This document summarizes a presentation on the local control of blood flow. It discusses various factors that regulate blood flow both acutely and long-term at the local tissue level. Some key points include:
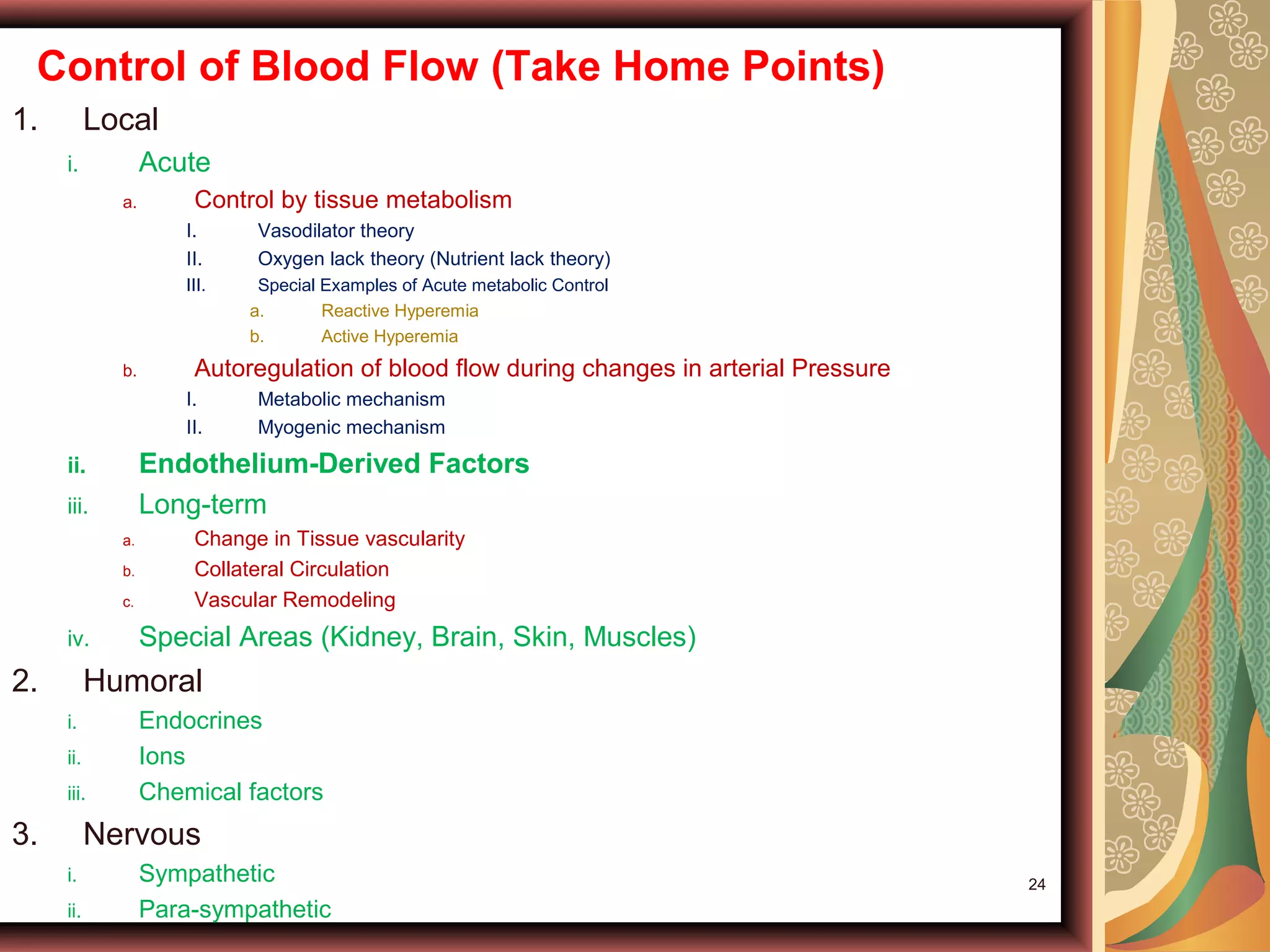
- Blood flow is regulated by local, humoral and nervous mechanisms. Multiple factors like metabolites, ions, hormones, and endothelium-derived factors control blood flow.
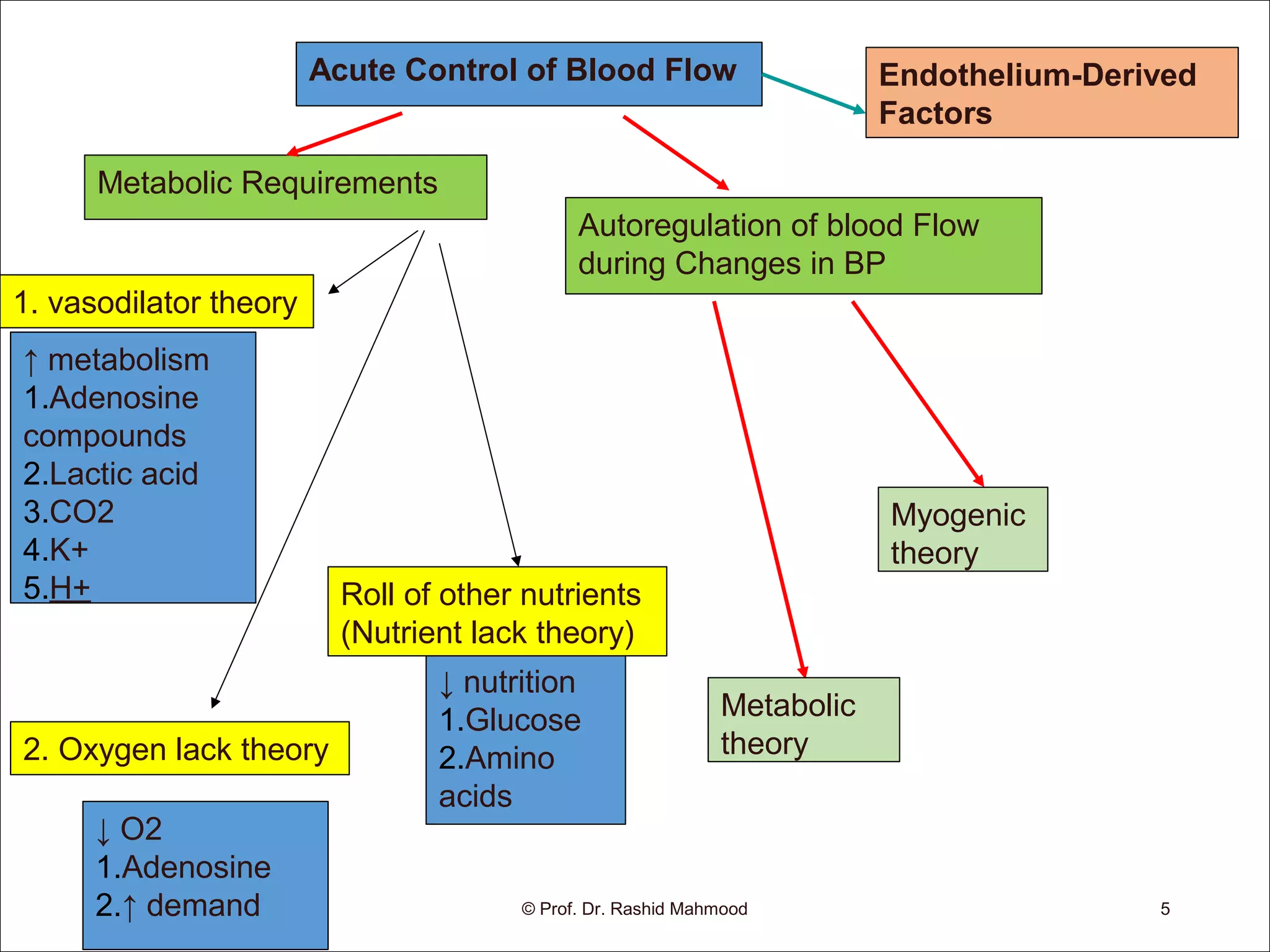
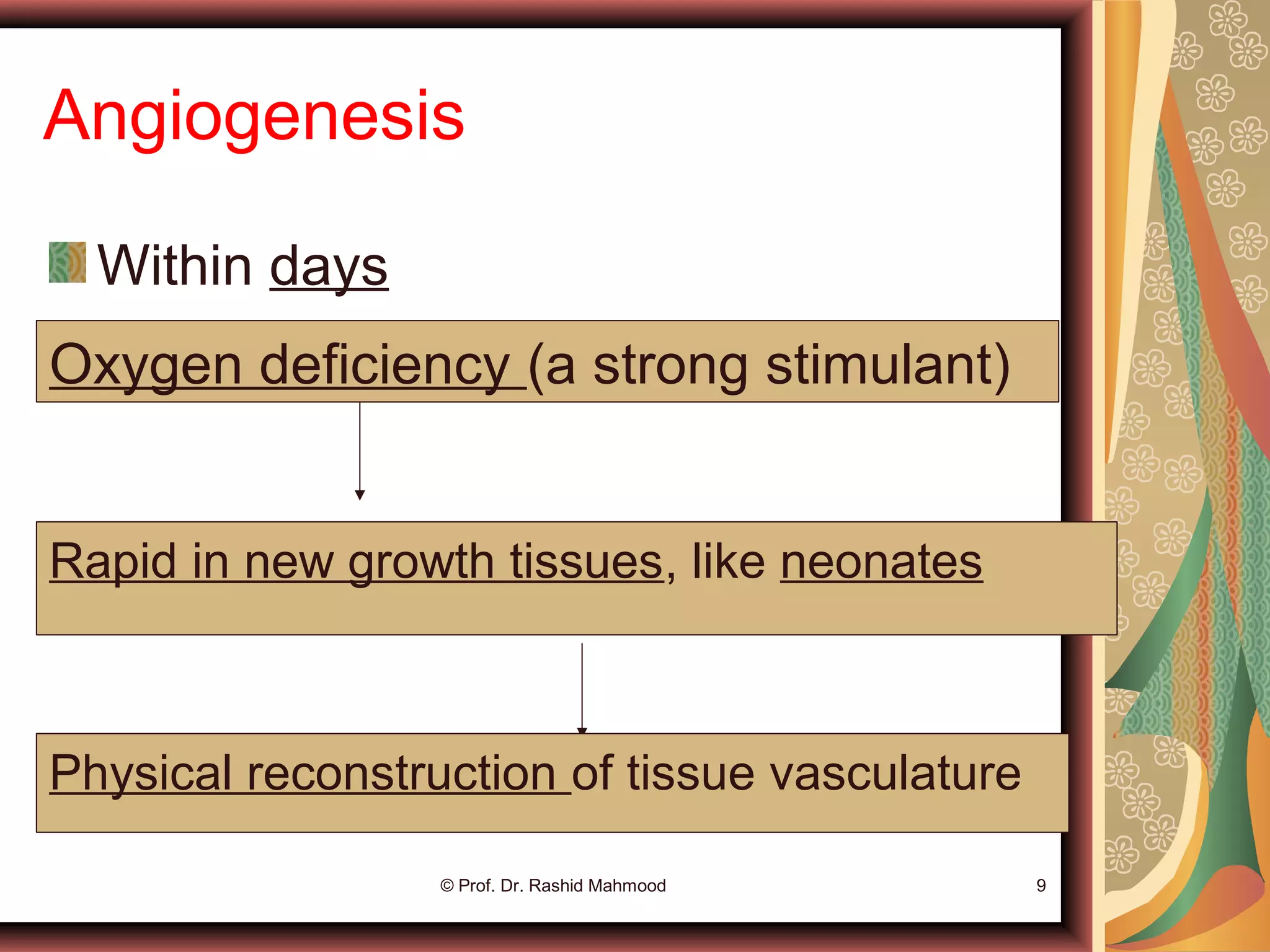
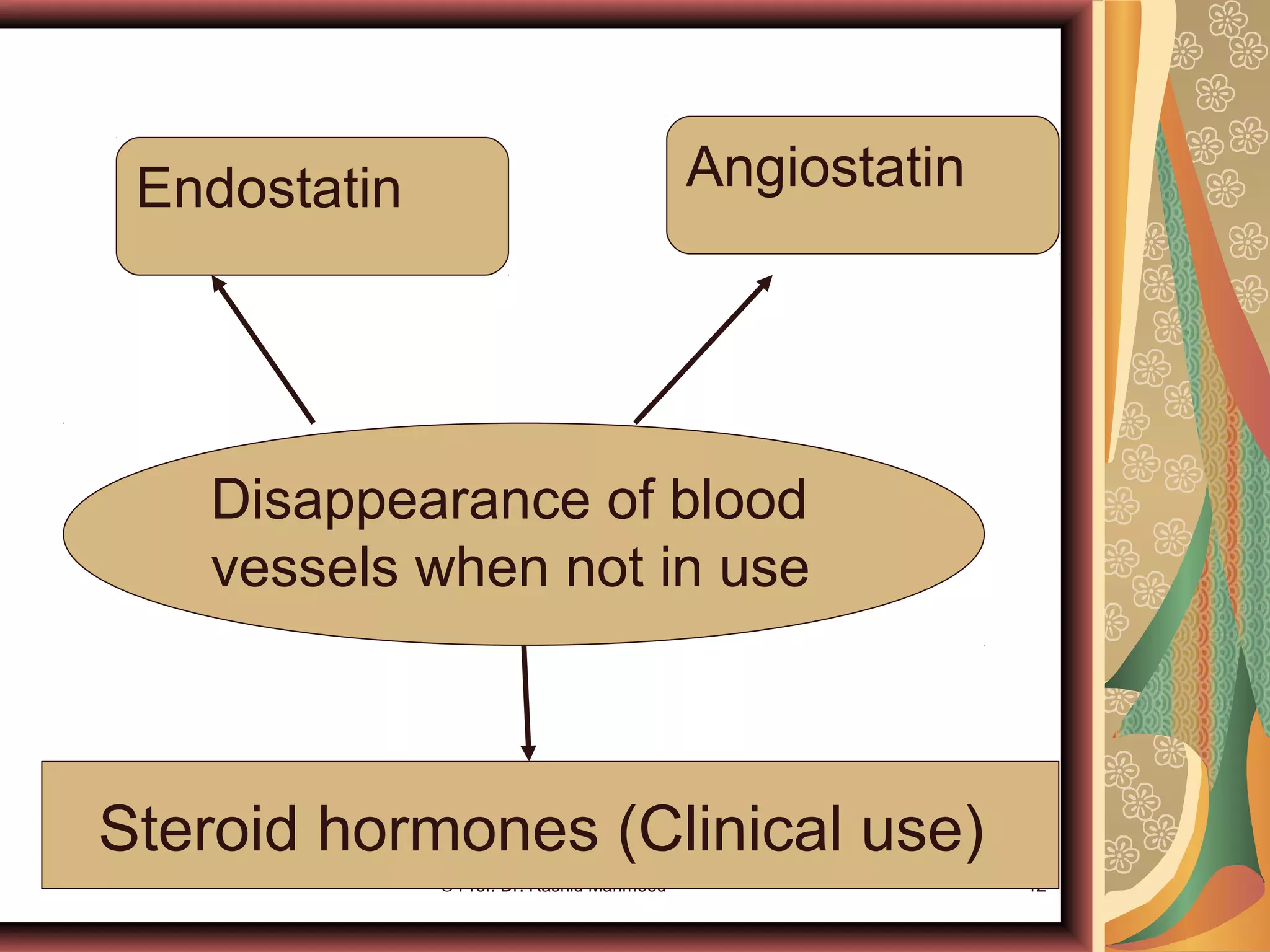
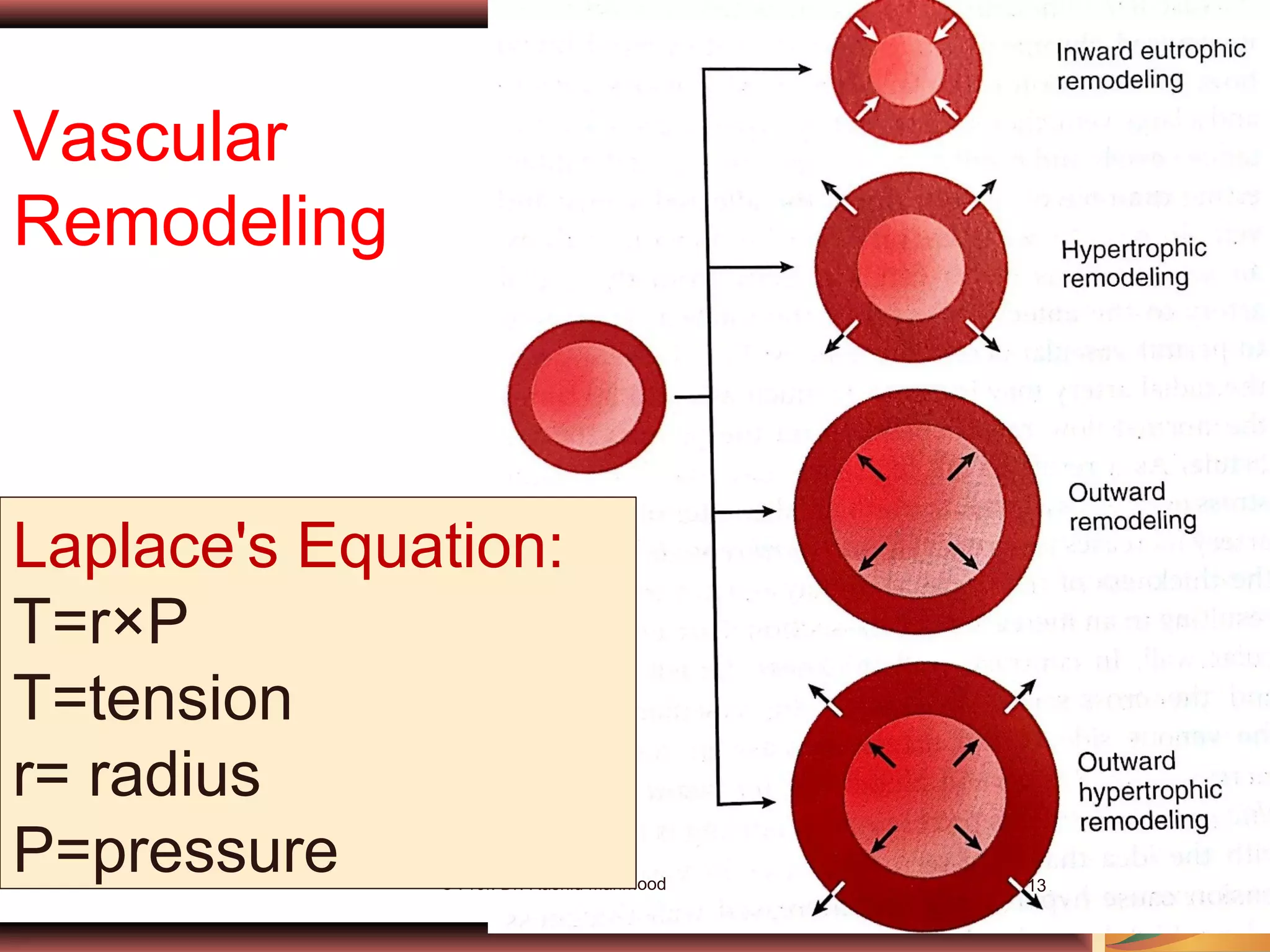
- Acute control is mediated by changes in local tissue metabolism, oxygen levels, and nutrients. Long-term control involves changing vascularity and the growth of new blood vessels (angiogenesis).
- Specific organs like the kidney, brain, skin and muscles have special blood flow control needs. Humoral control involves hormones from endocrine glands