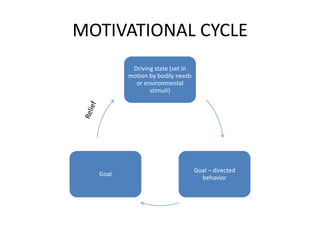
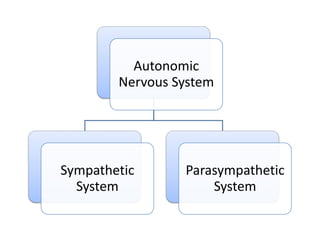
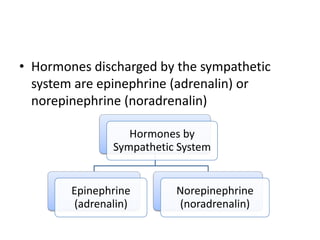
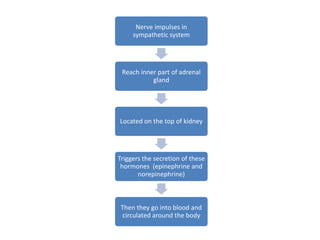
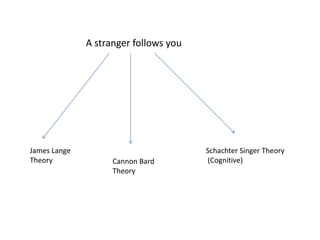
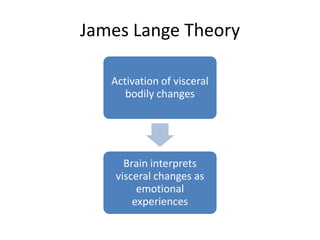
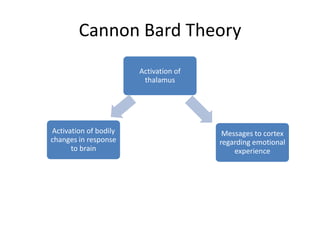
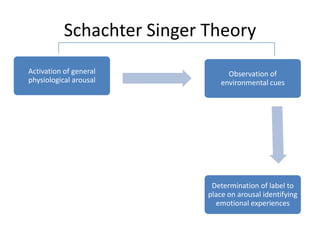
Motivation refers to driving and pulling forces that result in persistent goal-directed behavior. Motives are inferred from behavior and help explain and predict behavior. There are various theories of motivation including instinct, drive reduction, arousal, incentive, cognitive, and humanistic theories. Physiological needs like hunger and thirst are deeply rooted biological motives driven by bodily needs and regulated by mechanisms like the hypothalamus. Psychological needs for achievement, affiliation, and power also motivate behavior and are influenced by both innate and learned factors.