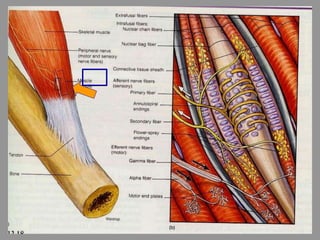
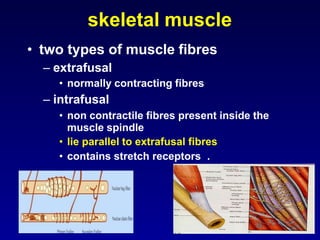
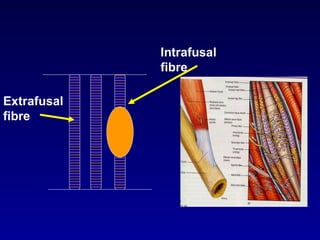
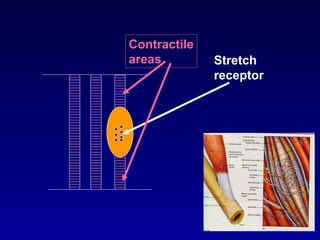
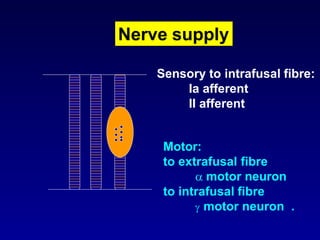
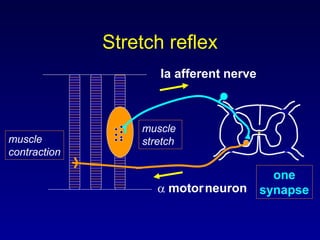
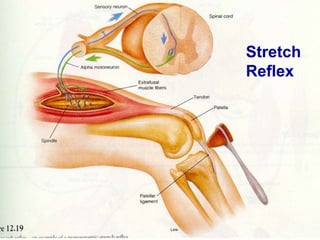
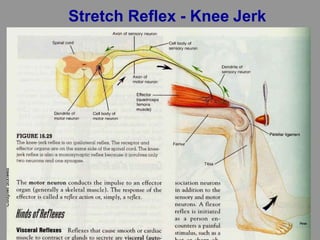
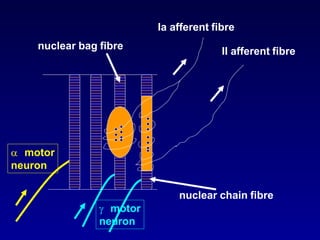
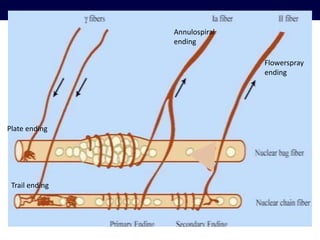
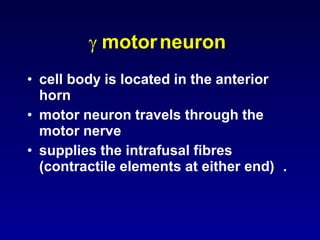
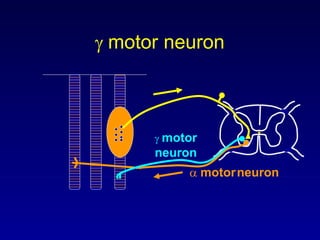
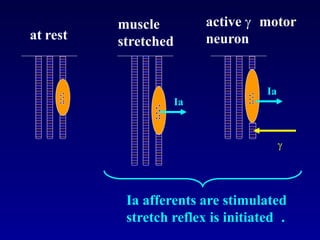
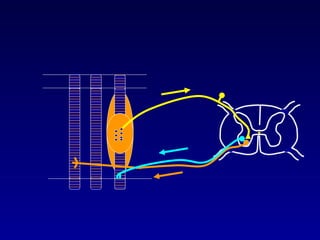
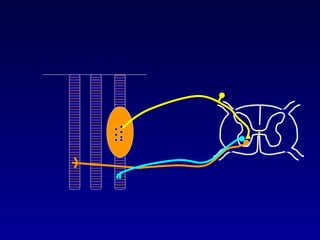
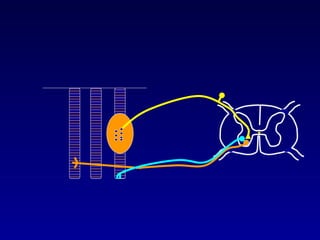
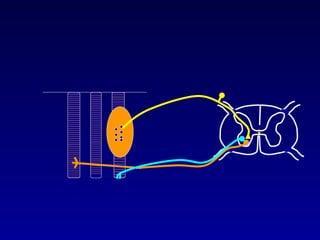
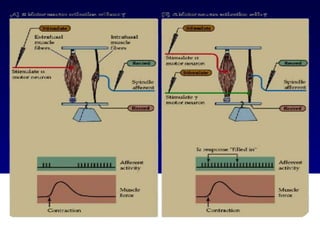
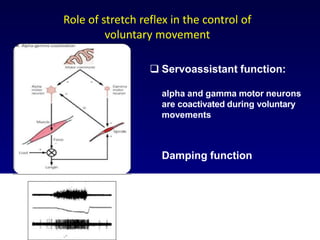
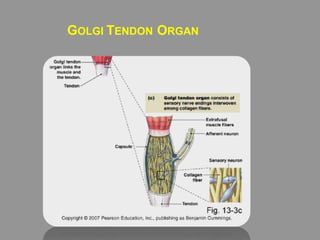
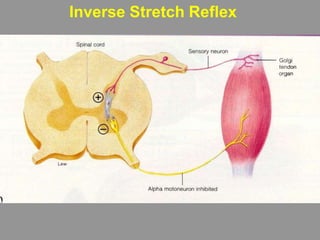
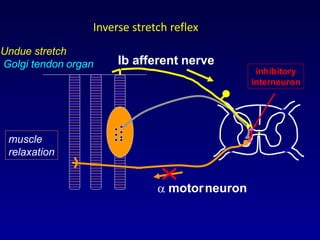
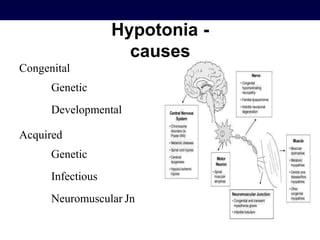
The document discusses the stretch reflex and muscle tone. It defines the stretch reflex as a monosynaptic reflex where stimulation of muscle spindles by stretching a muscle leads to contraction of the same muscle via alpha motor neurons. It describes the roles of gamma motor neurons in maintaining sensitivity of muscle spindles. Disorders of muscle tone like spasticity, rigidity, and hypotonia are explained in relation to lesions in the pyramidal and extrapyramidal systems. Clinical examination techniques for assessing muscle tone are also outlined.