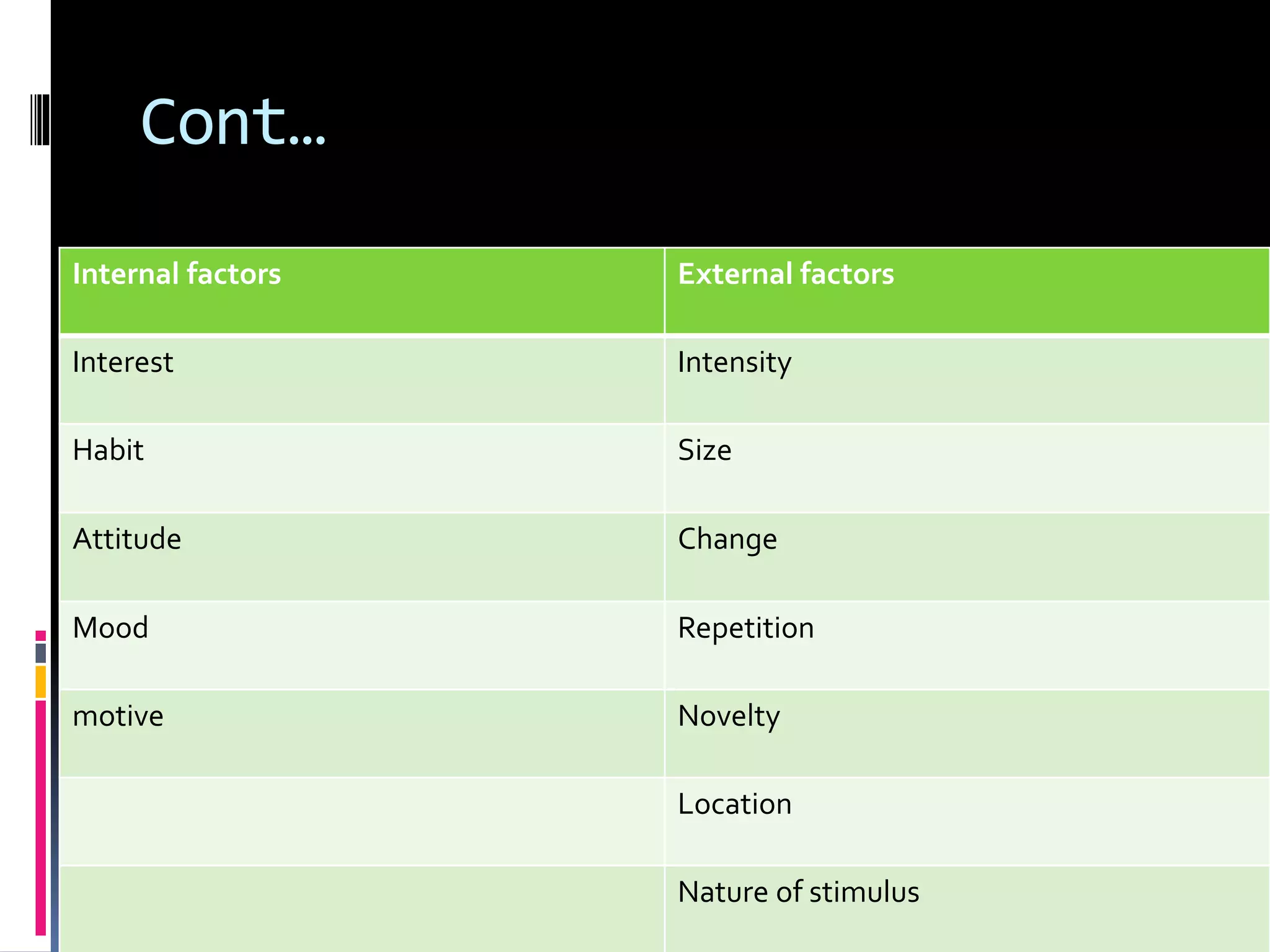
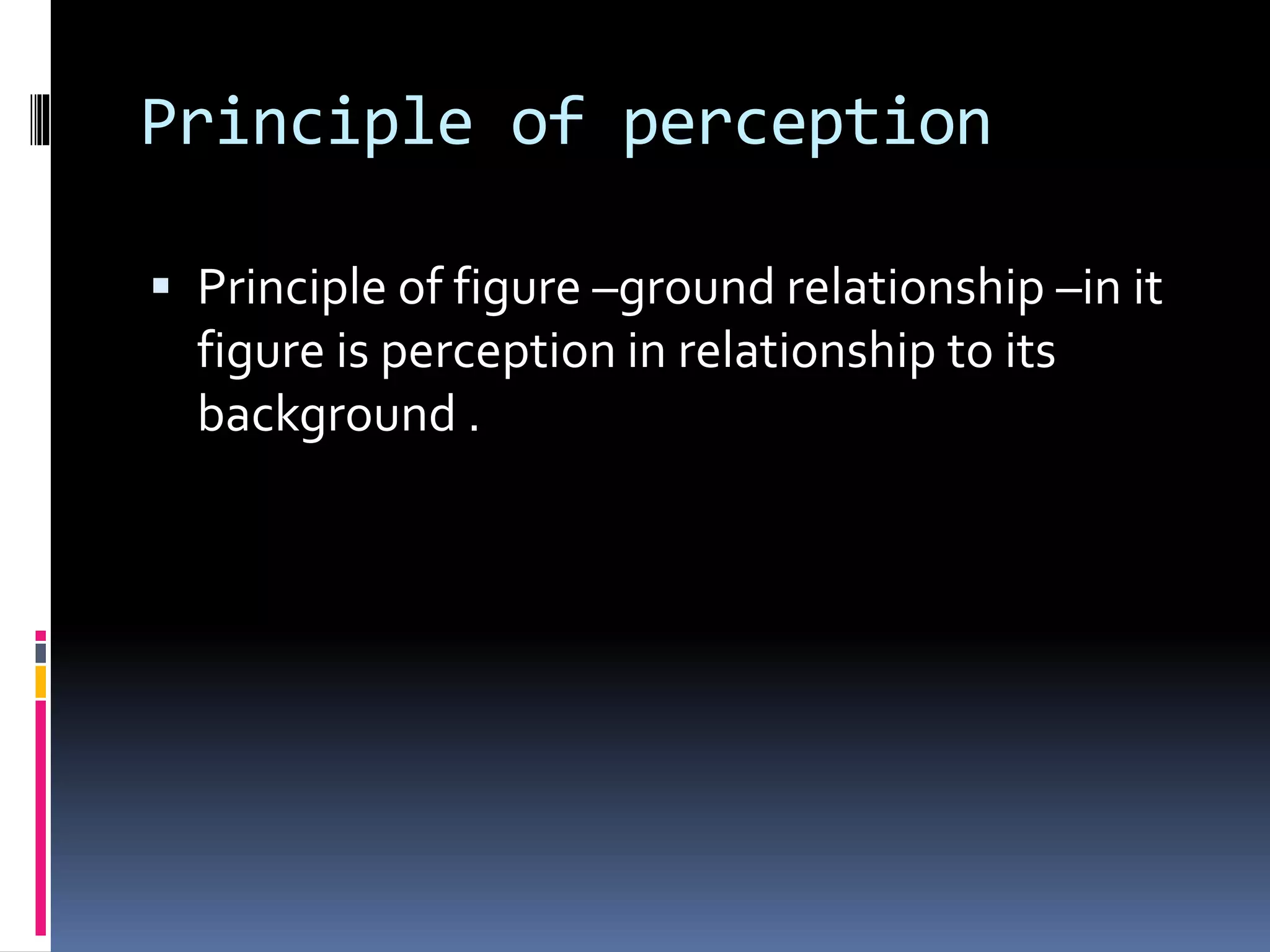
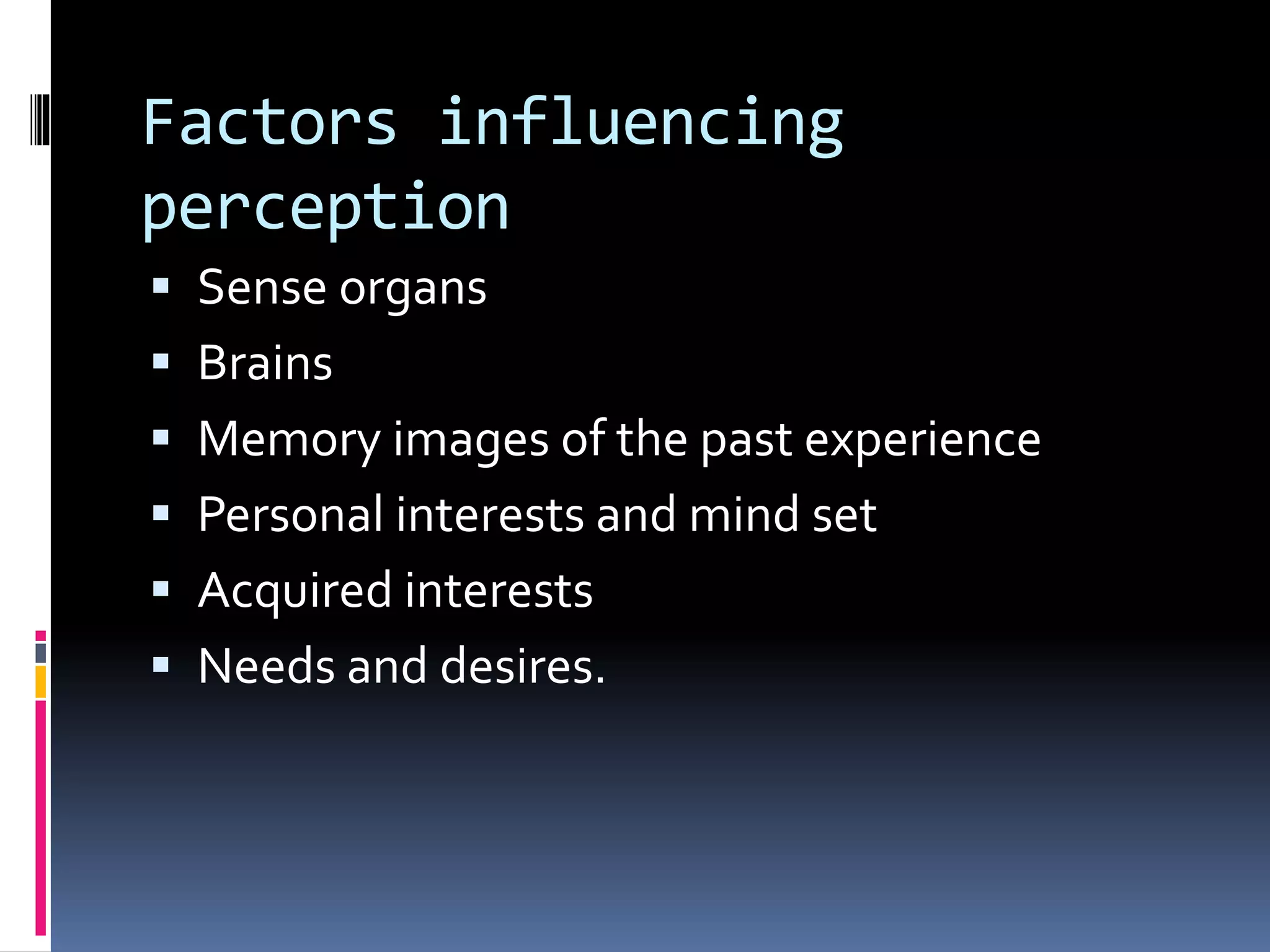
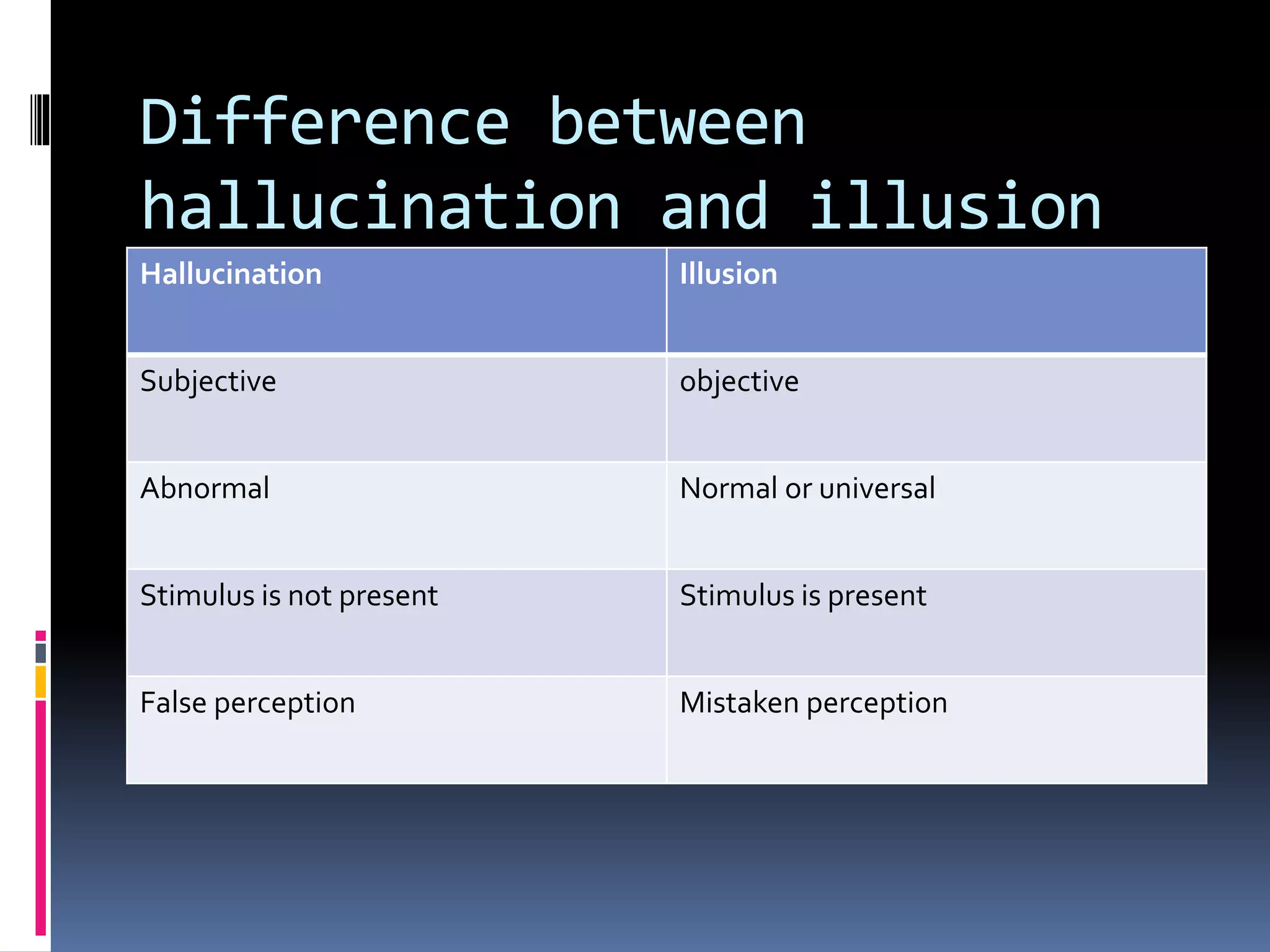
This document discusses various cognitive processes including attention, perception, learning, thinking, and intelligence. It defines attention as the selective concentration of consciousness on one object over others. Perception is defined as the interpretation of sensory stimuli based on past experiences. Learning is described as a relatively permanent change in behavior through experience. Thinking is defined as a problem-solving process using symbols. Intelligence refers to the ability to understand the world, think rationally, and adapt to changes. The document outlines different types and factors influencing each of these cognitive processes.