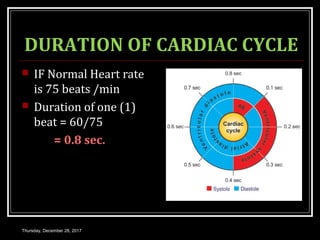
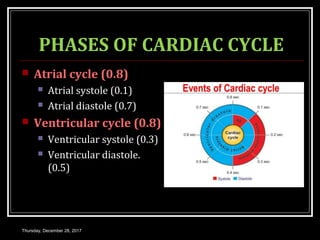
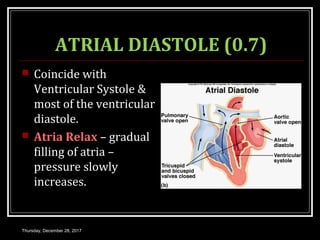
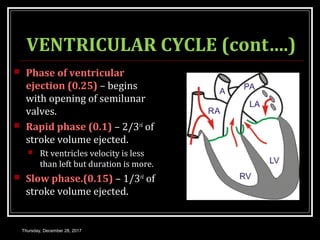
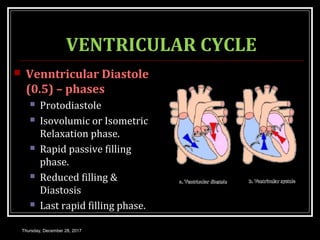
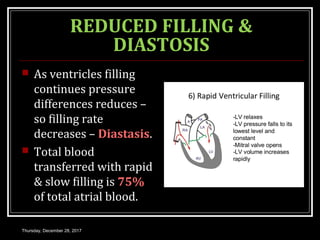
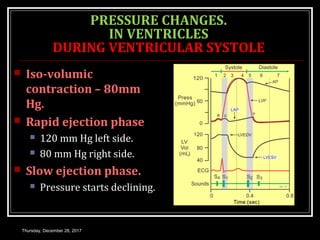
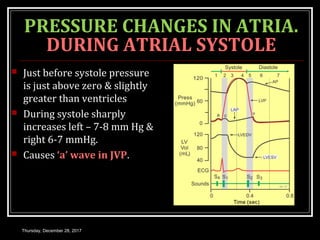
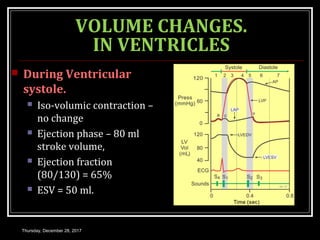
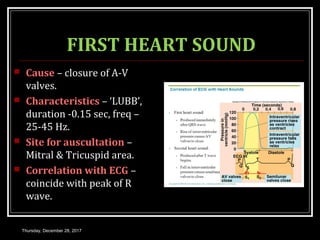
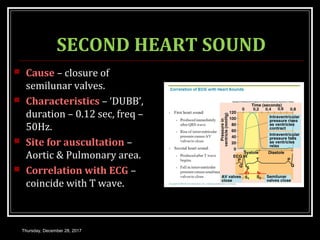
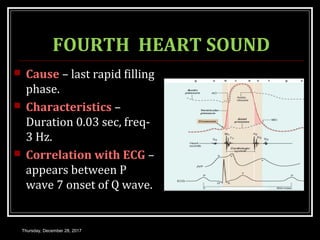
This document summarizes the cardiac cycle and its phases. It begins with an introduction to the heart as a dual pump and defines the cardiac cycle. It then describes the normal duration of the cardiac cycle and its various phases, including atrial systole, atrial diastole, ventricular systole, and ventricular diastole. It discusses the pressure and volume changes that occur in the atria, ventricles, aorta and pulmonary artery during each phase of the cardiac cycle. It also summarizes the heart sounds and murmurs that can occur.