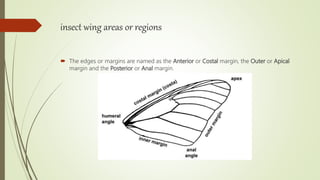
The document discusses the structure and function of insect wings. It notes that insect wings are found on the mesothorax and metathorax and are strengthened by longitudinal veins. The document outlines the different regions of insect wings and various modifications like tegmina, elytra, hemelytra and others. It concludes by stating insect wings serve functions like flight, gliding, parachuting, stability and thermoregulation.