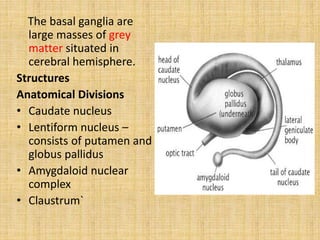
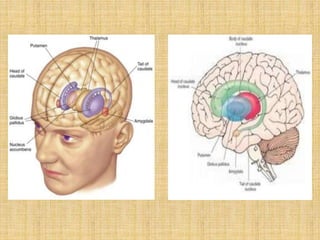
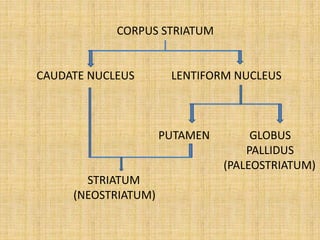
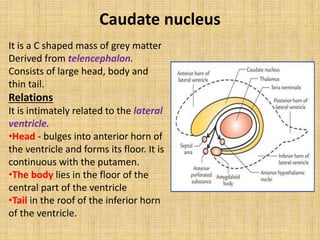
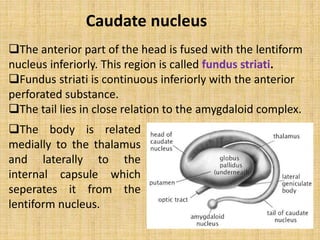
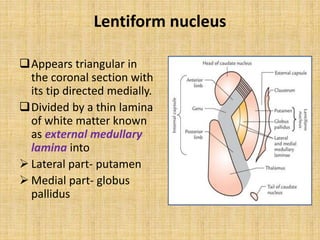
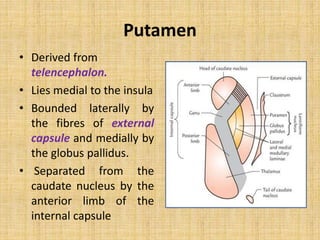
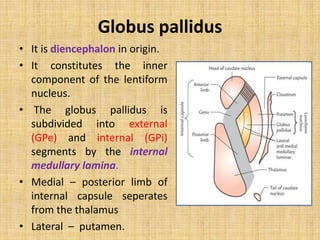
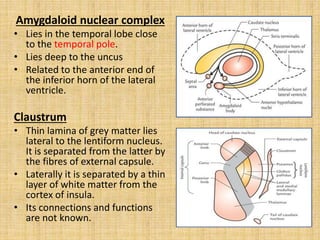
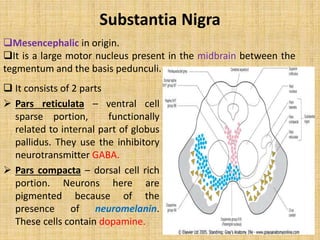
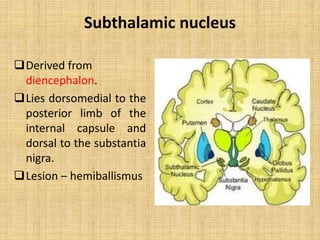
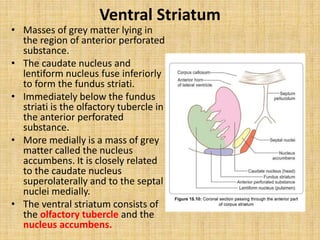
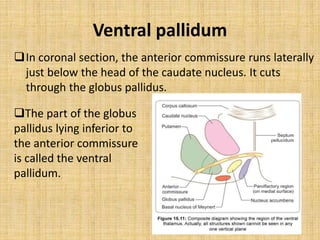
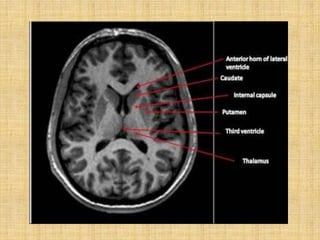
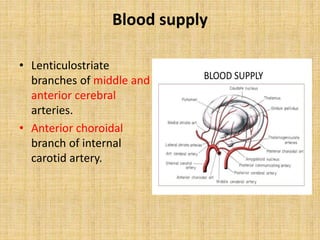
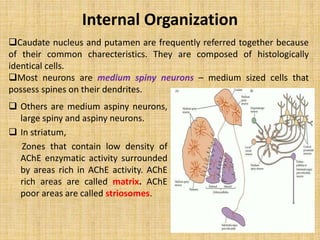
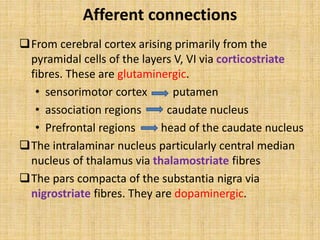
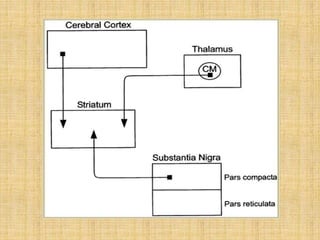
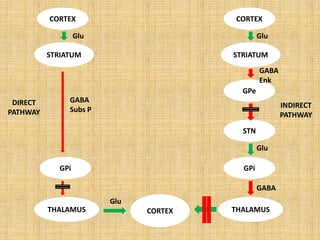
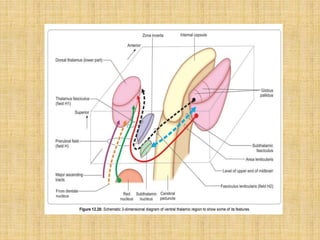
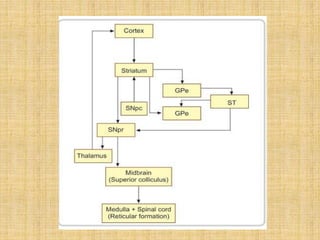
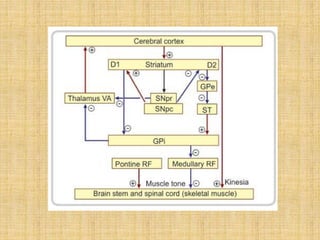
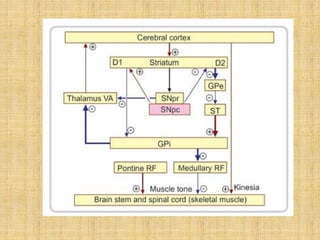
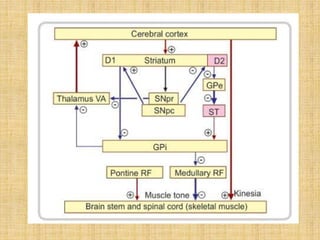
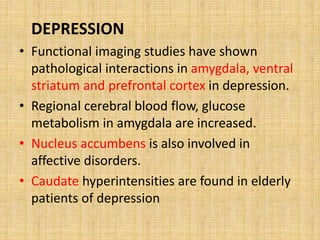
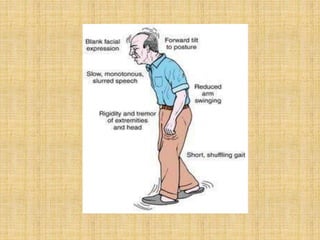
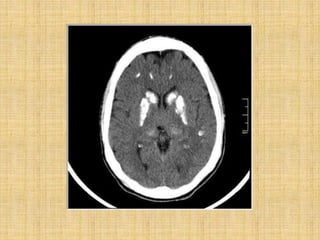
The basal ganglia are large masses of gray matter located in the cerebral hemispheres. They are comprised of the caudate nucleus, lentiform nucleus (putamen and globus pallidus), amygdaloid nuclear complex, and claustrum. The basal ganglia receive input from the cerebral cortex and thalamus and output mainly to the globus pallidus and substantia nigra. They are involved in motor control and planning through direct and indirect pathways that facilitate or inhibit motor activity. Disorders like Parkinson's and Huntington's result from disruptions to these circuits.