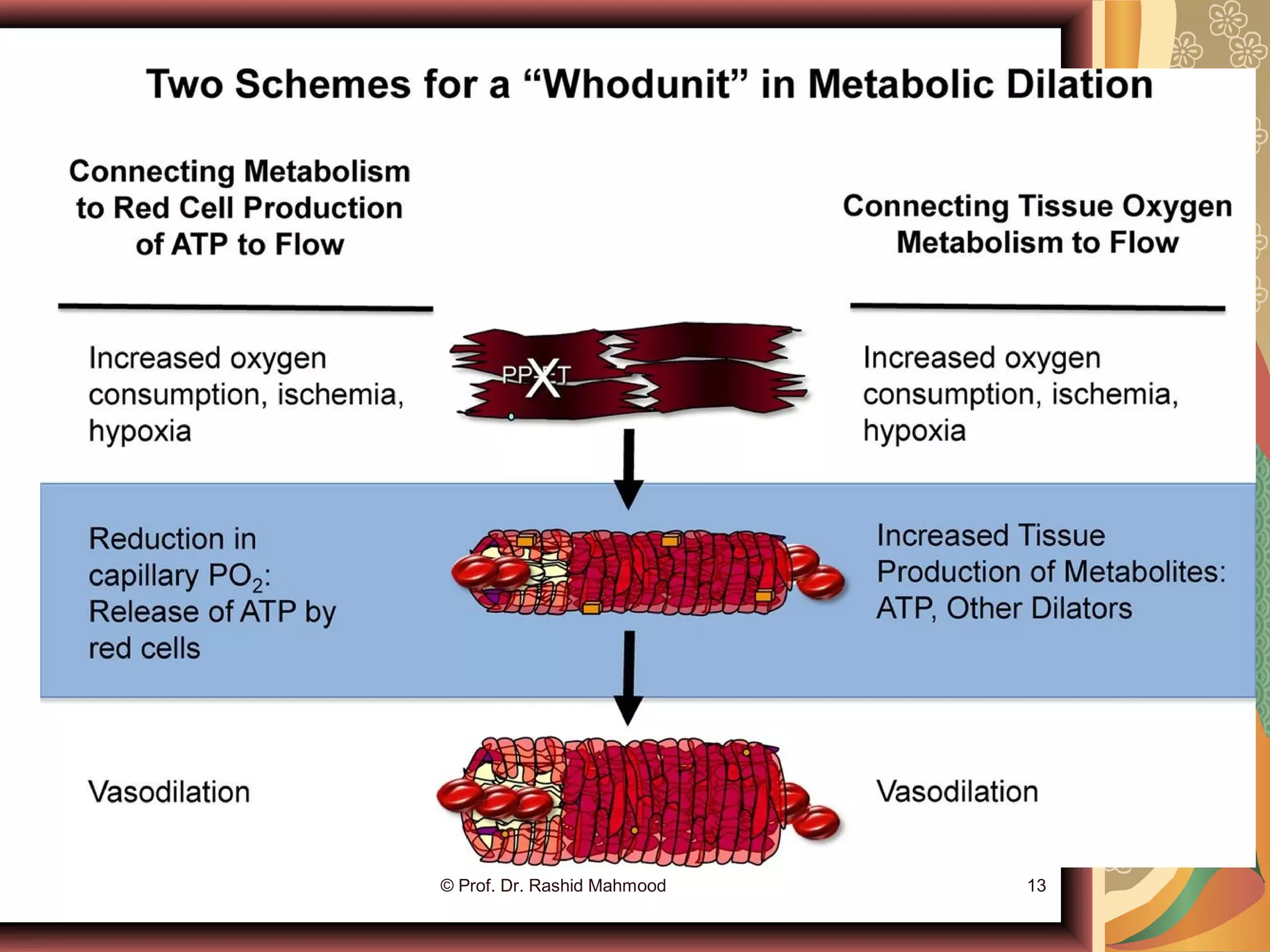
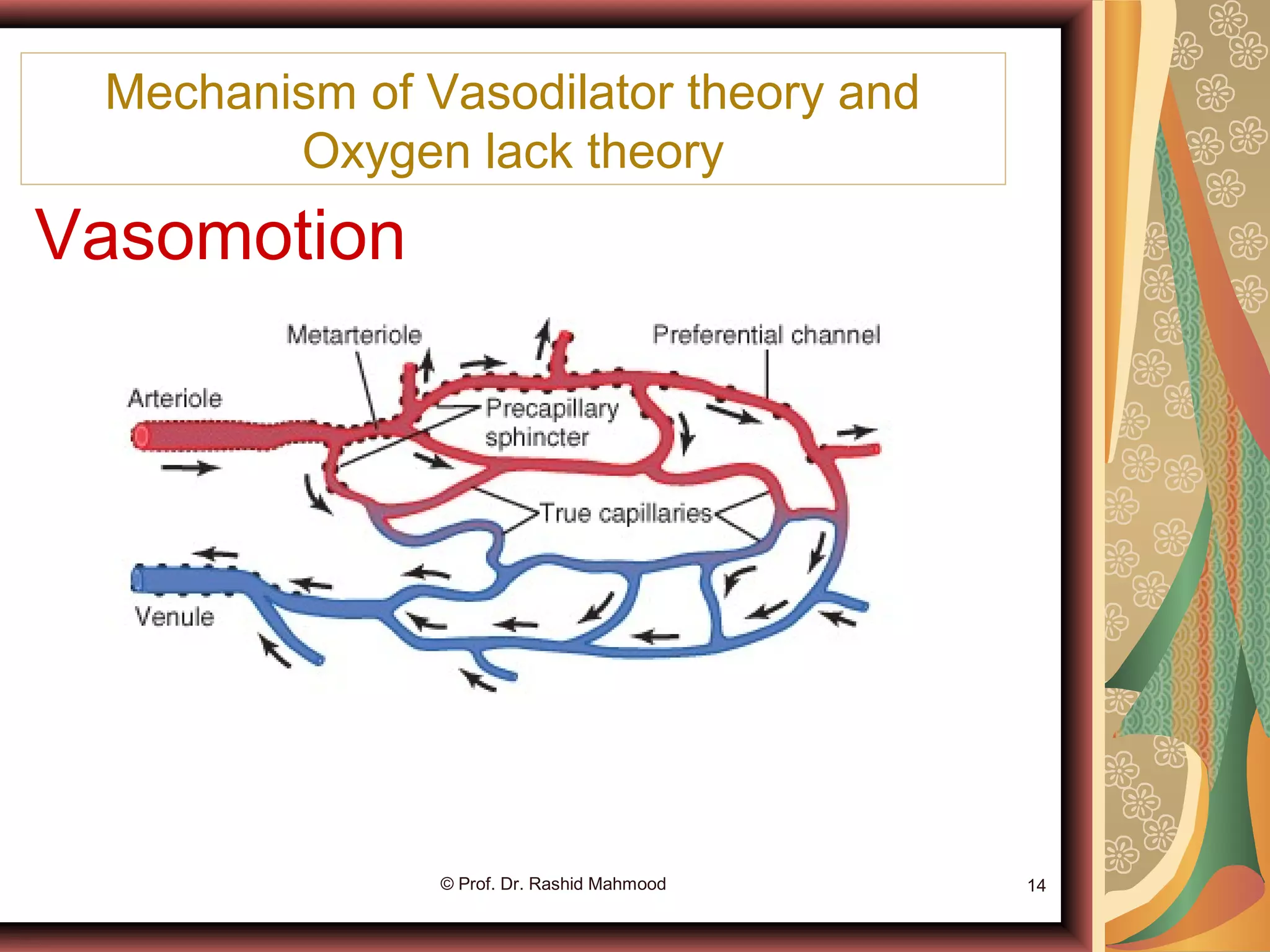
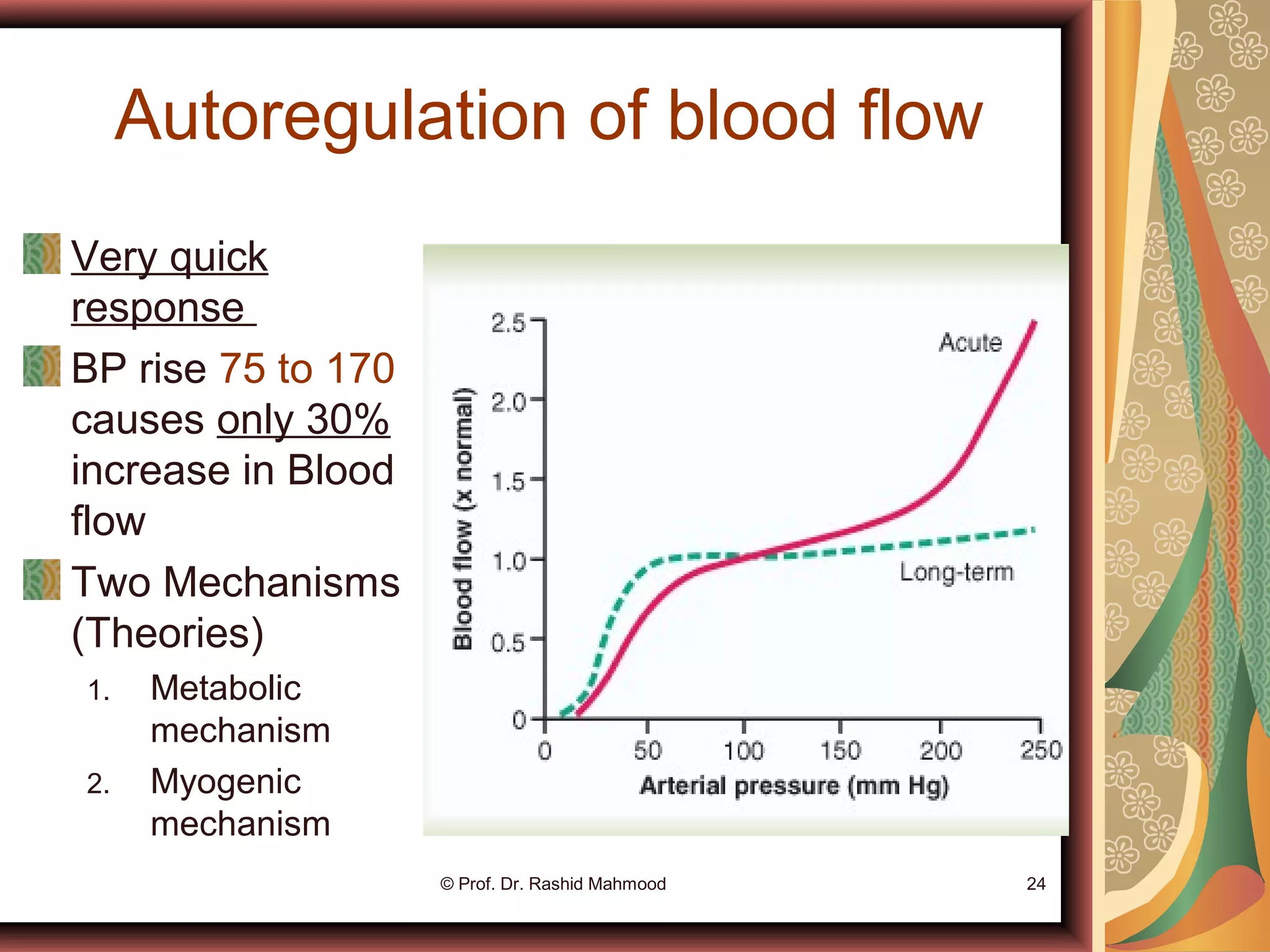
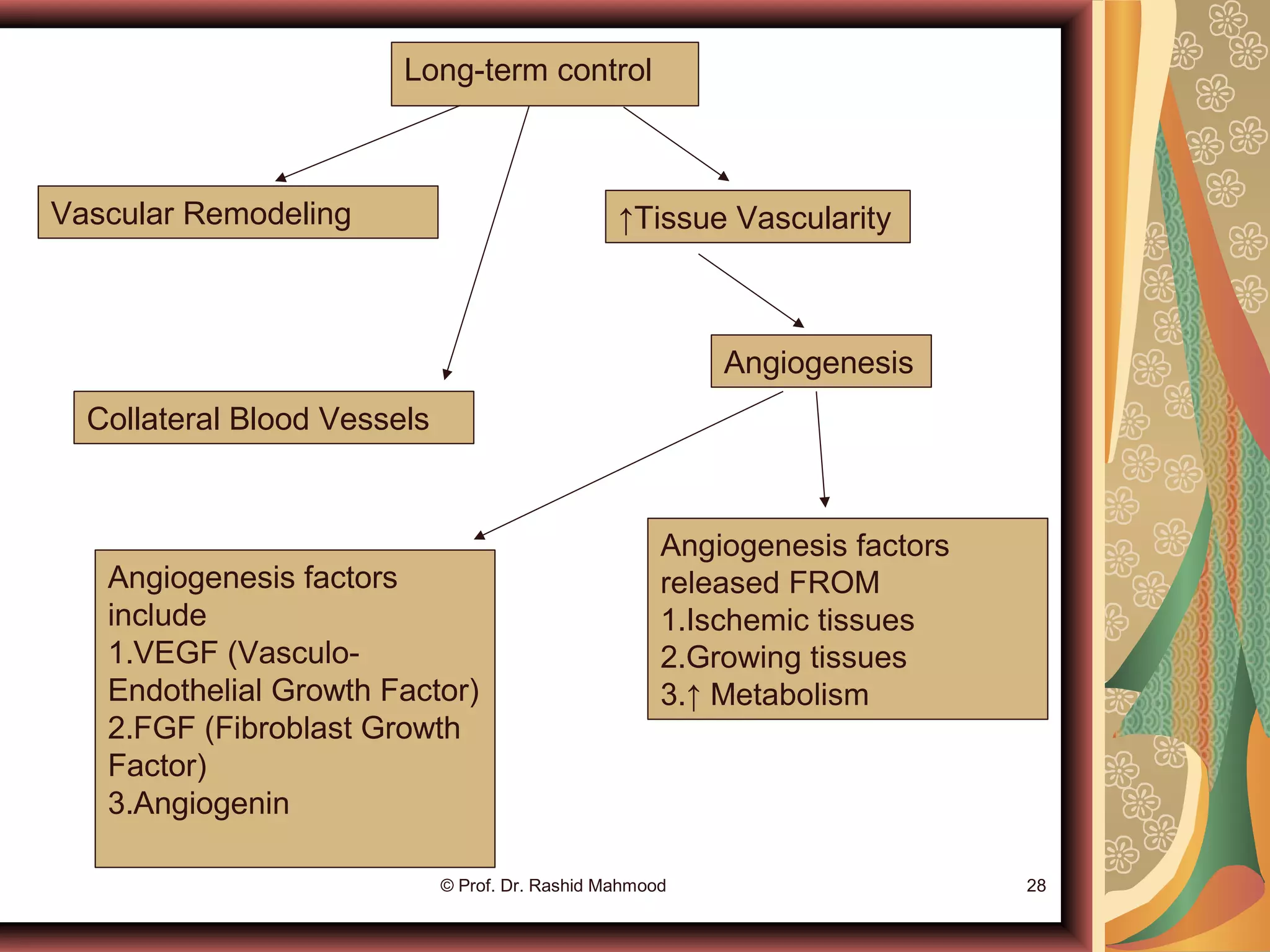
The document discusses local blood flow control. It notes that blood flow to tissues is regulated at the minimal level needed to supply tissue requirements. This ensures tissues do not suffer from oxygen or nutrient deficiencies while minimizing workload on the heart. Blood flow is controlled through local, humoral and nervous mechanisms. Acute control involves vasodilation or vasoconstriction to meet metabolic demands. Long term control involves increasing tissue vascularity or developing collateral blood vessels. Endothelial factors, hormones, ions and neurotransmitters also help regulate local blood flow.