1. The document describes a lab activity where students will create a model of a recombinant plasmid to demonstrate how they are made and their usefulness.
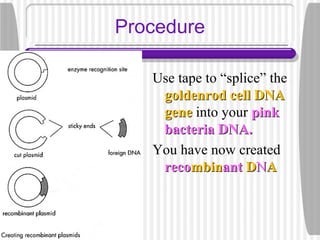
2. Students will cut out strips representing bacterial DNA and human DNA containing the insulin gene. They will use a restriction enzyme to cut the DNA strands, leaving complementary sticky ends, and fuse the insulin gene into the bacterial DNA to create a recombinant plasmid.
3. Recombinant plasmids allow bacteria to produce useful human proteins like insulin, helping treat diseases like diabetes. Restriction enzymes cut the DNA at specific sites, leaving ends that fuse together to insert human genes into bacterial DNA.