The document discusses three models of information system success:
1) The DeLone & McLean Model from 1992 which synthesizes six factors of IS success including system quality, information quality, use, user satisfaction, individual impact, and organizational impact.
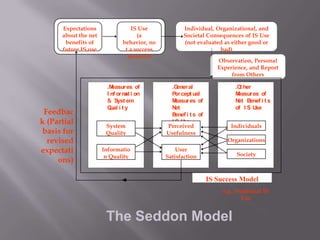
2) The Seddon Model from 1997 which focuses on the interrelationships among measures of information and system quality, IS use, and the benefits of IS use.
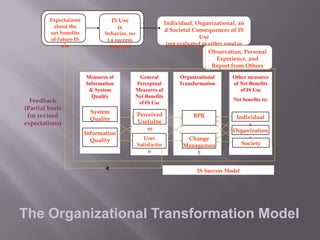
3) The Organizational Transformation Model which captures the organizational change dimension of successful IS implementation through its examination of system and information quality, organizational IS use, and organizational transformation due to IS.