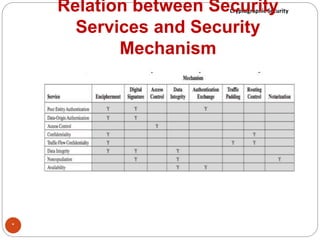
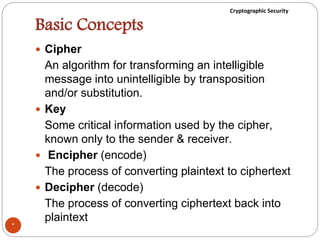
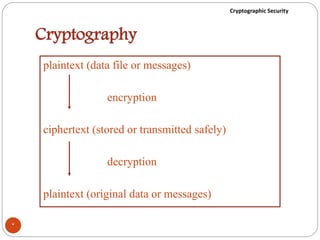
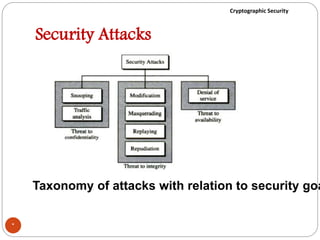
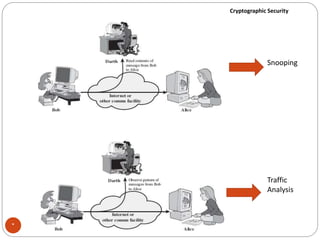
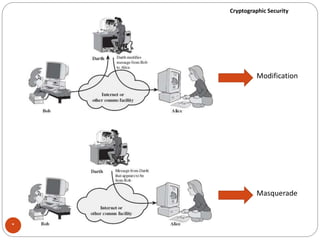
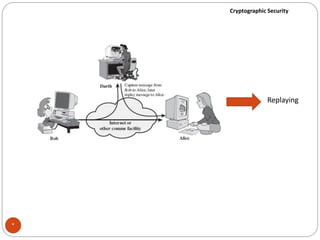
The document discusses cryptographic security. It outlines security goals of confidentiality, integrity, and availability. It describes common security attacks like snooping, traffic analysis, modification, masquerading, replaying, denial of service, and their classification as passive or active. It also discusses security services like authentication, data confidentiality, data integrity, and nonrepudiation. Various security mechanisms are presented like encipherment, digital signatures, access control, and traffic padding that provide the security services and defend against different attacks. Basic concepts of cryptography like plaintext, ciphertext, ciphers, keys, encryption, and decryption are also introduced.








![Cryptographic Security
Security Services
ITU-T(X.800)[International Telecommunication
Union-Telecommunication Standardization
Sector] has defined five services related to the
security goals and attacks.
Authentication: This service provides the
authentication of the party at the other end of the
line.
Peer entity authentication: In connection oriented
communication, it provides authentication of the
sender or receiver during the connection
establishment.
Data origin authentication: In connectionless
communication, it authenticates the source of the
data.
*](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securecommunication1-160716063152/85/Cryptographic-Security-13-320.jpg)