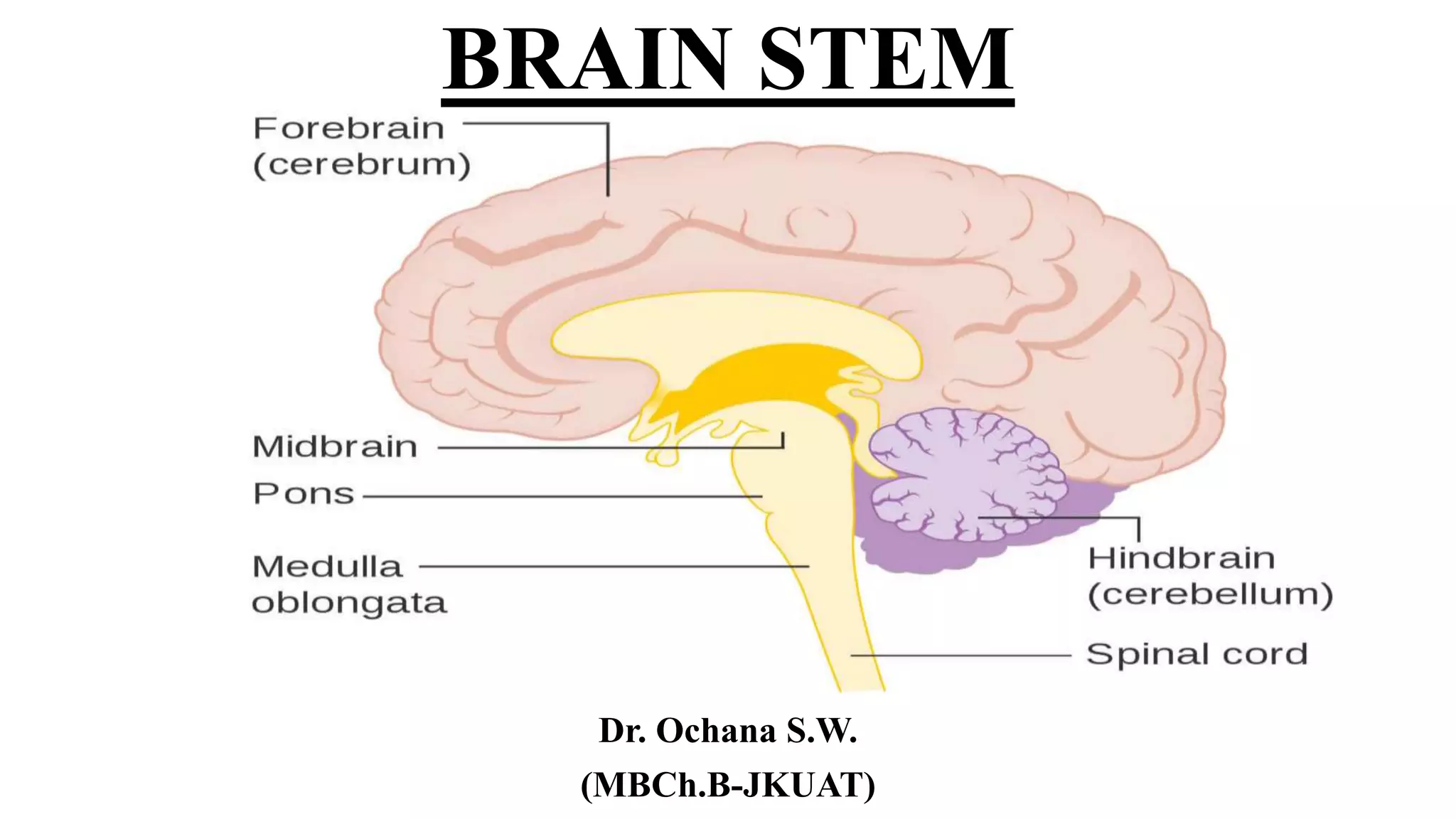
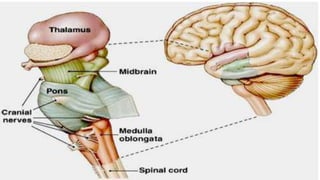
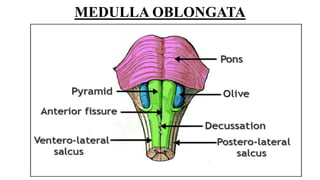
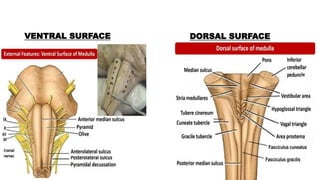
This document provides an overview of the brain stem, including its external features, internal structures, and clinical significance. It describes the medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain in detail. Key points include:
- The brain stem connects the spinal cord to the forebrain and contains cranial nerve nuclei, reflex centers, and tracts connecting different brain regions.
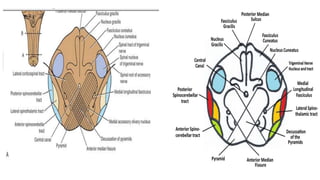
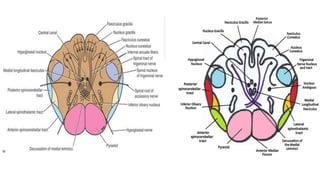
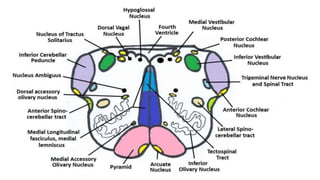
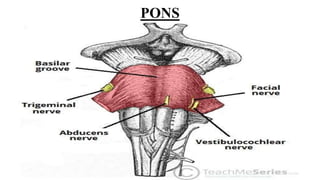
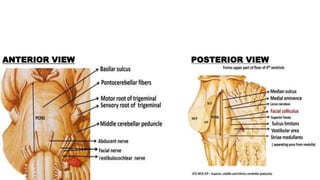
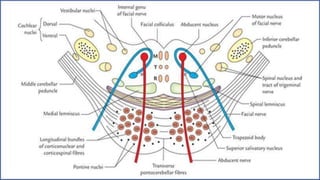
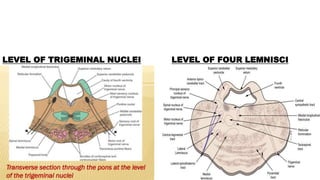
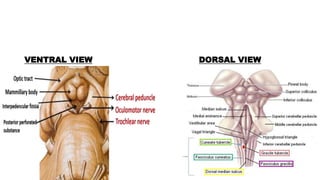
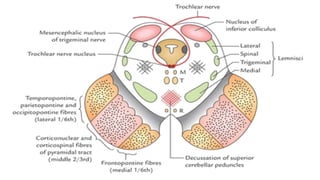
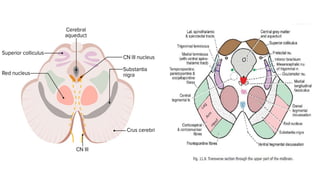
- Structures in the medulla include the pyramids, olives, cranial nerve nuclei, and tracts like the medial lemniscus. The pons contains cranial nerve nuclei and connects the medulla to midbrain. The midbrain contains the cerebral aqueduct and superior and inferior colliculi.
- Trans