1. Evolution is the process of change over time from early life forms to today's diversity due to natural selection.
2. Charles Darwin proposed the theory of evolution by natural selection after observing species diversity on the Galapagos Islands and realizing that species evolved over generations to be better suited for their environments.
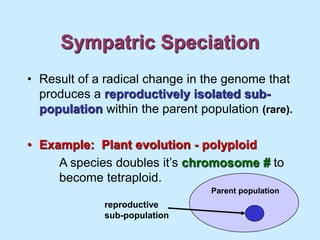
3. Speciation, the evolution of new species, occurs through mechanisms like reproductive isolation, geographic barriers causing allopatric speciation, or adaptive radiation of a species exploiting new environments.