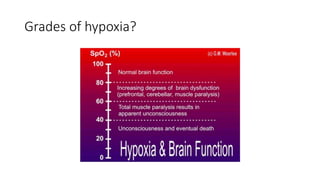
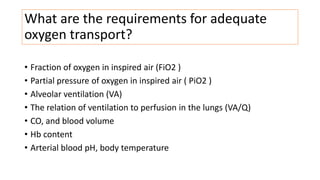
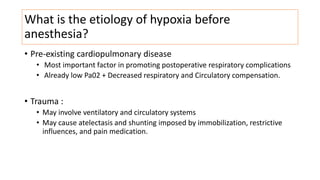
This document discusses perioperative hypoxia. It begins by defining different types of hypoxia and the organs most sensitive to hypoxia. It then discusses the body's defenses against hypoxia like increased ventilation and circulation. Potential causes of preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative hypoxia are outlined. These include patient factors like underlying lung disease as well as issues with oxygen delivery systems. Methods for diagnosing hypoxia like pulse oximetry and blood gas analysis are also covered. The document concludes by noting management involves addressing the underlying cause of low oxygen levels and optimizing oxygen delivery.