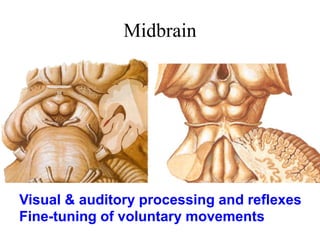
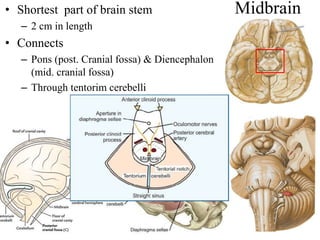
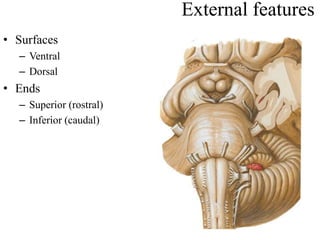
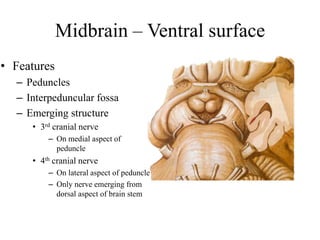
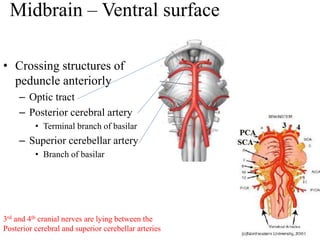
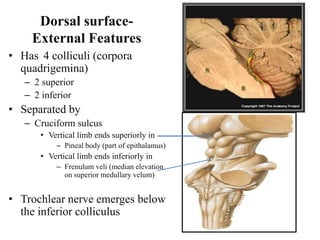
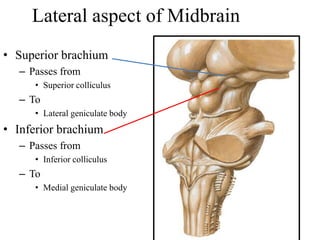
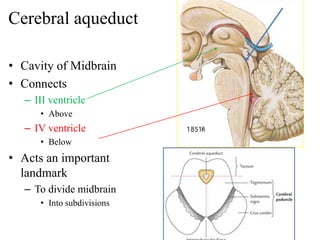
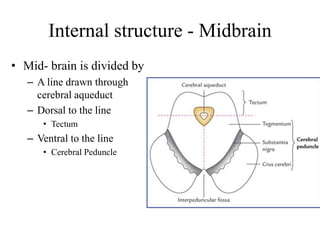
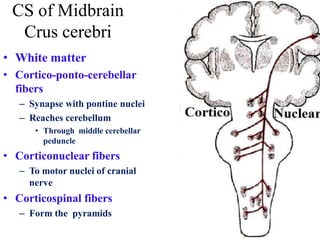
The midbrain processes visual and auditory information and reflexes. It connects the pons and diencephalon. It contains the cerebral peduncles and four colliculi. The substantia nigra lies within the midbrain and is involved in motor control. The midbrain contains ascending and descending tracts as well as cranial nerve nuclei that are involved in visual, auditory, motor and sensory processing.