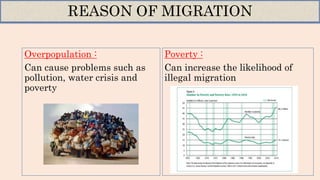
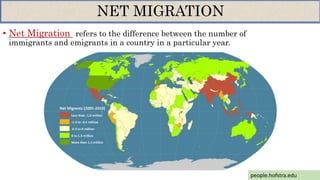
This document discusses migration and its determinants. It provides definitions of migration, emigration, and immigration. Some key points:
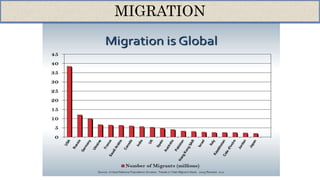
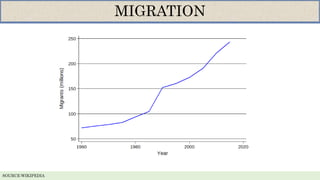
- 191 million people lived outside their country of birth in 2005, and the number of international migrants has doubled since World War II.
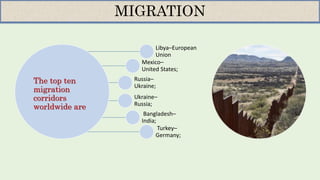
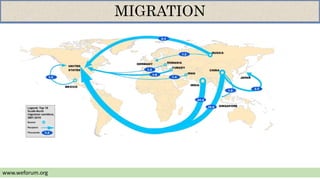
- The top countries for immigration are the US, Russia, Germany, and Saudi Arabia. The top countries of origin are Mexico, Spain, China, and Ukraine.
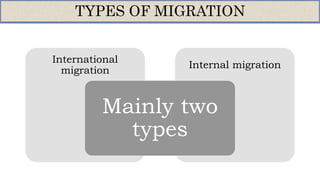
- There are two main types of migration - internal (within a country) and international. Internal migration includes rural-urban and seasonal movements.
- Migration can be voluntary or involuntary (forced). Involuntary migrants include refugees fleeing persecution or conflict.
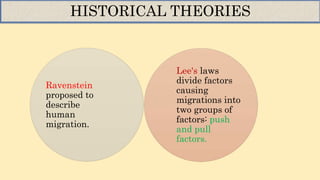
- Major theories