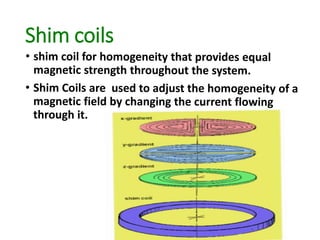
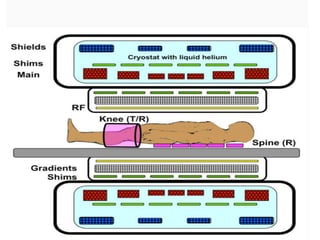
MRI coils play an essential role in generating MRI images. There are several types of coils that work together, including gradient coils, shim coils, and radiofrequency (RF) coils. Gradient coils use magnetic fields to spatially encode the MRI signal and allow for imaging in different planes. RF coils transmit and receive radiofrequency signals to and from the body, converting these signals into data used to construct the final images. Different coil designs, such as volume, surface, and phased array coils, are optimized for imaging different body regions and provide better signal-to-noise ratios.