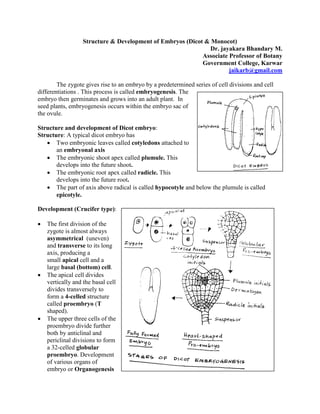
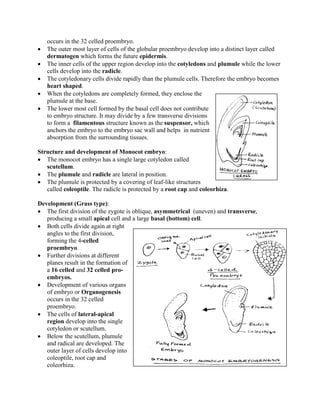
The document summarizes the structure and development of dicot and monocot embryos. It states that in dicots, the embryo typically has two cotyledons, an embryonic shoot apex (plumule), and an embryonic root apex (radicle). It describes the asymmetrical cell divisions that form a proembryo and later a globular proembryo in dicots. In monocots, the embryo has a single large cotyledon called a scutellum with lateral plumule and radicle protected by coleoptile and coleorhiza. It notes the first oblique cell division in monocots also forms a proembryo that develops organs through further cell divisions