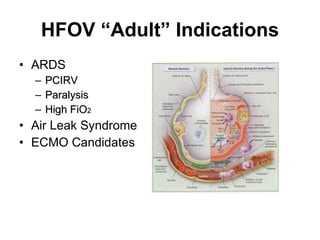
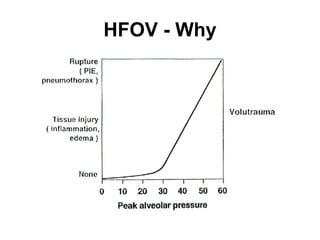
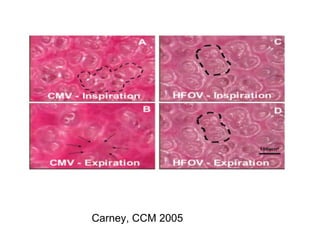
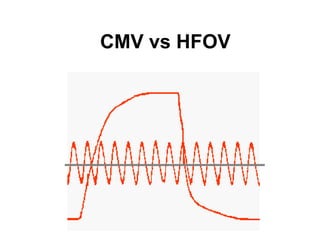
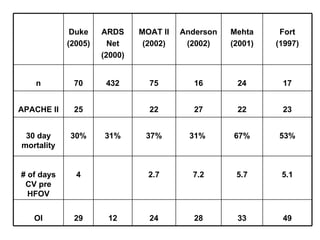
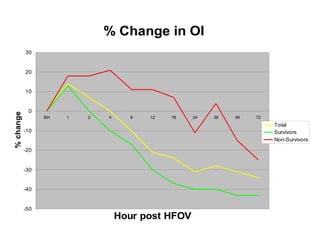
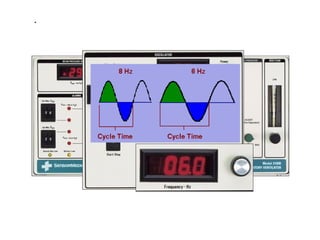
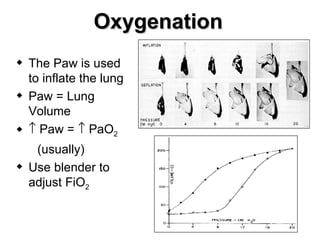
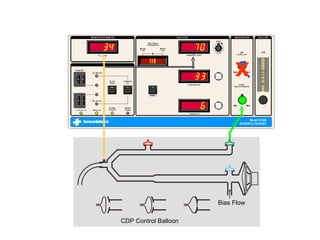
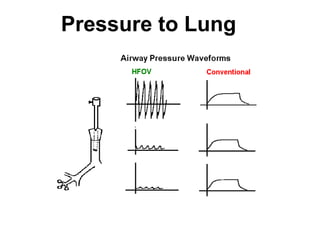
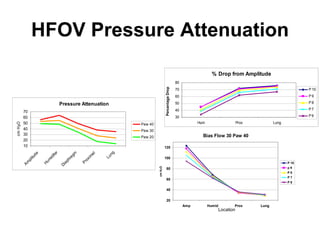
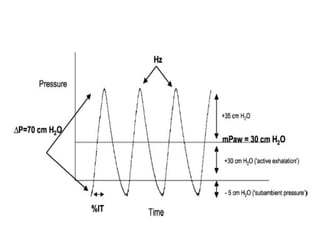
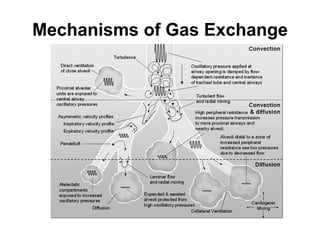
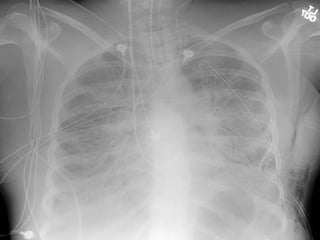
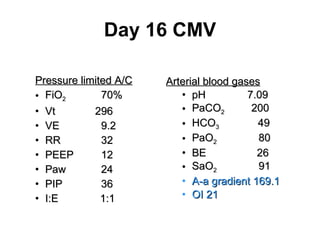
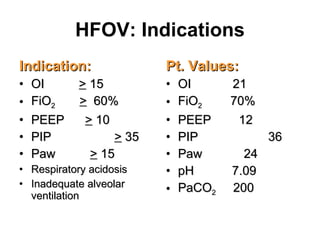
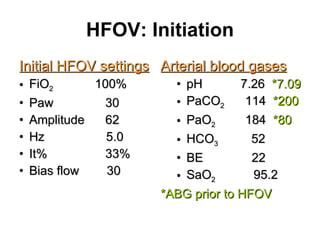
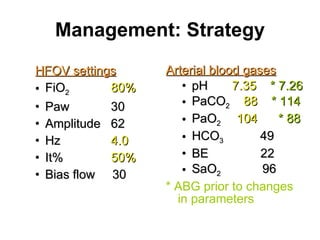
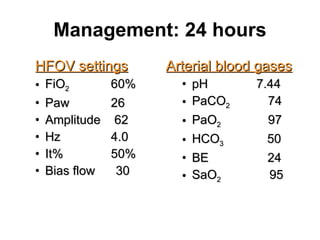
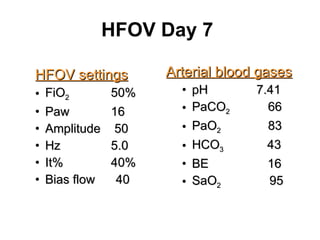
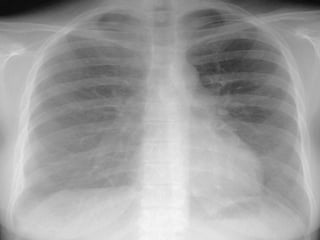
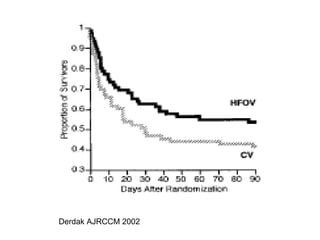
The document discusses High Frequency Oscillatory Ventilation (HFOV), including its uses in neonatal and adult patients, how it works, and how to operate it. HFOV aims to support lung oxygenation and CO2 removal while reducing ventilator-induced lung injury. It works by using very small, high frequency breaths to gently inflate the lungs rather than large tidal volumes. The settings control pressure and flow to optimize gas exchange while protecting the lung tissue.