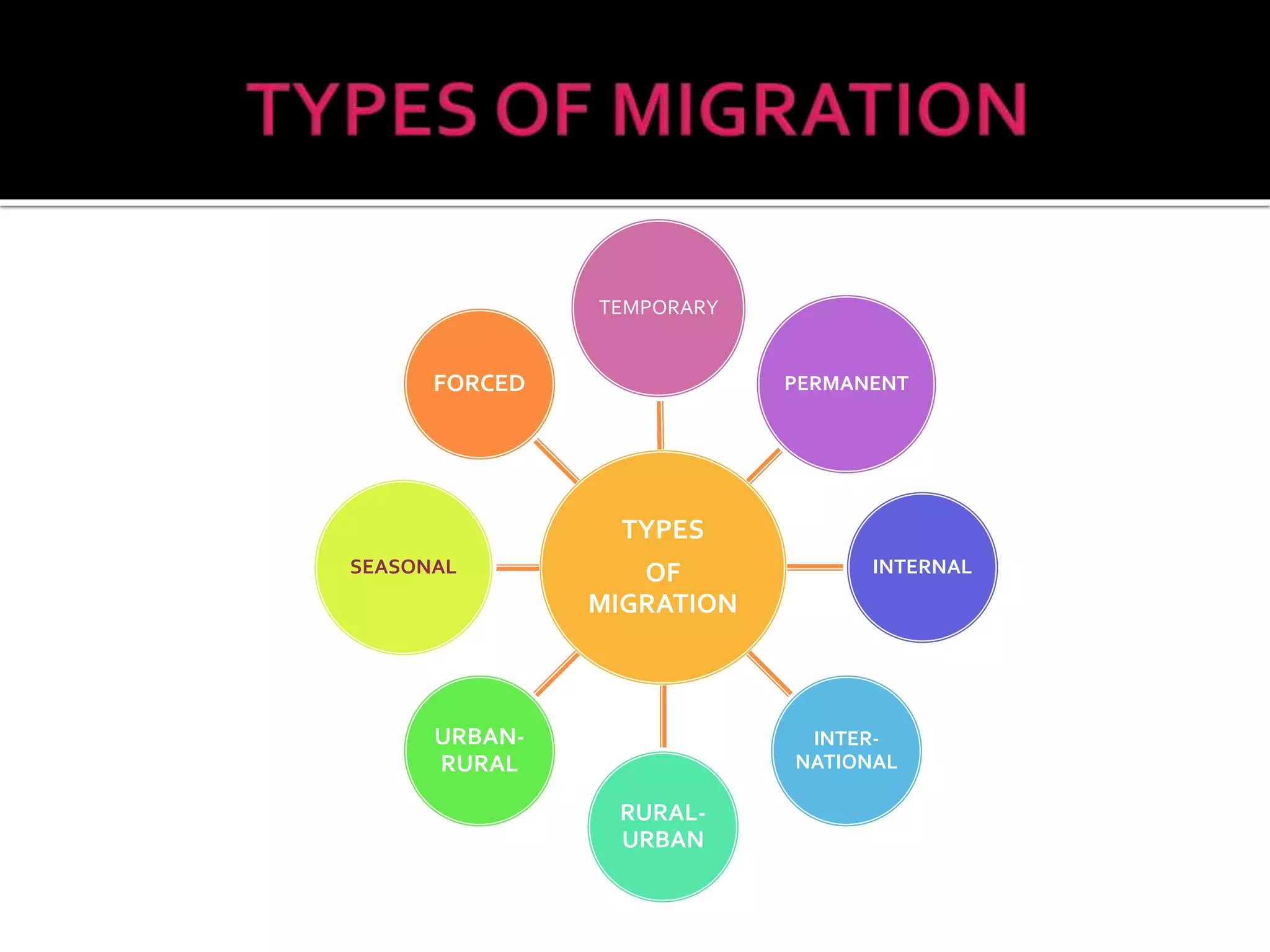
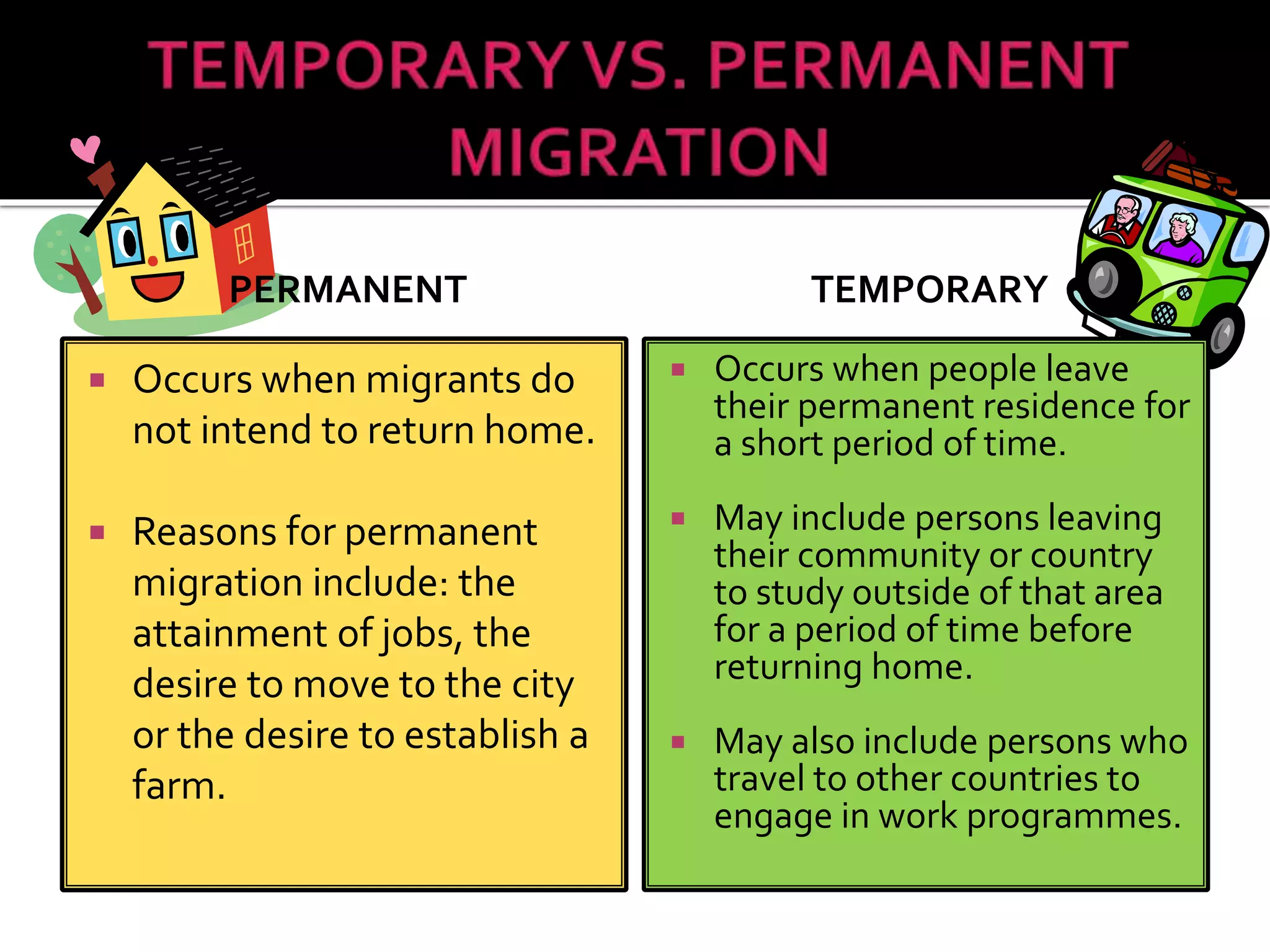
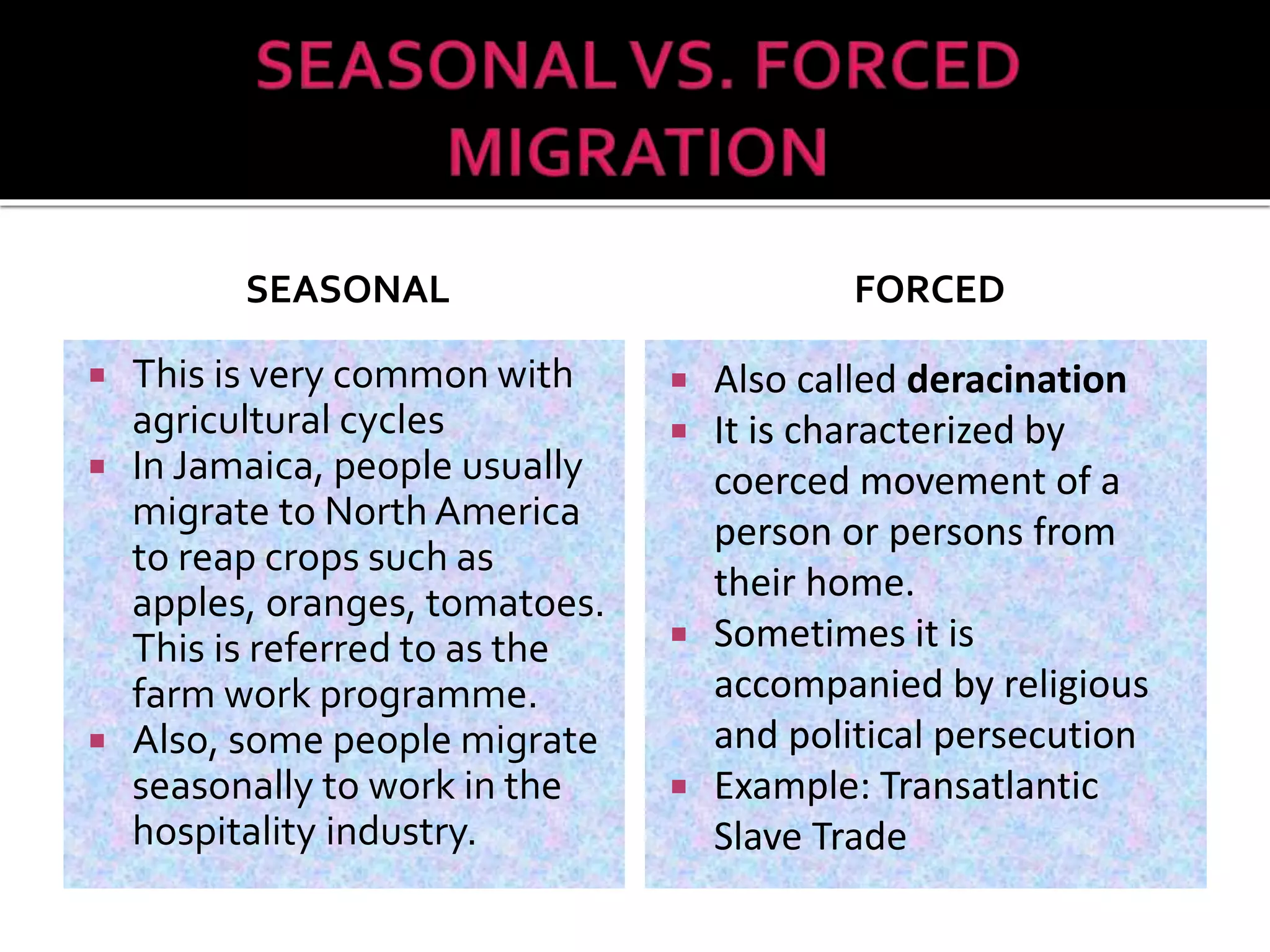
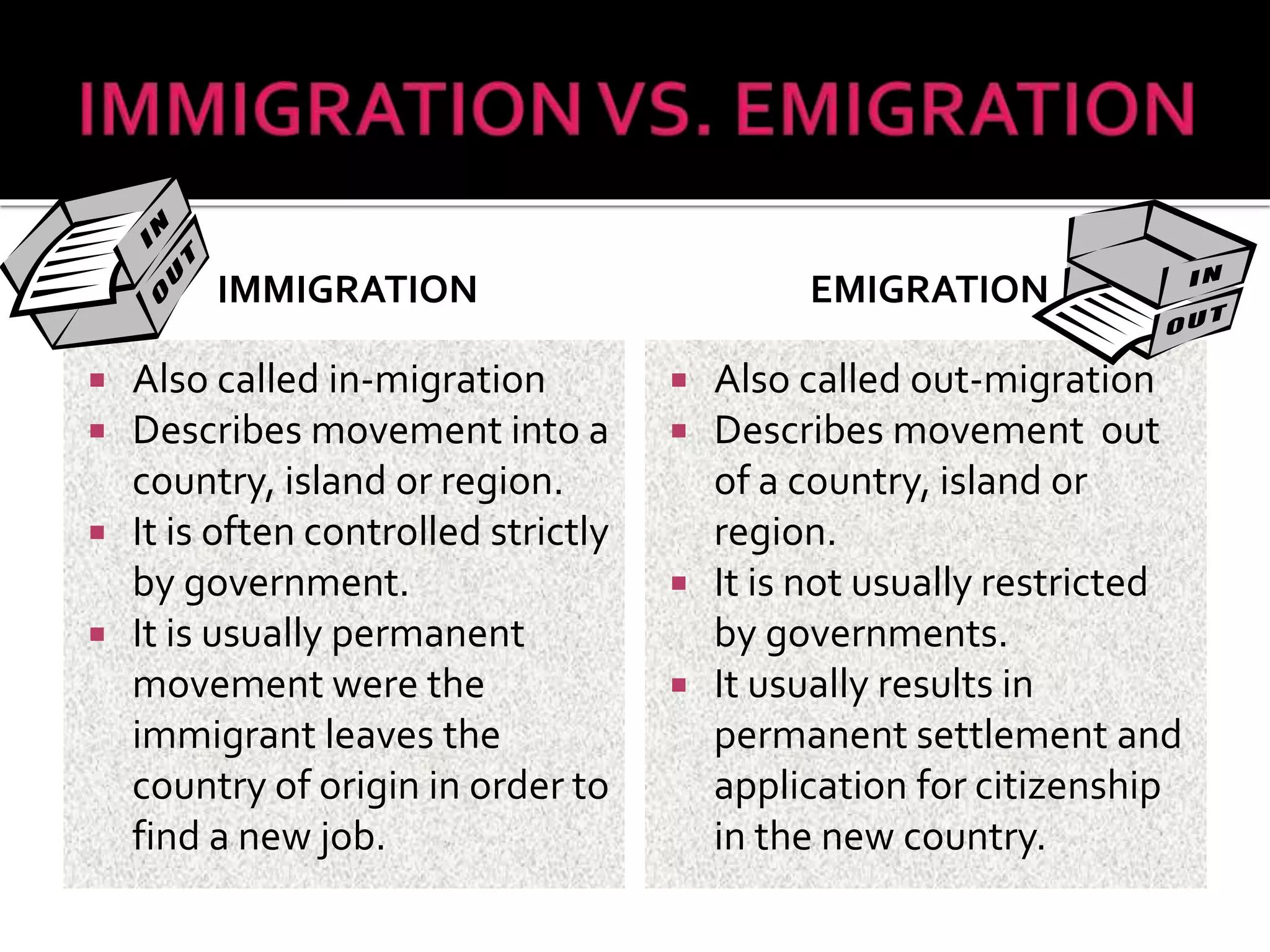
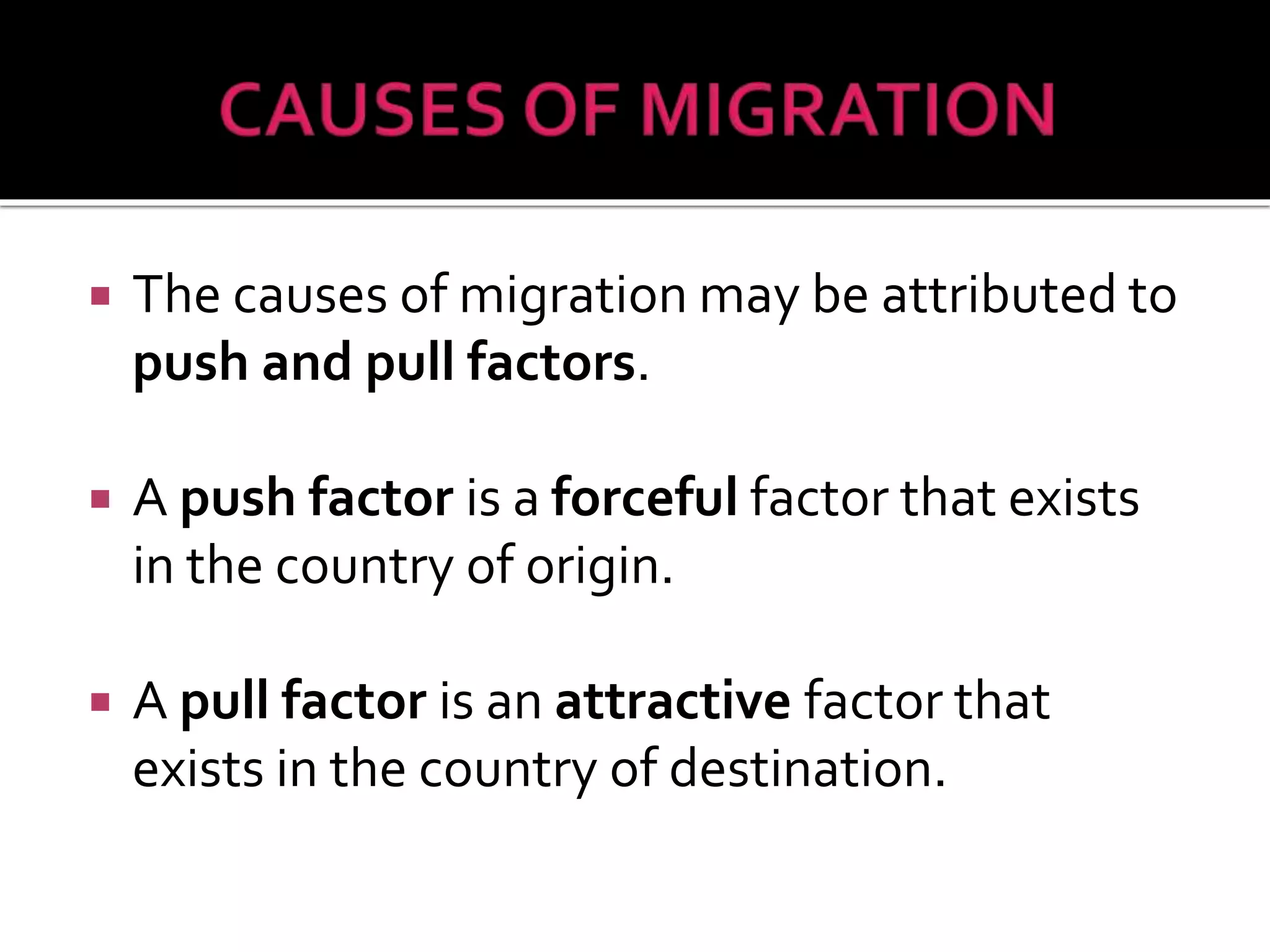
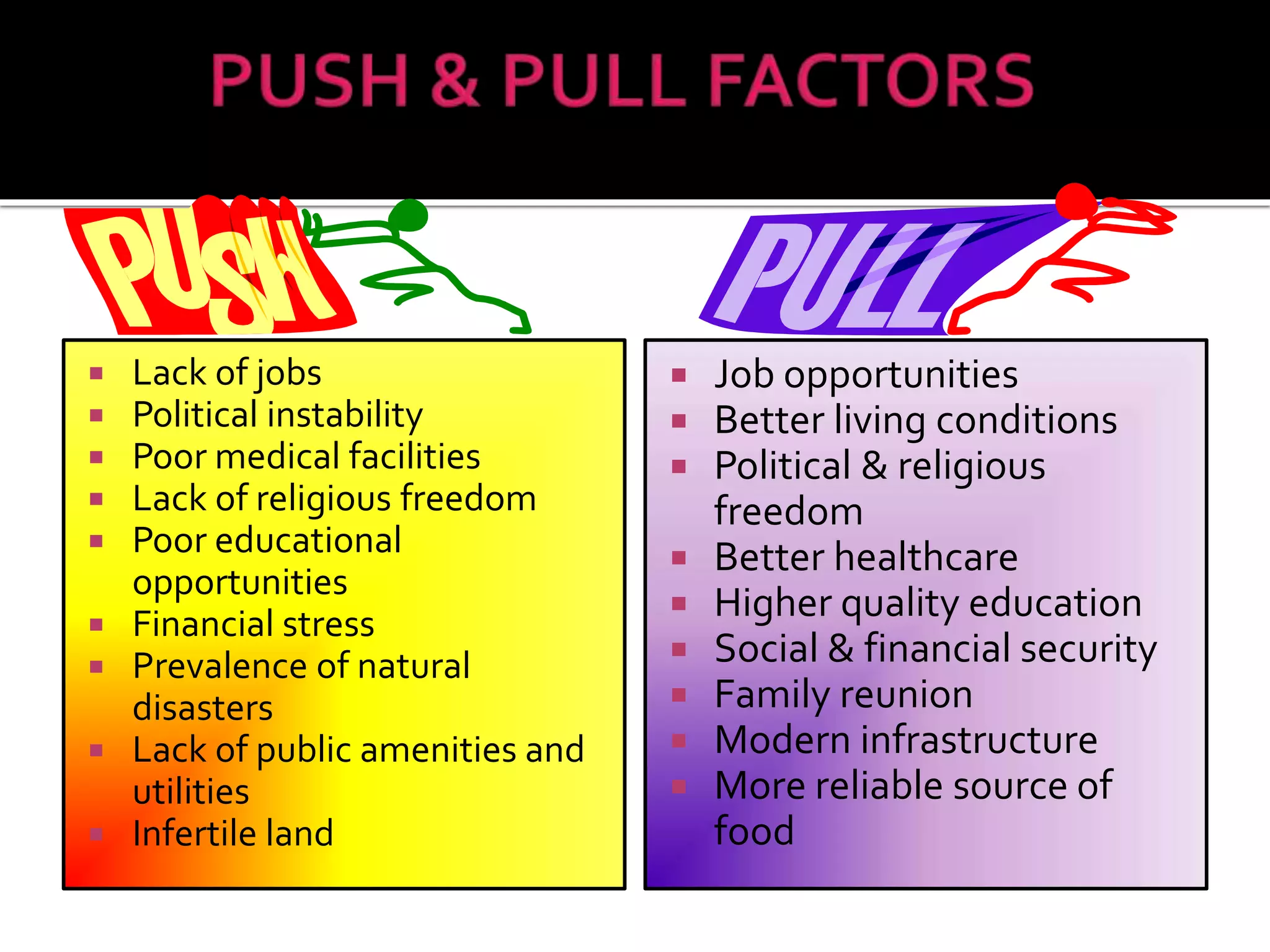
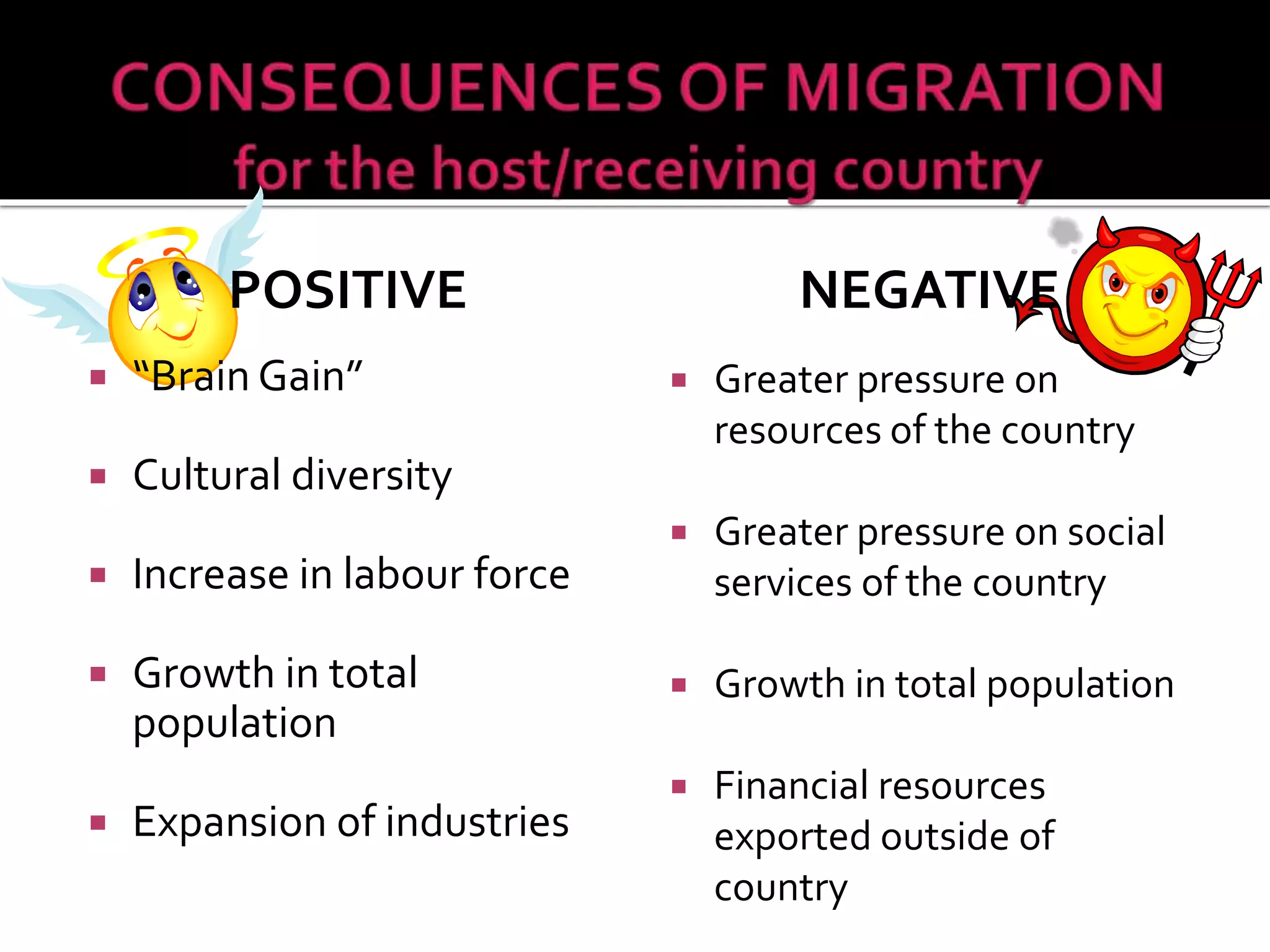
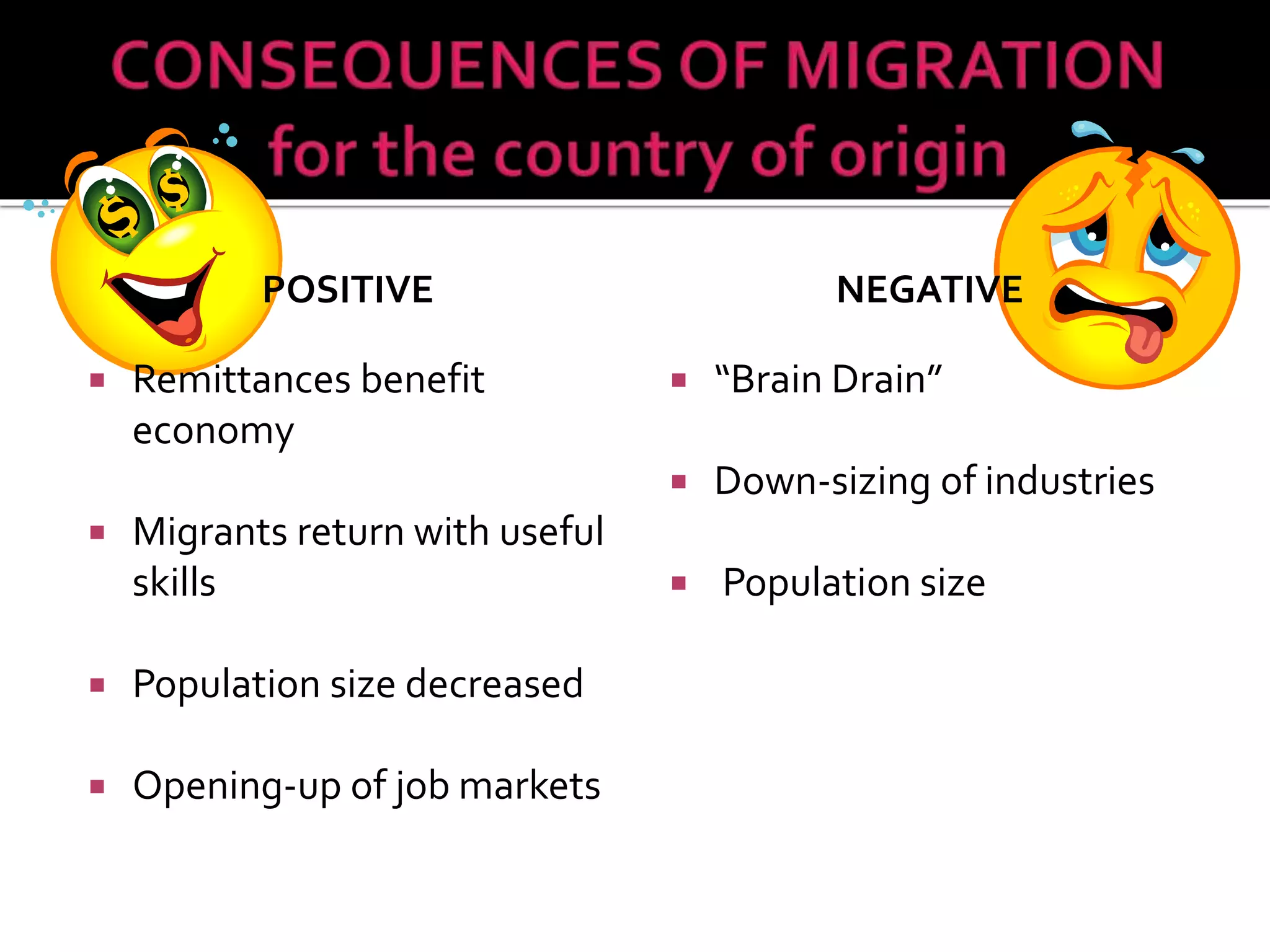
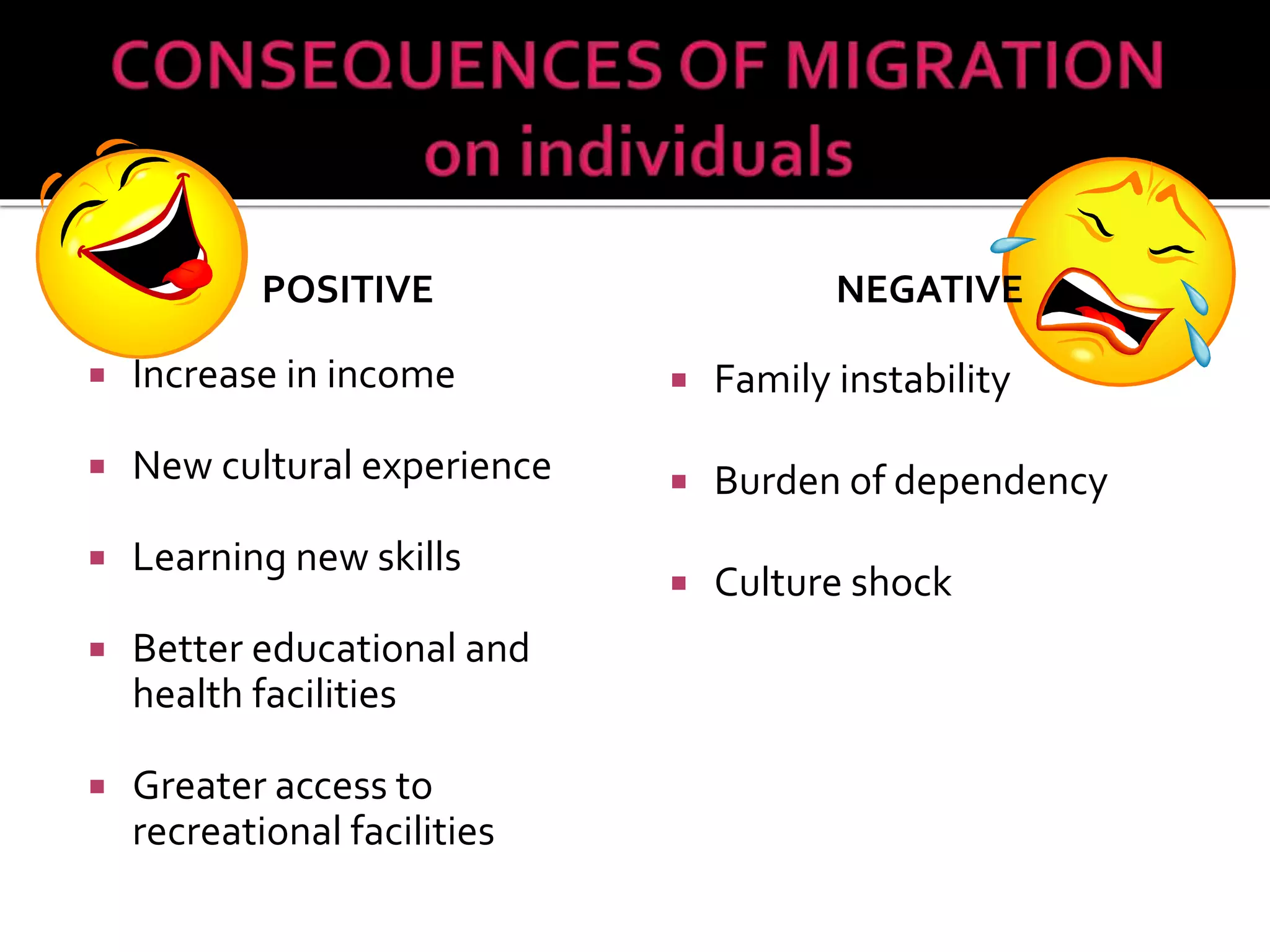
This document discusses different types of human migration including permanent, temporary, internal, international, rural-urban and forced migration. It defines each type and provides examples. Key points include that temporary migration involves short term movement while permanent migration means not returning home. Internal migration is within a country often from rural to urban areas. International migration crosses country borders. Rural-urban migration sees movement from farms to cities. Forced migration is involuntary due to issues like persecution. Migration has push factors like lack of jobs in the origin country and pull factors like opportunities in the destination country. Consequences of migration can be positive such as cultural diversity or negative like population pressure on resources.