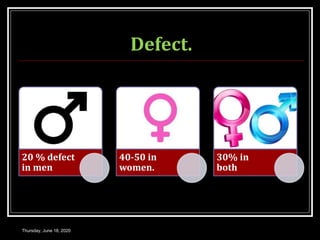
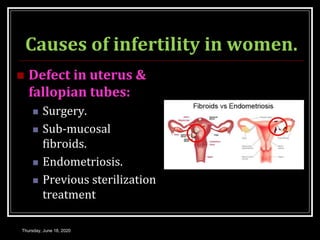
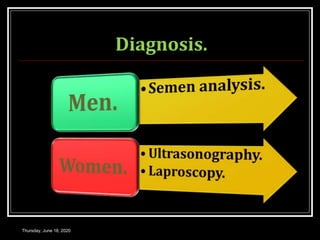
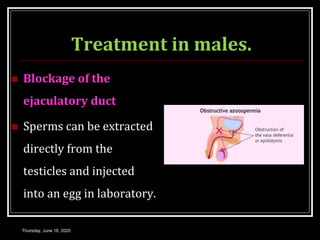
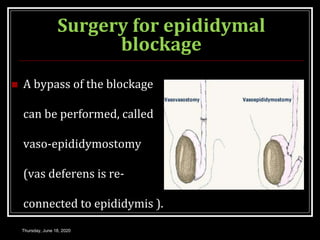
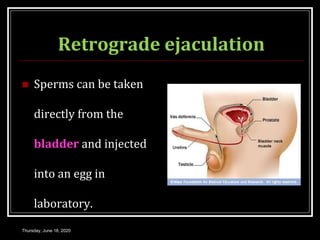
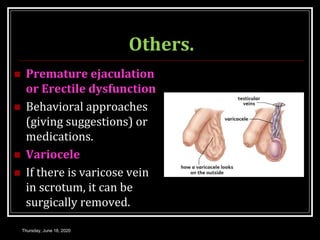
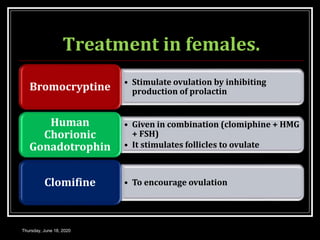
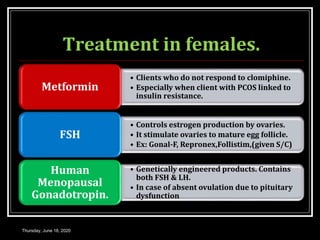
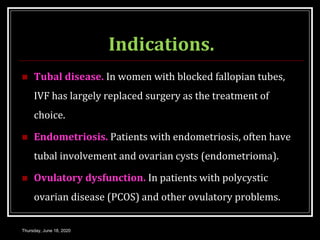
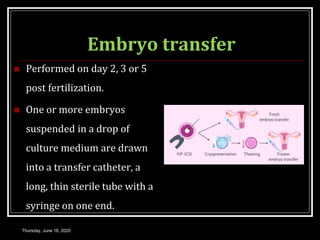
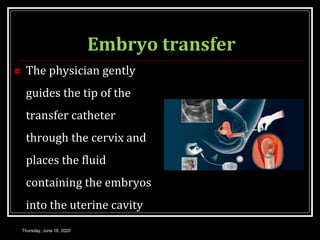
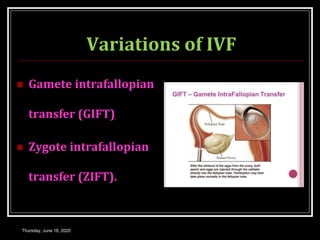
This document provides information about infertility and IVF. It begins with definitions of infertility and discusses causes of infertility in both men and women. It then describes the diagnosis process and various treatment options for infertility, including counseling, medications to stimulate ovulation, and assisted reproduction techniques like IUI, IVF, and ICSI. The document explains the IVF process in detail, from initial evaluation and hormone suppression to embryo transfer. It discusses the history of IVF and provides indications for its use.