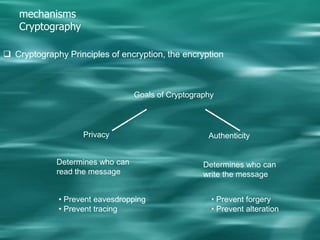
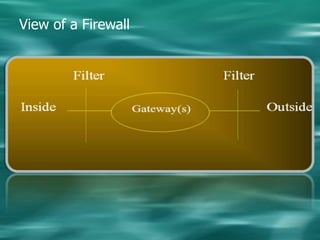
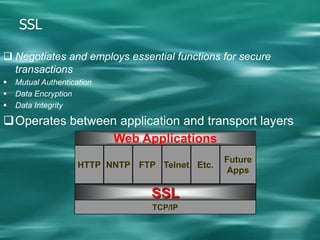
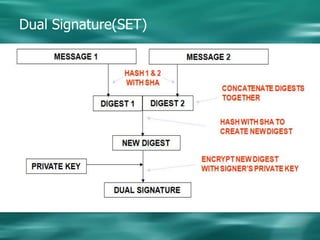
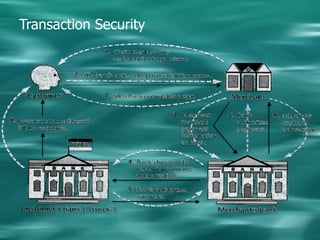
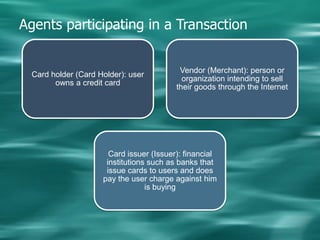
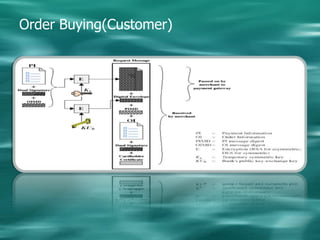
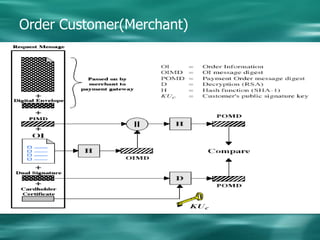
1. Cryptography is used to provide security in electronic commerce by ensuring privacy, authenticity, and preventing forgery, alteration, eavesdropping and tracing of messages.
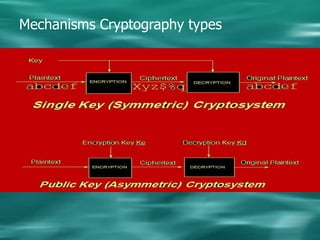
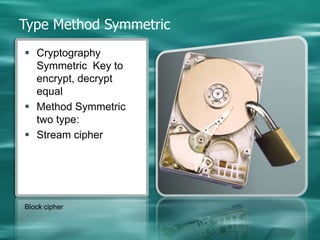
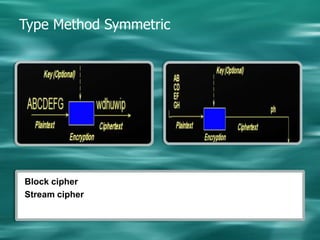
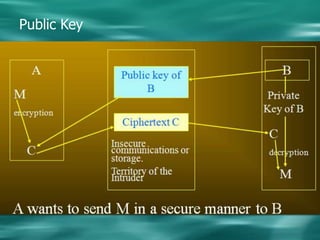
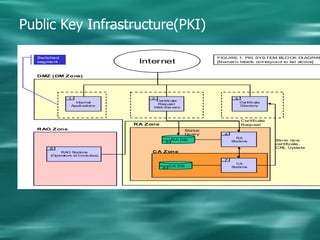
2. There are two main types of cryptography - symmetric which uses the same key for encryption and decryption, and asymmetric (public key) which uses different keys for encryption and decryption.
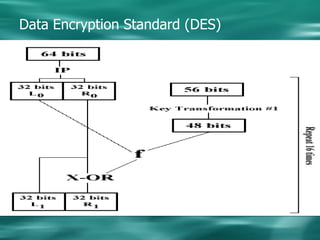
3. Common symmetric algorithms are DES and AES while RSA is an example of an asymmetric algorithm commonly used for digital signatures and encryption.