1) Hypoxia can lead to decreased ATP synthesis, lactic acidosis, impaired protein synthesis, and irreversible cell changes due to increased cytosolic calcium.
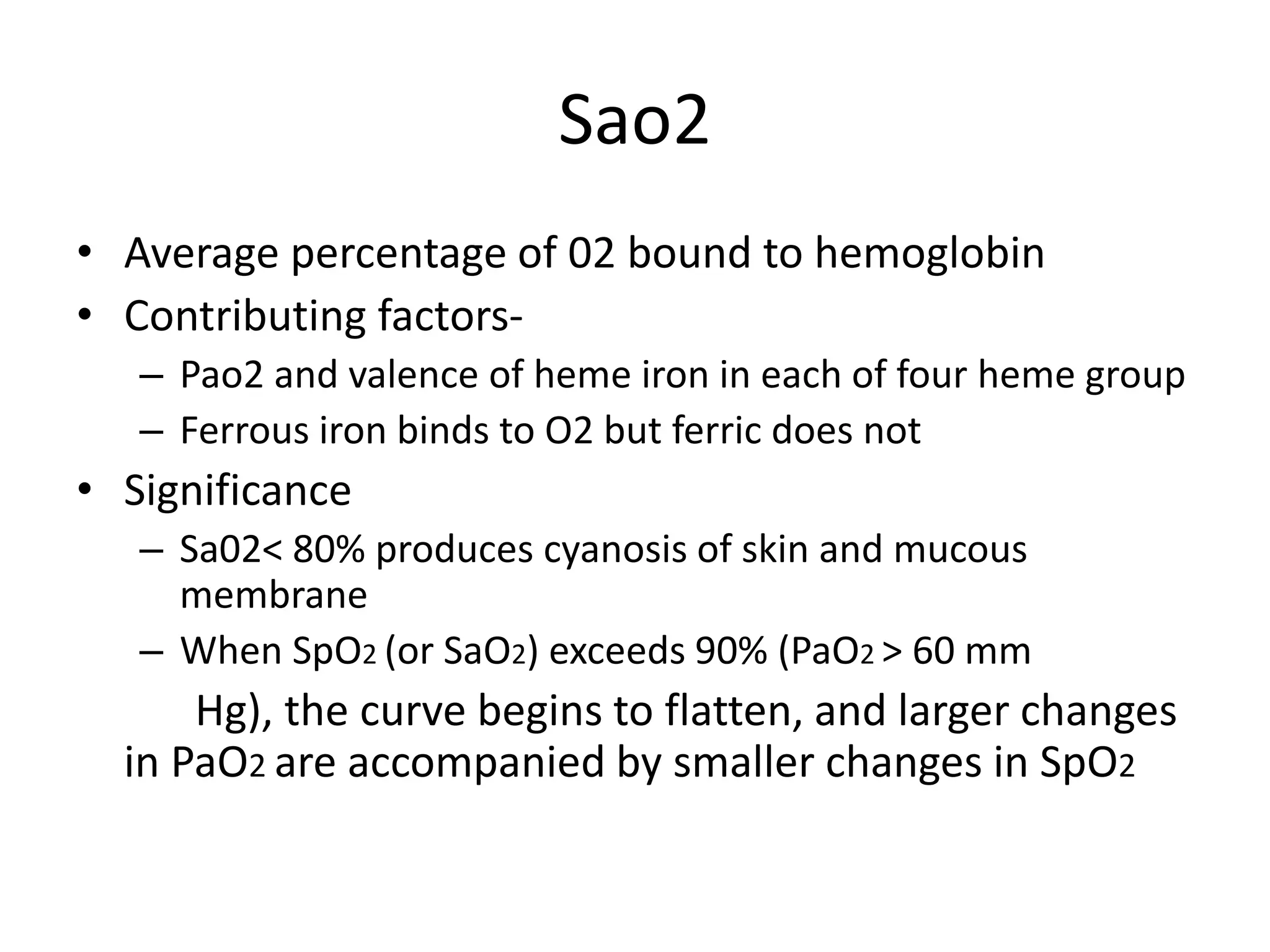
2) Pao2, Sao2, and oxygen content are important measures of oxygen levels in the blood. Pulse oximetry can monitor Sao2 non-invasively but has limitations.
3) Arterial blood gas analysis precisely measures oxygen, carbon dioxide, pH, and bicarbonate levels to assess oxygenation and ventilation.










![ABG
• The ABG analyser measures:
• Hydrogen ion concentration, reported as either hydrogen ion
concentration [H+] or pH (-log10[H+] ) .
• A lower pH value is more acidotic
• Oxygen tension (PaO2), reported in kilopascals (kPa) or mmHg.
• Carbon dioxide tension (PaCO2) (kPa or mmHg)
• bicarbonate [HC03-] expressed in mmol l-1 and Base Excess/Deficit
(BE/D), are calculated](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hpoxiadrssir-180209183902/75/Monitoring-Hypoxia-and-oxygen-supplementation-12-2048.jpg)

![• The level of PaCO2 is a balance between
production (cellular aerobic metabolism) and
clearance.
• CO2 is cleared in two ways.
– First, by ventilation (acute adaption over seconds)
and second,
– metabolic compensation (renal excretion) after
conversion to HCO3- (chronic, over hours and days).
[HCO3-] level indicates the adaptive responses to
acidosis or alkalosis.
– Low [HCO3-] indicates acidosis, high alkalosis](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hpoxiadrssir-180209183902/75/Monitoring-Hypoxia-and-oxygen-supplementation-14-2048.jpg)













