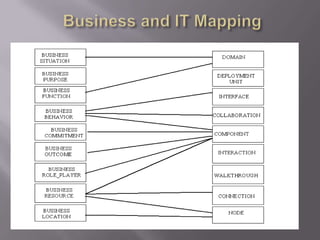
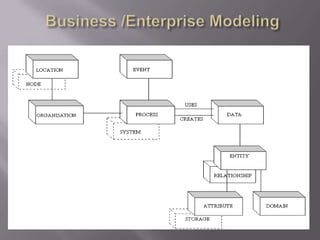
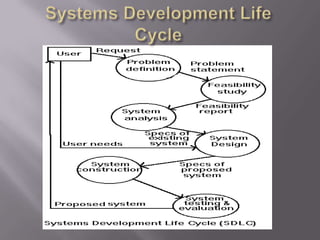
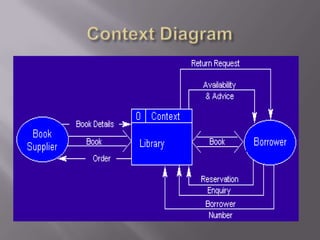
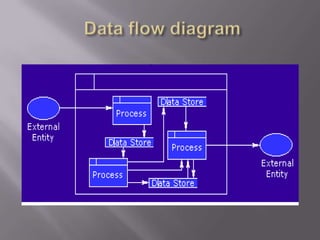
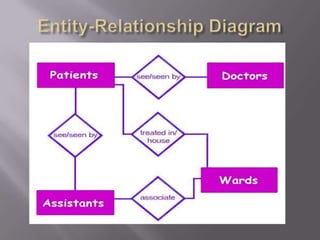
The document discusses business modeling and how modeling systems can help businesses redesign processes to cut costs. It states that a business model must be adaptable to changing customer needs and priorities. The modeling system allows businesses to link IT systems to organizational information and processes in a relational way to facilitate redesigning processes.