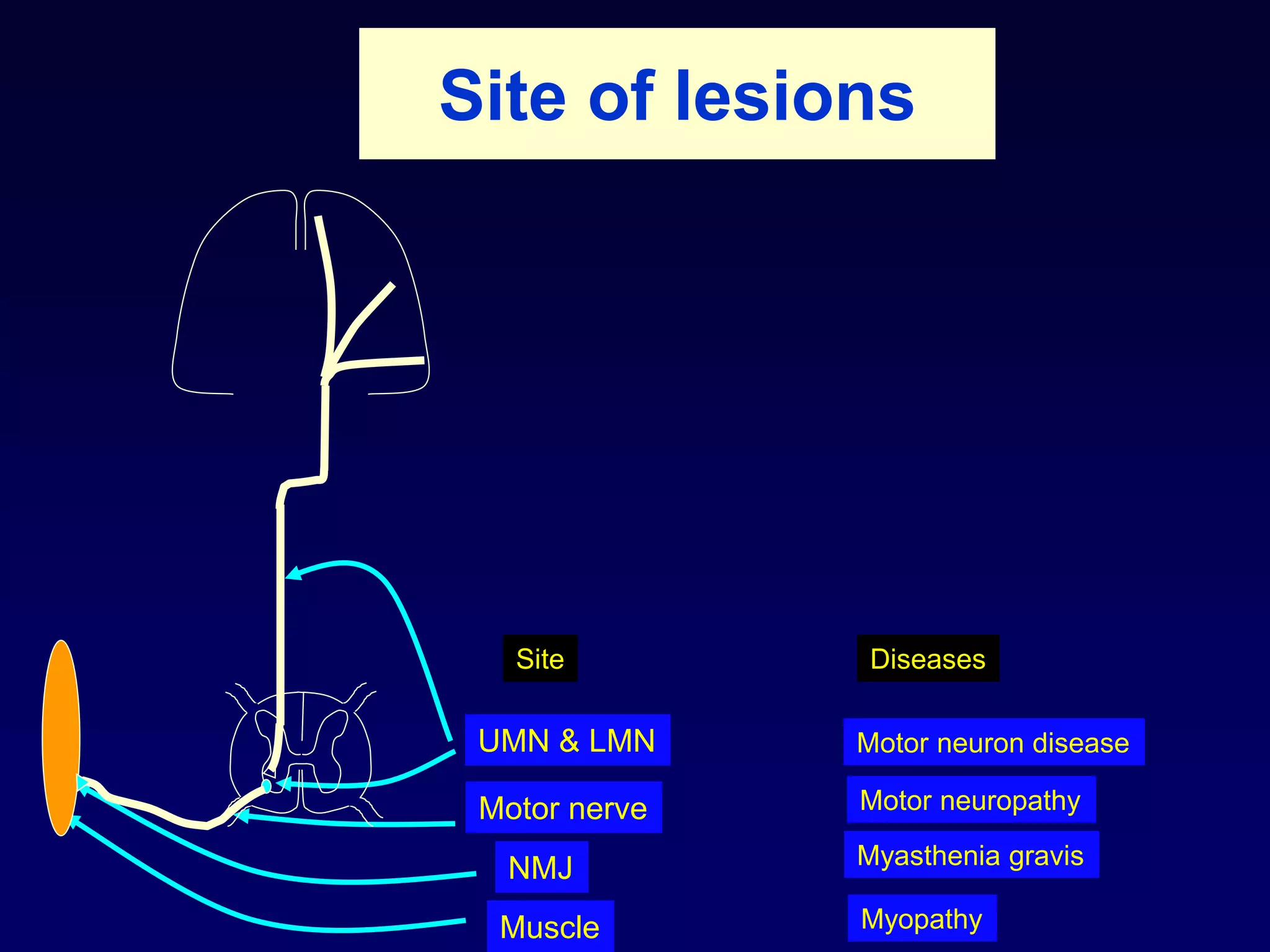
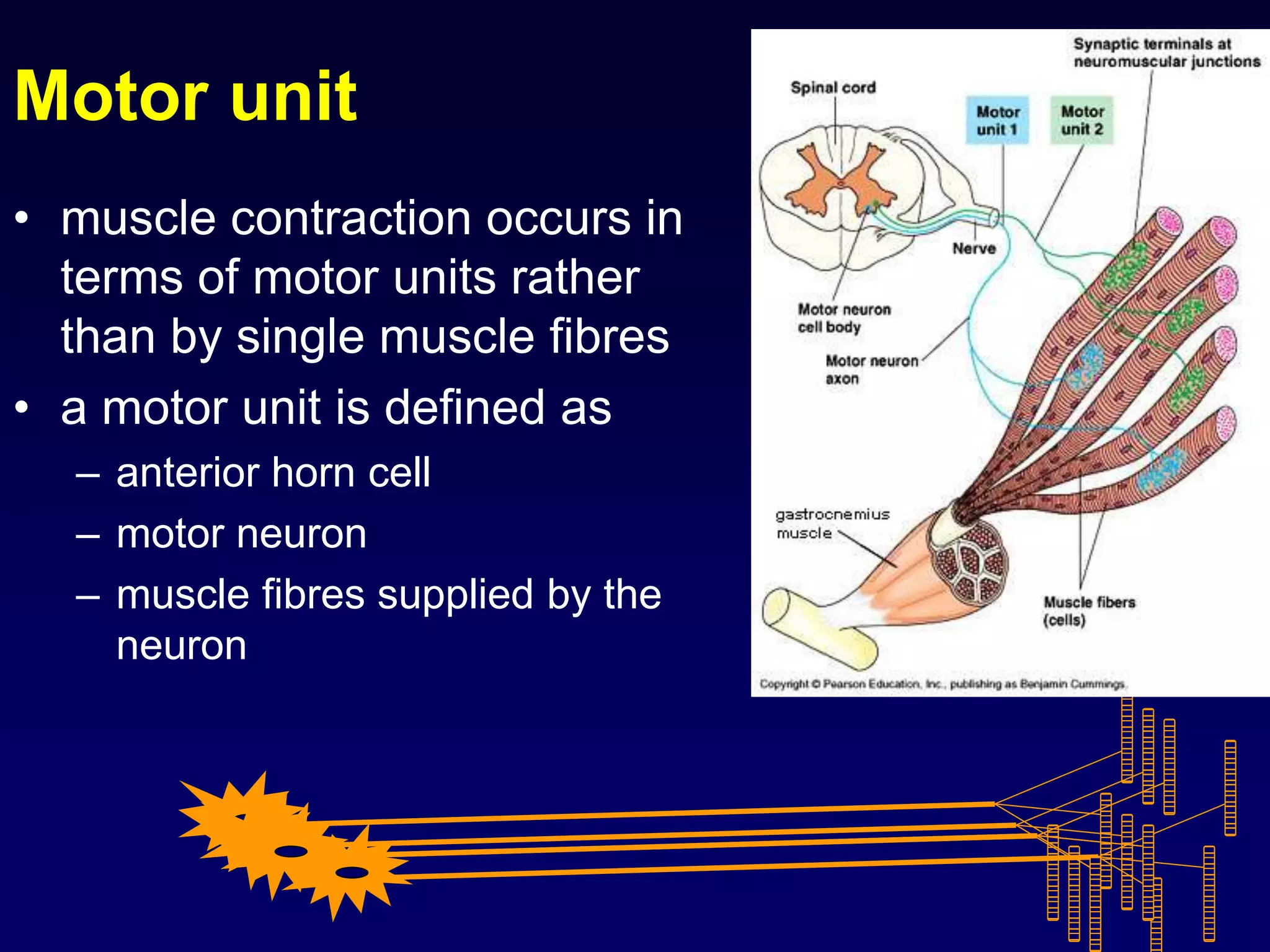
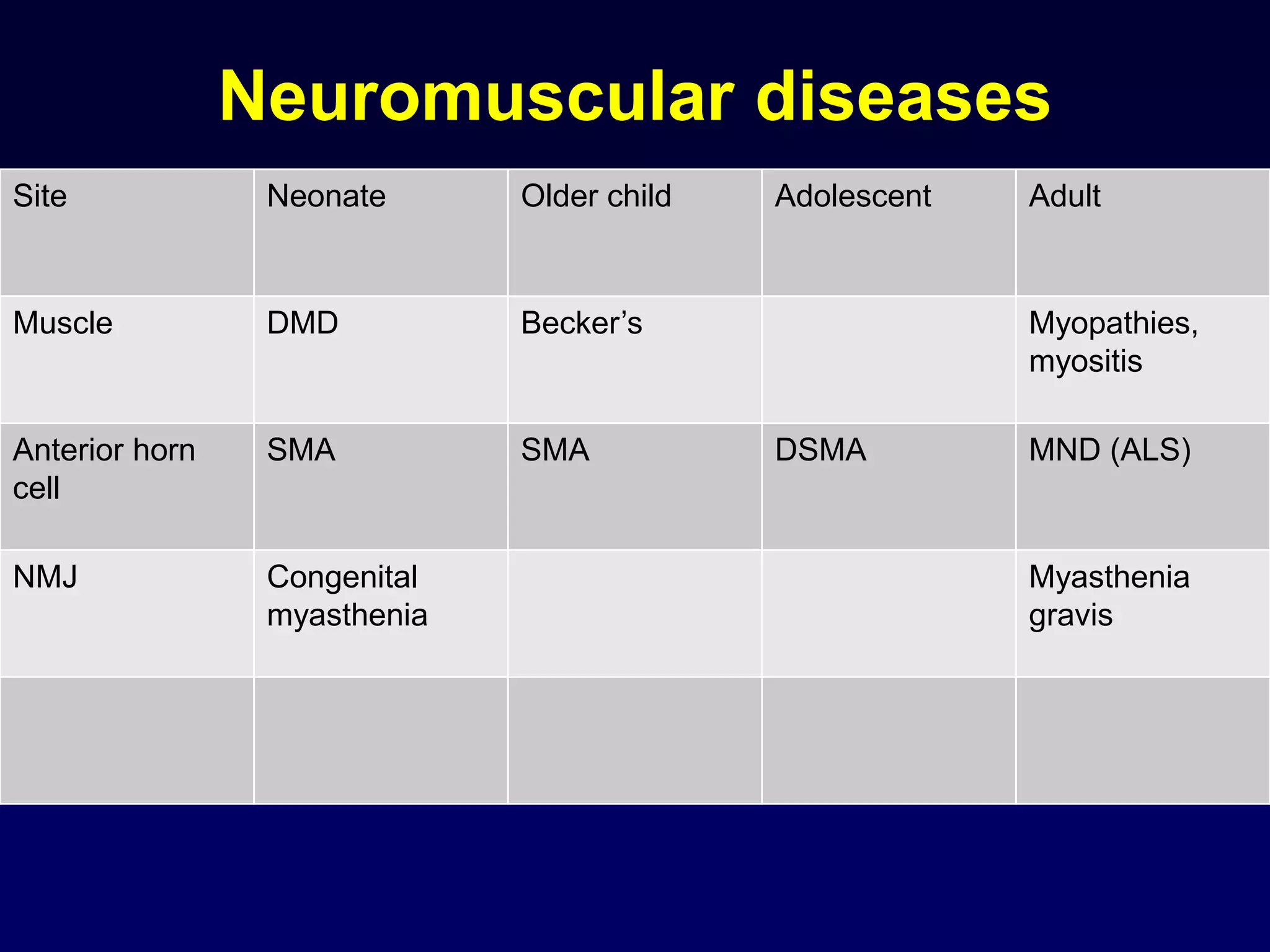
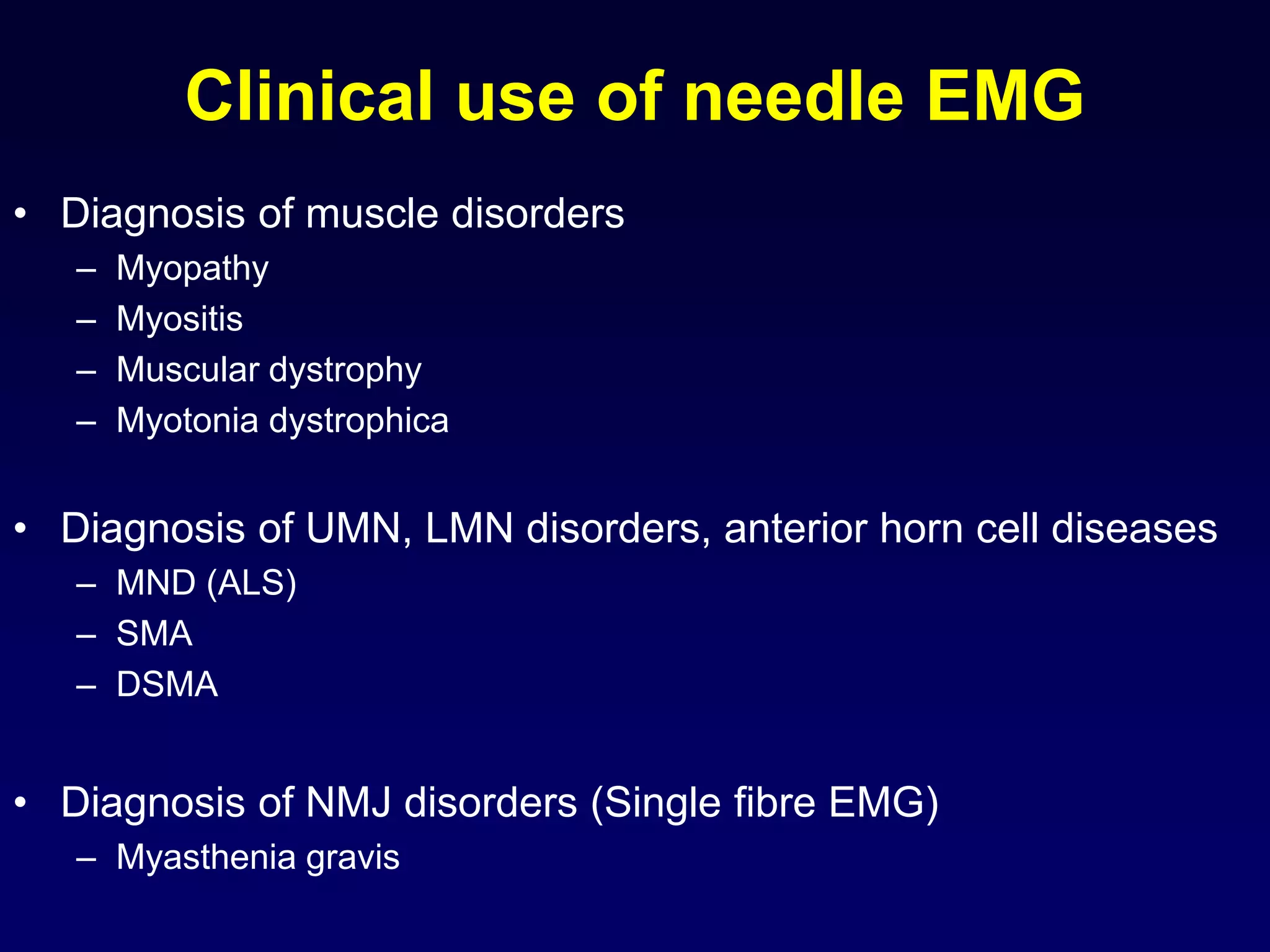
1. The document discusses various mechanisms of muscle dysfunction including disorders at the motor neuron, neuromuscular junction, and muscle levels.
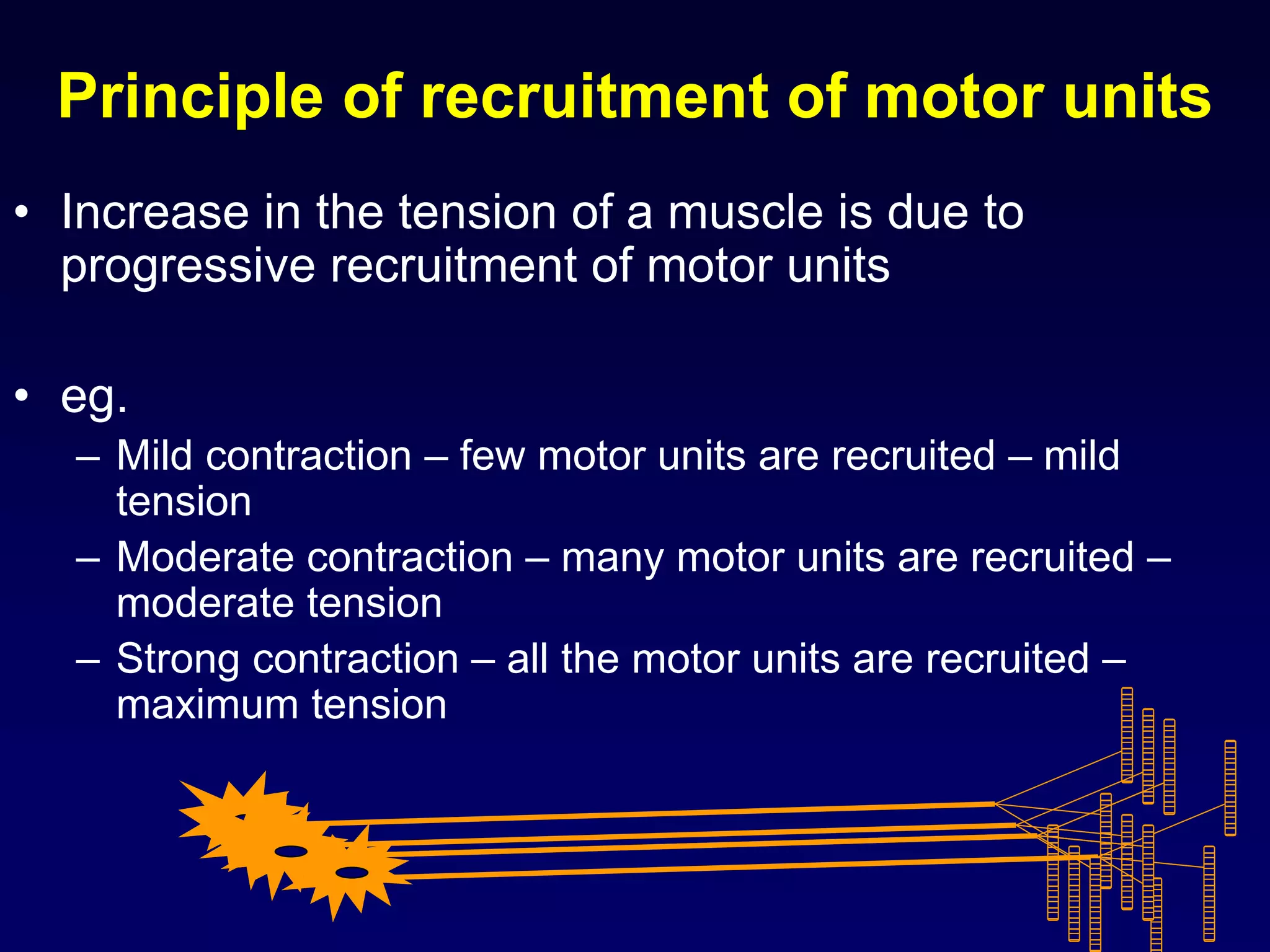
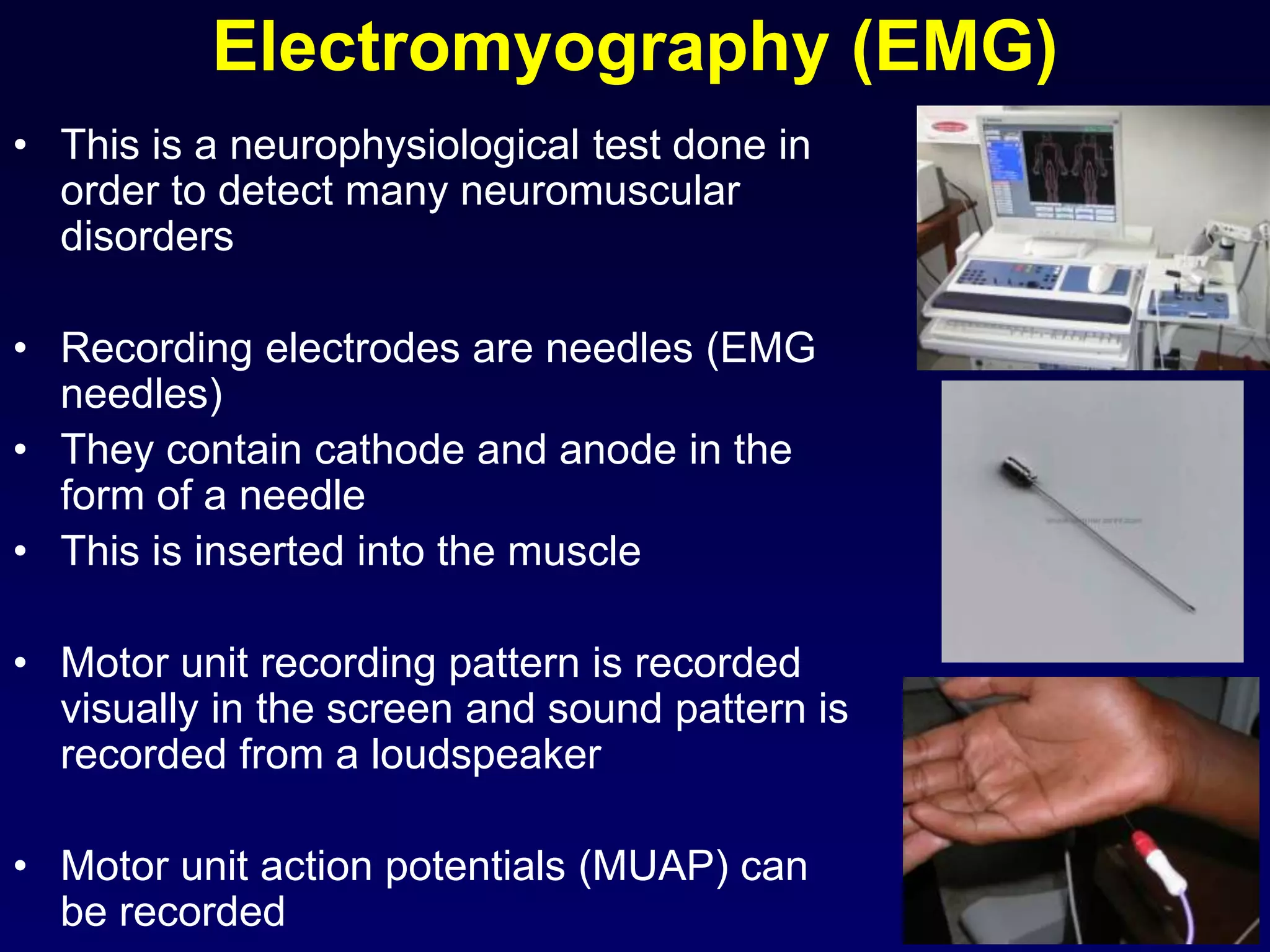
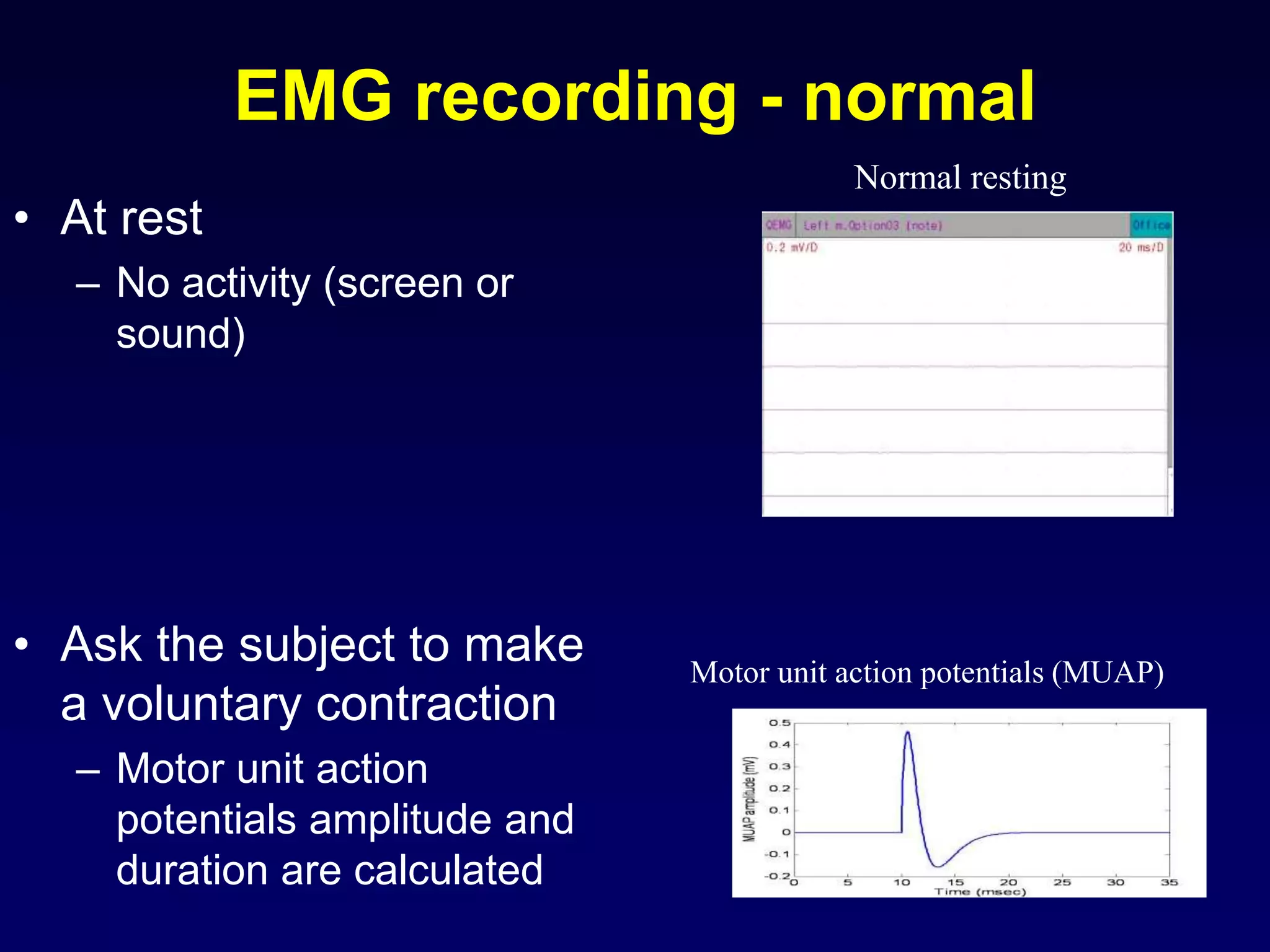
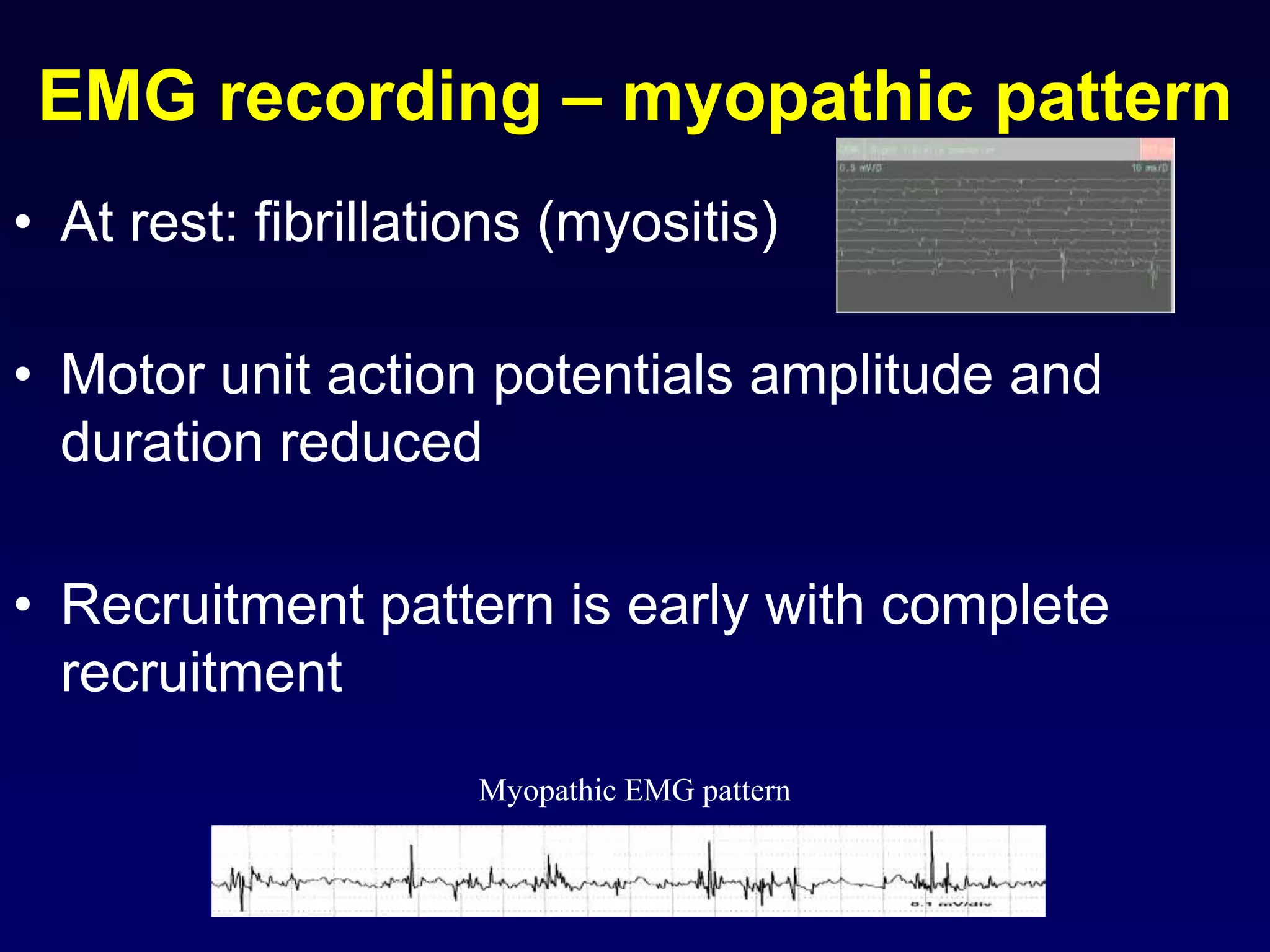
2. Electromyography is described as a key test to detect neuromuscular disorders by examining motor unit recruitment patterns and action potentials.
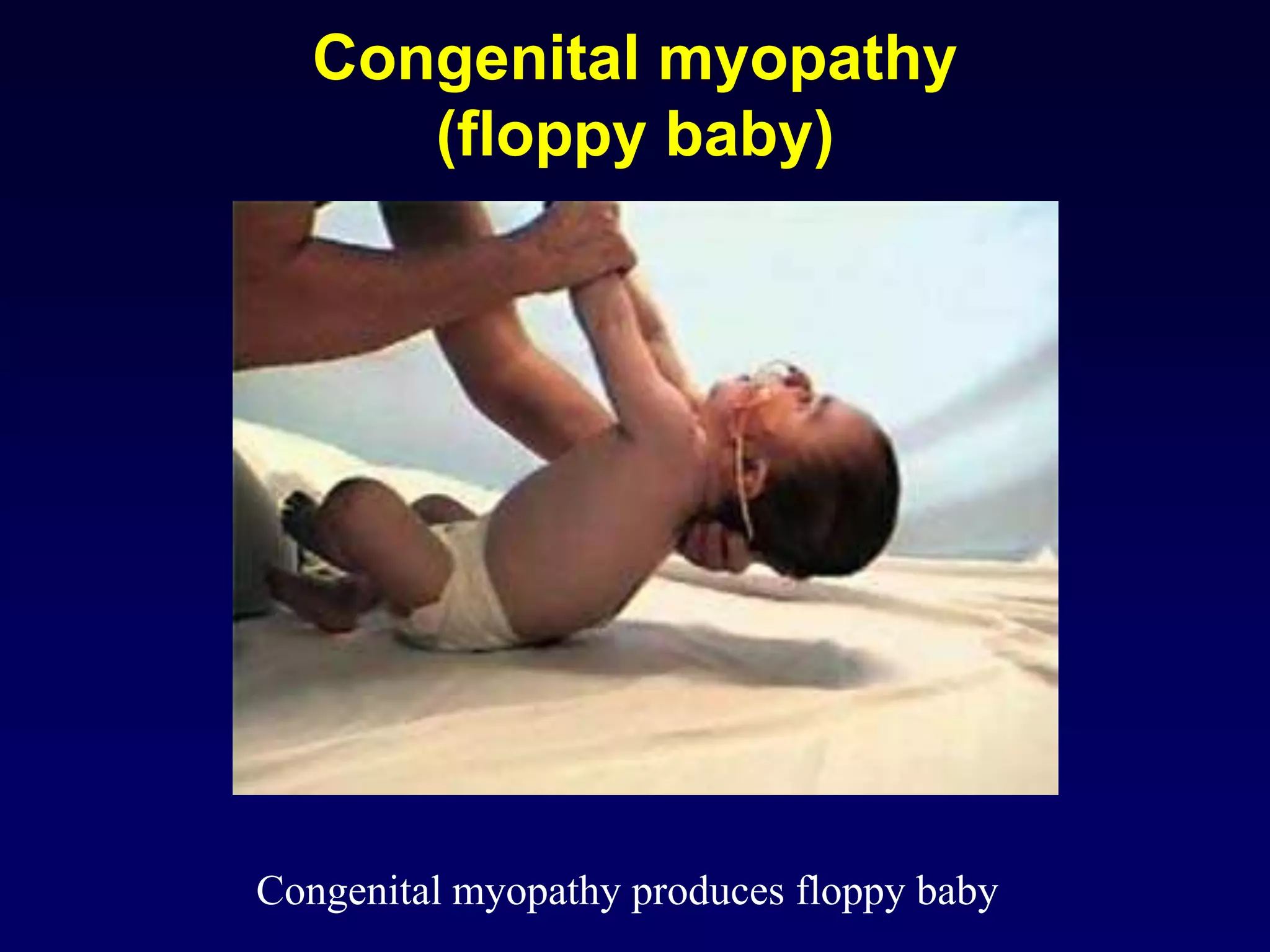
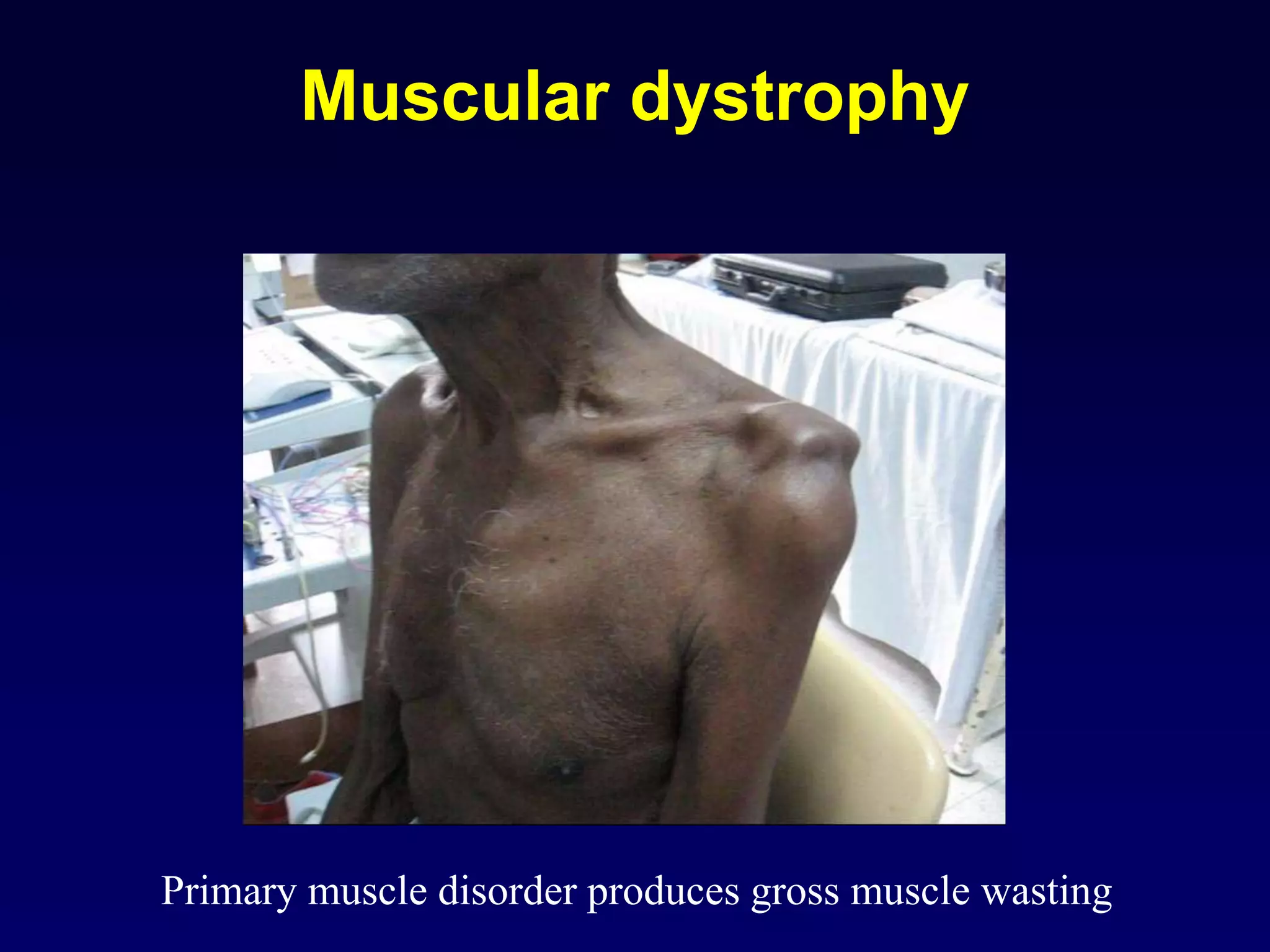
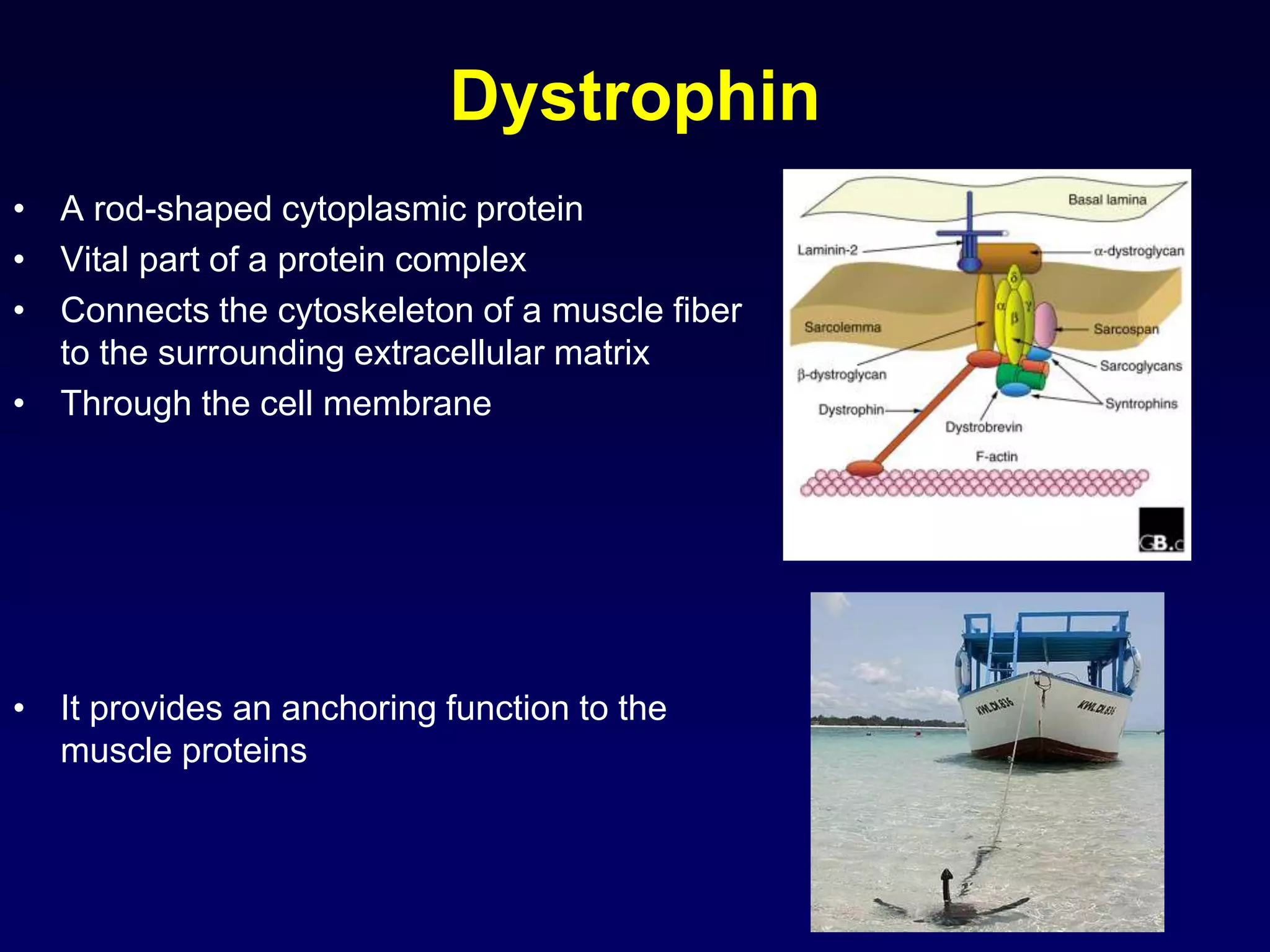
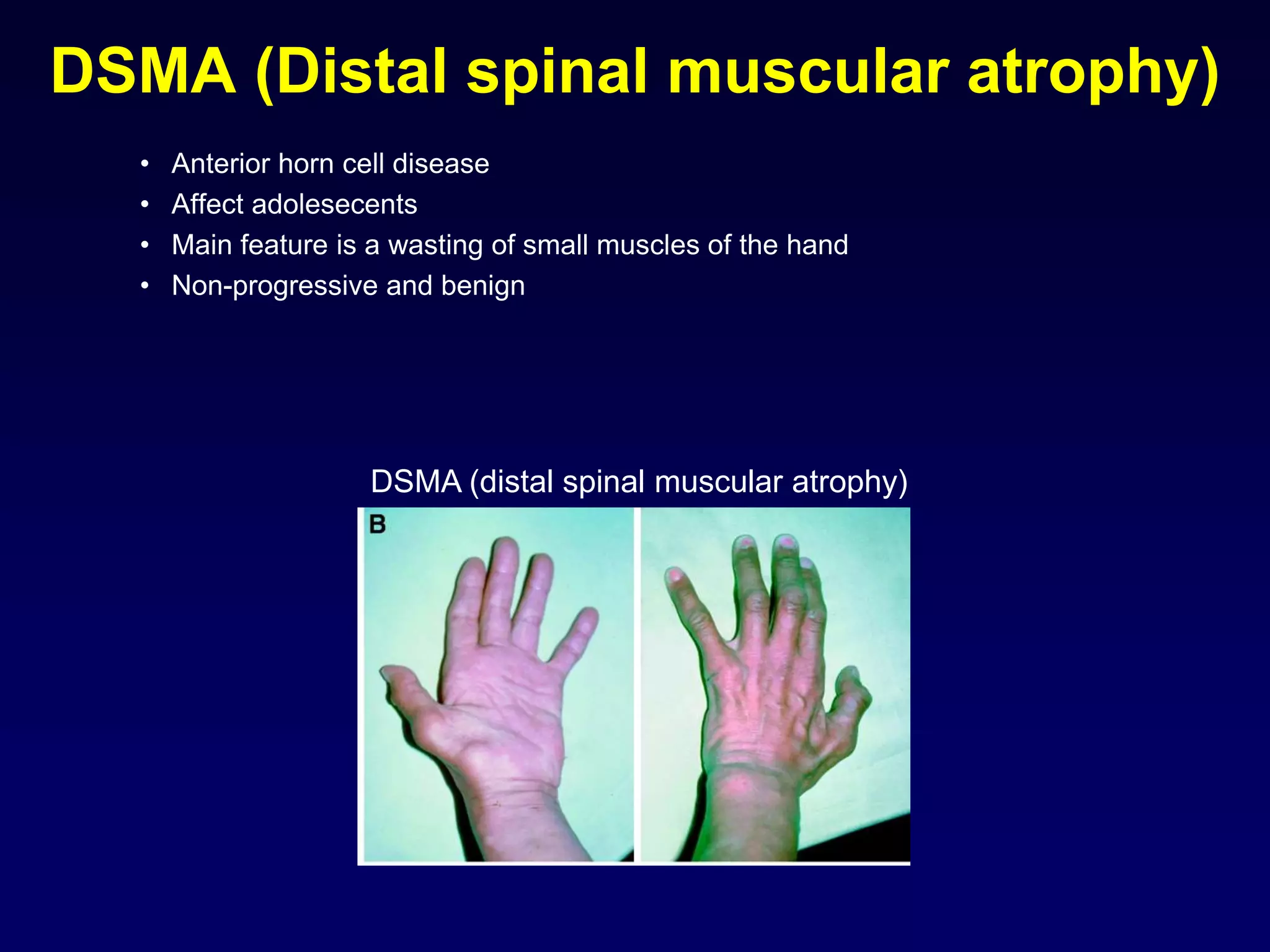
3. Specific muscle and nerve diseases are outlined like myopathies, motor neuropathies, myasthenia gravis, muscular dystrophies, motor neuron disease and spinal muscular atrophy.
4. The roles, features, causes and electromyography patterns of these diseases are explained to characterize different types of muscle dysfunction.