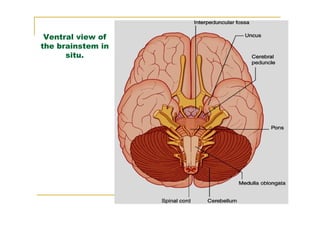
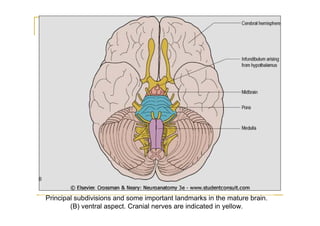
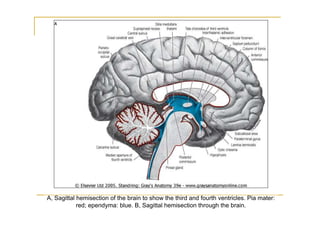
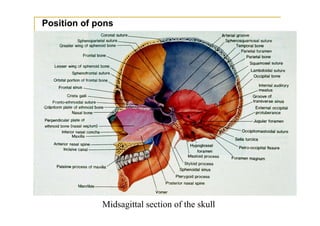
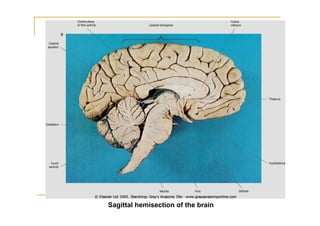
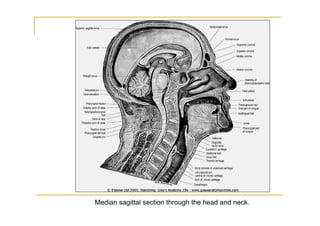
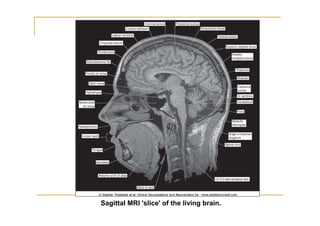
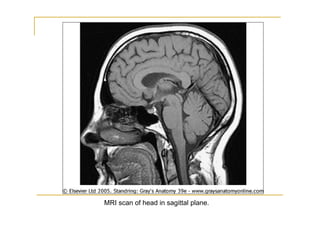
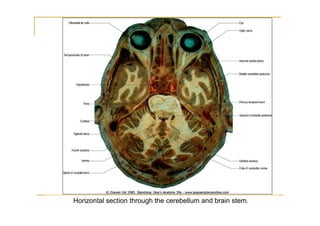
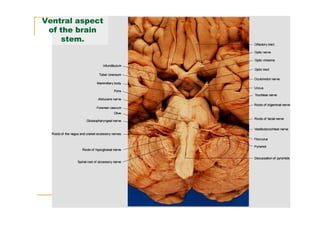
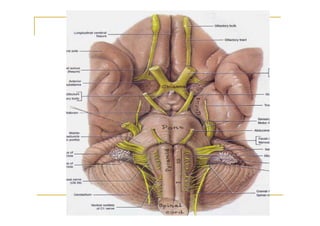
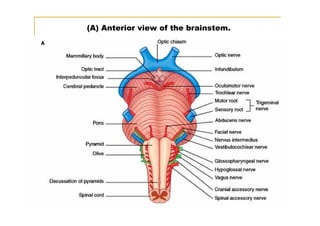
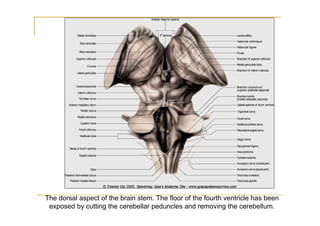
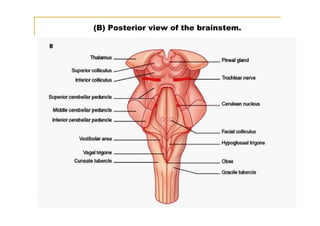
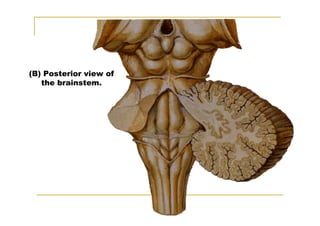
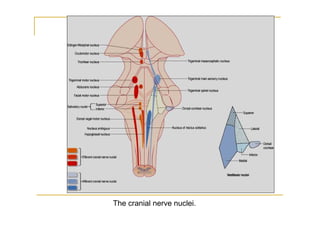
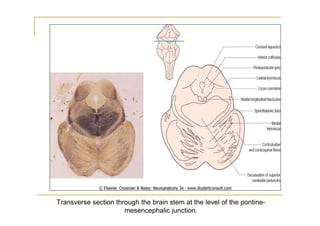
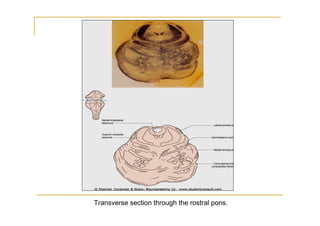
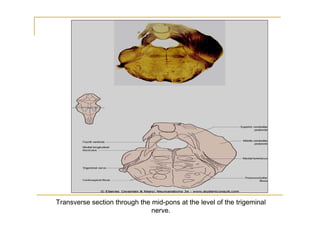
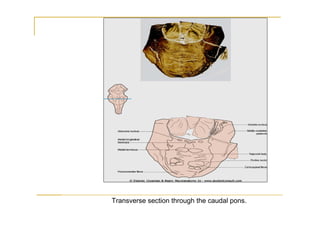
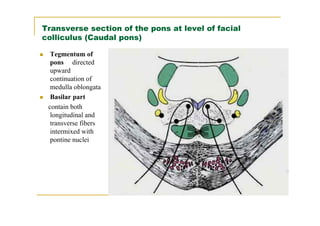
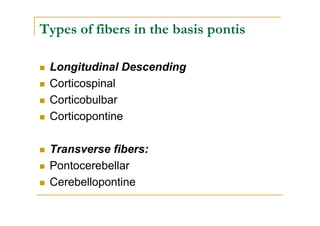
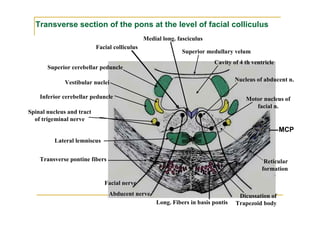
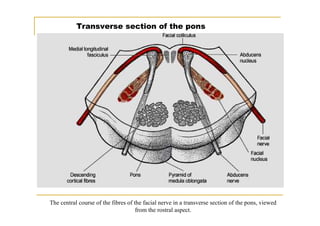
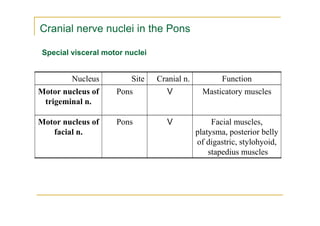
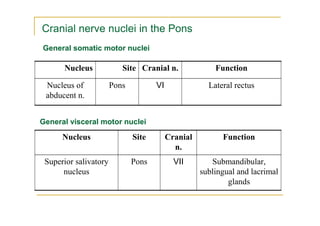
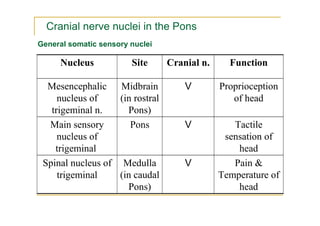
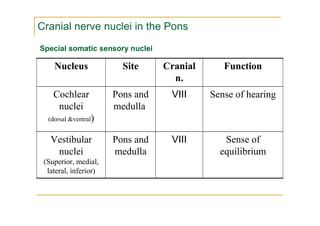
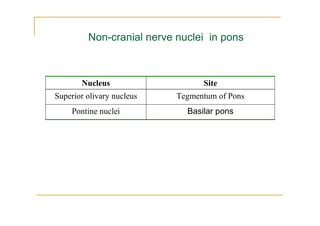
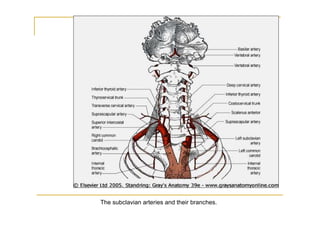
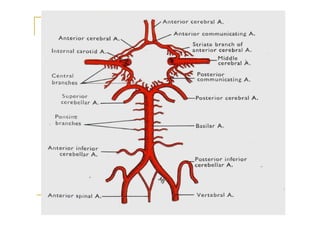
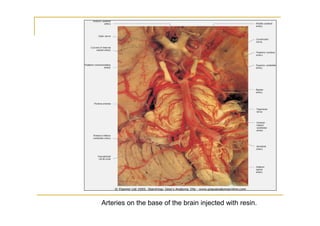
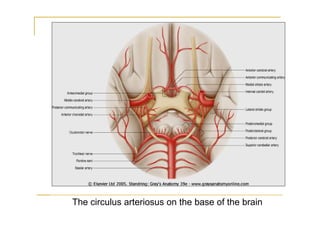
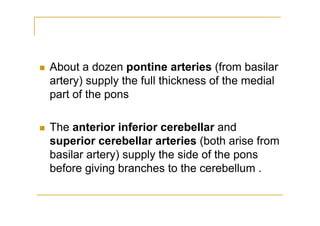
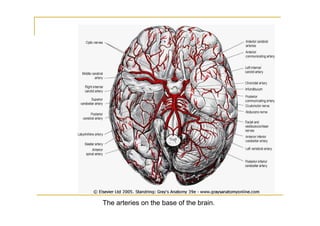
The pons is located in the brainstem, between the midbrain and medulla oblongata. It contains fibers that connect the cerebellum and cerebrum, and nuclei for several cranial nerves including the trigeminal, facial, and abducent nerves. The pons receives its blood supply primarily from the basilar artery and its branches, as well as the anterior inferior cerebellar and superior cerebellar arteries. It plays an important role in motor functions and sensory processes.