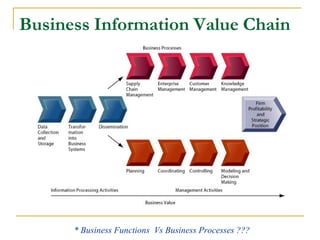
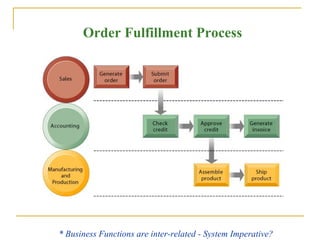
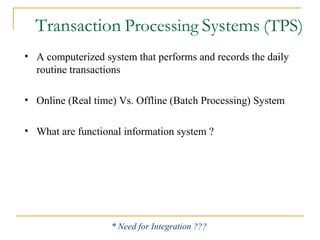
This document provides an overview of enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. It discusses how ERP systems enable seamless integration and information flow across key business processes through interdependent software modules and a common central database. The document also outlines some of the benefits of ERP systems, such as helping to unify an organization's structure, enabling more efficient operations and customer-driven processes, and providing firm-wide knowledge-based management. However, it also notes challenges in implementing ERP systems, such as requiring significant changes to how a business operates and large investments of time and money.